相关数据结构:树
相关算法:递归 || 深度优先搜索+回溯法+中序遍历
LeetCode 46
给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
示例:
输入: [1,2,3] 输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [3,2,1] ]
递归思路:固定一个数,求出后面的其他数的全排列。再固定一个数,求出后面其他数的全排列,直到只剩一个数,这样就确定了所有数的一种排列方式。递归此过程。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<vector<int>> ans; 4 vector<vector<int>> per(int i,int n,vector<int>& res) 5 { 6 if(i==n) 7 ans.push_back(res); 8 else 9 { 10 for(int j=i;j<=n;++j) 11 { 12 swap(res[i],res[j]); 13 per(i+1,n,res); 14 swap(res[i],res[j]); 15 } 16 } 17 return ans; 18 } 19 vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) { 20 return per(0,nums.size()-1,nums); 21 } 22 };
DFS回溯法:全排列要求序列中的元素不被重复使用,而从根节点开始遍历一棵树正好能得到所有元素的所有排列方式。
构建一棵树将所有元素存储进去再进行一次中序遍历即可。
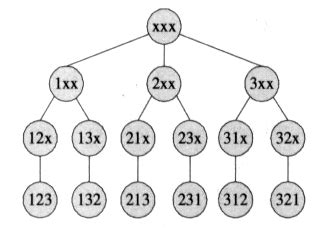
观察可知凡是会在某节点的子树节点中出现的元素,都不可能是已经在该节点的兄弟节点以及父节点中出现的元素。
所以,开一个标记数组,记录每一个元素是否已经被存进树中。当所有子节点已经扩展结束时,回溯至其父节点,递归此过程。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 //树形问题:回溯法、递归 4 vector<vector<int>> res; 5 vector<bool> used;//状态记录 6 7 //构造递归函数 8 //p中保存了index个元素的全排列 9 //末尾添加第index+1个元素,获得index + 1个元素的全排列 10 void generatePermute(const vector<int>& nums, int index, vector<int>& p){ 11 //到达叶子节点,保存结果 12 if( index == nums.size() ){ 13 res.push_back(p); 14 return; 15 } 16 17 for(int i = 0; i != nums.size(); i++){ 18 if( !used[i] ){ 19 p.push_back(nums[i]); 20 used[i] = true; 21 generatePermute(nums, index+1, p); 22 //状态回溯 23 used[i] = false; 24 p.pop_back(); 25 } 26 } 27 return;//返回上一层 28 } 29 30 vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) { 31 res.clear(); 32 if(nums.size() == 0) 33 return res; 34 used = vector<bool>( nums.size(), false); 35 vector<int> p; 36 generatePermute(nums, 0, p); 37 return res; 38 } 39 };
STL Permutation:
先把STL源码糊在这儿...

1 // next_permutation and prev_permutation, with and without an explicitly 2 // supplied comparison function. 3 //next_permutation获取[first,last)区间所标示序列的下一个排列组合,若果没有下一个排序组合,则返回false;否则返回true; 4 /* 5 函数功能:Rearranges the elements in the range [first,last) into the next lexicographically greater permutation. 6 函数原型: 7 default (1) :版本一采用less-than操作符 8 template <class BidirectionalIterator> 9 bool next_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first, 10 BidirectionalIterator last); 11 custom (2) :版本二采用仿函数comp决定 12 template <class BidirectionalIterator, class Compare> 13 bool next_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first, 14 BidirectionalIterator last, Compare comp); 15 */ 16 //版本一 17 template <class _BidirectionalIter> 18 bool next_permutation(_BidirectionalIter __first, _BidirectionalIter __last) { 19 __STL_REQUIRES(_BidirectionalIter, _BidirectionalIterator); 20 __STL_REQUIRES(typename iterator_traits<_BidirectionalIter>::value_type, 21 _LessThanComparable); 22 if (__first == __last) 23 return false;//若为空,则返回false 24 _BidirectionalIter __i = __first; 25 ++__i; 26 if (__i == __last)//区间只有一个元素 27 return false; 28 //若区间元素个数不小于两个 29 __i = __last;//i指向尾端 30 --__i;//不断后移 31 32 for(;;) { 33 //下面两行是让ii和i成为相邻的元素 34 //其中i为第一个元素,ii为第二个元素 35 _BidirectionalIter __ii = __i;// 36 --__i; 37 //以下在相邻元素判断 38 if (*__i < *__ii) {//若前一个元素小于后一个元素, 39 //则再从最尾端开始往前检查,找出第一个大于*i的元素,令该元素为*j,将*i和*j交换 40 //再将ii之后的所有元素颠倒排序 41 _BidirectionalIter __j = __last;//令j指向最尾端 42 while (!(*__i < *--__j))//由尾端往前检查,直到遇到比*i大的元素 43 {} 44 iter_swap(__i, __j);//交换迭代器i和迭代器j所指的元素 45 reverse(__ii, __last);//将ii之后的元素全部逆向重排 46 return true; 47 } 48 if (__i == __first) {//进行到最前面 49 reverse(__first, __last);//整个区间全部逆向重排 50 return false; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 //版本二 55 template <class _BidirectionalIter, class _Compare> 56 bool next_permutation(_BidirectionalIter __first, _BidirectionalIter __last, 57 _Compare __comp) { 58 __STL_REQUIRES(_BidirectionalIter, _BidirectionalIterator); 59 __STL_BINARY_FUNCTION_CHECK(_Compare, bool, 60 typename iterator_traits<_BidirectionalIter>::value_type, 61 typename iterator_traits<_BidirectionalIter>::value_type); 62 if (__first == __last) 63 return false; 64 _BidirectionalIter __i = __first; 65 ++__i; 66 if (__i == __last) 67 return false; 68 __i = __last; 69 --__i; 70 71 for(;;) { 72 _BidirectionalIter __ii = __i; 73 --__i; 74 if (__comp(*__i, *__ii)) { 75 _BidirectionalIter __j = __last; 76 while (!__comp(*__i, *--__j)) 77 {} 78 iter_swap(__i, __j); 79 reverse(__ii, __last); 80 return true; 81 } 82 if (__i == __first) { 83 reverse(__first, __last); 84 return false; 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 //next_permutation函数举例: 89 /* 90 #include <iostream> // std::cout 91 #include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation, std::sort 92 93 int main () { 94 int myints[] = {1,2,3,4}; 95 96 std::sort (myints,myints+4); 97 98 std::cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements: "; 99 do { 100 std::cout << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] <<' ' << myints[3]<< ' '; 101 } while ( std::next_permutation(myints,myints+4) ); 102 103 //std::next_permutation(myints,myints+4); 104 std::cout << "After loop: " << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << ' ' << myints[3]<<' '; 105 106 return 0; 107 } 108 Output: 109 The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements: 110 1 2 3 4 111 1 2 4 3 112 1 3 2 4 113 1 3 4 2 114 1 4 2 3 115 1 4 3 2 116 2 1 3 4 117 2 1 4 3 118 2 3 1 4 119 2 3 4 1 120 2 4 1 3 121 2 4 3 1 122 3 1 2 4 123 3 1 4 2 124 3 2 1 4 125 3 2 4 1 126 3 4 1 2 127 3 4 2 1 128 4 1 2 3 129 4 1 3 2 130 4 2 1 3 131 4 2 3 1 132 4 3 1 2 133 4 3 2 1 134 After loop: 1 2 3 4 135 */ 136 137 //prev_permutation获取[first,last)区间所标示序列的上一个排列组合,若果没有上一个排序组合,则返回false;否则返回true; 138 /* 139 函数功能:Rearranges the elements in the range [first,last) into the previous lexicographically-ordered permutation. 140 函数原型: 141 default (1) :版本一采用less-than操作符 142 template <class BidirectionalIterator> 143 bool prev_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first, 144 BidirectionalIterator last ); 145 custom (2) :版本二采用仿函数comp 146 template <class BidirectionalIterator, class Compare> 147 bool prev_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first, 148 BidirectionalIterator last, Compare comp); 149 */ 150 //版本一 151 template <class _BidirectionalIter> 152 bool prev_permutation(_BidirectionalIter __first, _BidirectionalIter __last) { 153 __STL_REQUIRES(_BidirectionalIter, _BidirectionalIterator); 154 __STL_REQUIRES(typename iterator_traits<_BidirectionalIter>::value_type, 155 _LessThanComparable); 156 if (__first == __last) 157 return false;//若区间为空,返回false 158 _BidirectionalIter __i = __first; 159 ++__i; 160 if (__i == __last)//区间只有一个元素 161 return false;//返回false 162 //若区间元素个数不小于两个 163 __i = __last; 164 --__i; 165 166 for(;;) { 167 //下面两行是让ii和i成为相邻的元素 168 //其中i为第一个元素,ii为第二个元素 169 _BidirectionalIter __ii = __i; 170 --__i; 171 //以下在相邻元素判断 172 if (*__ii < *__i) {//若前一个元素大于后一个元素, 173 //则再从最尾端开始往前检查,找出第一个小于*i的元素,令该元素为*j,将*i和*j交换 174 //再将ii之后的所有元素颠倒排序 175 _BidirectionalIter __j = __last;//令j指向最尾端 176 while (!(*--__j < *__i))//由尾端往前检查,直到遇到比*i小的元素 177 {} 178 iter_swap(__i, __j); //交换迭代器i和迭代器j所指的元素 179 reverse(__ii, __last);//将ii之后的元素全部逆向重排 180 return true; 181 } 182 if (__i == __first) {//进行到最前面 183 reverse(__first, __last);//把区间所有元素逆向重排 184 return false; 185 } 186 } 187 } 188 //版本二 189 template <class _BidirectionalIter, class _Compare> 190 bool prev_permutation(_BidirectionalIter __first, _BidirectionalIter __last, 191 _Compare __comp) { 192 __STL_REQUIRES(_BidirectionalIter, _BidirectionalIterator); 193 __STL_BINARY_FUNCTION_CHECK(_Compare, bool, 194 typename iterator_traits<_BidirectionalIter>::value_type, 195 typename iterator_traits<_BidirectionalIter>::value_type); 196 if (__first == __last) 197 return false; 198 _BidirectionalIter __i = __first; 199 ++__i; 200 if (__i == __last) 201 return false; 202 __i = __last; 203 --__i; 204 205 for(;;) { 206 _BidirectionalIter __ii = __i; 207 --__i; 208 if (__comp(*__ii, *__i)) { 209 _BidirectionalIter __j = __last; 210 while (!__comp(*--__j, *__i)) 211 {} 212 iter_swap(__i, __j); 213 reverse(__ii, __last); 214 return true; 215 } 216 if (__i == __first) { 217 reverse(__first, __last); 218 return false; 219 } 220 } 221 } 222 //prev_permutation函数举例 223 /* 224 #include <iostream> // std::cout 225 #include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation, std::sort, std::reverse 226 227 int main () { 228 int myints[] = {1,2,3}; 229 230 std::sort (myints,myints+3); 231 std::reverse (myints,myints+3); 232 233 std::cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements: "; 234 do { 235 std::cout << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << ' '; 236 } while ( std::prev_permutation(myints,myints+3) ); 237 238 std::cout << "After loop: " << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << ' '; 239 240 return 0; 241 } 242 Output: 243 The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements: 244 3 2 1 245 3 1 2 246 2 3 1 247 2 1 3 248 1 3 2 249 1 2 3 250 After loop: 3 2 1 251 */
