1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)
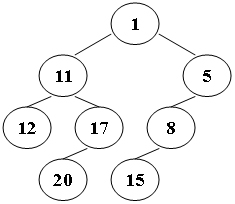
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
12 11 20 17 1 15 8 5
12 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15题目大意:给出二叉树的中根遍历和后根遍历序列,给出zigzag遍历序列,就是隔层从左到右,从右到左这样转换遍历。
//这个我当然是不会了,好久没做二叉树的题目了。
转自:https://www.liuchuo.net/archives/3758
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; vector<int> in, post, result[35]; int n, tree[35][2], root; struct node { int index, depth;//保存index和深度。 }; //将二叉树的结构存储在了tree中。 void dfs(int &index, int inLeft, int inRight, int postLeft, int postRight) { if (inLeft > inRight) return; index = postRight;//进来之后再赋值,真的厉害。 int i = 0; while (in[i] != post[postRight]) i++; dfs(tree[index][0], inLeft, i - 1, postLeft, postLeft + (i - inLeft) - 1); dfs(tree[index][1], i + 1, inRight, postLeft + (i - inLeft), postRight - 1); } //dfs函数得到的root实际上是post遍历中的下标。 void bfs() { queue<node> q; q.push(node{root, 0}); while (!q.empty()) { node temp = q.front(); q.pop(); result[temp.depth].push_back(post[temp.index]); if (tree[temp.index][0] != 0)//左子树不为空。 q.push(node{tree[temp.index][0], temp.depth + 1}); //那么此时push进的是左子树,并且深度+1. if (tree[temp.index][1] != 0)//右子树不为空。 q.push(node{tree[temp.index][1], temp.depth + 1}); } } int main() { cin >> n; in.resize(n + 1), post.resize(n + 1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> in[i];//输入中序遍历 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> post[i];//输入后序遍历 dfs(root, 1, n, 1, n);//将根存在了root中。 bfs(); printf("%d", result[0][0]); for (int i = 1; i < 35; i++) { if (i % 2 == 1) { for (int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) printf(" %d", result[i][j]); } else { for (int j = result[i].size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) printf(" %d", result[i][j]); } } return 0; }
//柳神真厉害。
1.使用dfs在遍历的过程中传进去index引用参数,直接赋值,并且使用tree二维数组存储二叉树的结构
2.使用结构体node,存储下标和层数,下标是在post序列中可以寻到节点的。
3.对奇数层和偶数层,分别用不同的方式打印。
代码来自:https://www.cnblogs.com/chenxiwenruo/p/6506517.html
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <string.h> #include <string> #include <map> #define LEFT 0 #define RIGHT 1 using namespace std; const int maxn=35; int inorder[maxn]; int postorder[maxn]; int level[maxn][maxn]; //每层的节点id int levelcnt[maxn]; //每层的节点个数 int maxlayer=0; int cnt=0; //节点id struct Node{ int left=-1,right=-1; int val; }node[maxn]; //根据中序遍历和后序遍历建立树 void build(int inL,int inR,int postL,int postR,int fa,int LorR){ if(inL>inR) return; int val=postorder[postR]; int idx; //在中序遍历中找出父亲节点的索引,其左边是左子树,右边是右子树 for(int i=inL;i<=inR;i++){ if(inorder[i]==val){ idx=i; break; } } int lnum=idx-inL;//左子树的节点个数 cnt++; node[cnt].val=val; if(LorR==LEFT) node[fa].left=cnt; else if(LorR==RIGHT) node[fa].right=cnt; int tmp=cnt; build(inL,idx-1,postL,postL+lnum-1,tmp,LEFT); //这里的left标志是当前深度遍历中是左子树还是右子树。 build(idx+1,inR,postL+lnum,postR-1,tmp,RIGHT); } void dfs(int root,int layer){ if(root==-1) return; maxlayer=max(layer,maxlayer); level[layer][levelcnt[layer]]=root; levelcnt[layer]++; dfs(node[root].left,layer+1); dfs(node[root].right,layer+1); } int main() { int n; cin>>n; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>inorder[i]; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>postorder[i]; build(1,n,1,n,-1,-1); dfs(1,1); bool flag=true; printf("%d",node[1].val); for(int i=2;i<=maxlayer;i++){ if(flag){ for(int j=0;j<levelcnt[i];j++) printf(" %d",node[level[i][j]].val); } else{ for(int j=levelcnt[i]-1;j>=0;j--) printf(" %d",node[level[i][j]].val); } flag=!flag; } return 0; }
1.这个是使用函数建树,具体的代码理解在代码里。