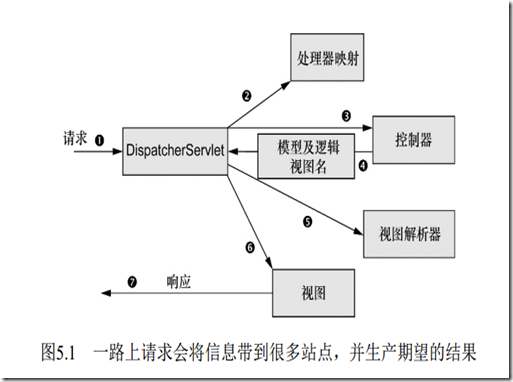
上图表示当客户请求来到时,spring架构作出响应的流程,可以从图中看到看到请求分发的中心就是 DispatcherServlet 类,DispatcherServlet的任务是将请求发送给Spring MVC控制器(controller) 。 控制器是一个用于处理请求的Spring组件。 在典型的应用程序中可能会有多个控制器, DispatcherServlet需要知道应该将请求发送给哪个控制器。 所以DispatcherServlet以会查询一个或多个处理器映射(handler mapping) 来确定请求的下一站在哪里。 处理器映射会根据请求所携带的URL信息来进行决策。
理解 DispatcherServlet 和 ContextLoadListener
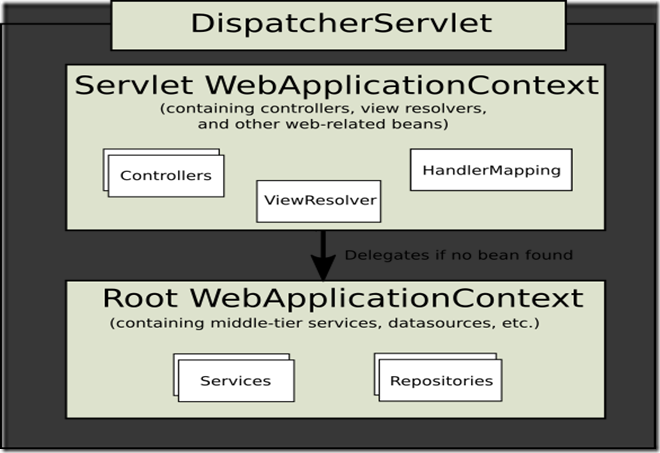
DispatcherServlet 需要一个继承自ApplicationContext 的 WebApplicationContext 作为参数来配置自己。WebApplicationContext 是 ServletContext 和 Servlet 的关联者,对于很多应用,一个 WebApplicationContext 是足够并且可以充分发挥作用的,也有可能当我们有多个DispatcherServlet 并且想共享一下共同的bean 在这个应用中,这样我们可以定义一个root ApplicationContext里面包含所有的共同的bean 和
根WebApplicationContext (root WebApplicationContext )实际上已经包含了通常包含基础的beans ,例如数据存储(data repostitories )和需要被多个Servlet 实例共享的业务服务(business services)。这些beans可以被继承同时可以被重写(overridden)在 特定的Servlet中,或是在包含本地给定Servlet 的 child WebApplicationContext 中。而child WebApplicationContext 就是如下图的 Servlet WebApplicaitonContext .
以下引用参考文章中的解释
Spring's
ApplicationContextprovides the capability of loading multiple (hierarchical) contexts, allowing each to be focused on one particular layer, such as the web layer of an application or middle-tier services.One of the canonical examples of using hierarchical
ApplicationContextis when we have multipleDispatcherServlets in a web application and we're gonna share some of the common beans such asdatasourcesbetween them. This way, we can define a rootApplicationContextthat contain all the common beans and multipleWebApplicationContexts that inherit the common beans from the root context.In the Web MVC framework, each
DispatcherServlethas its ownWebApplicationContext, which inherits all the beans already defined in the rootWebApplicationContext. These inherited beans can be overridden in the servlet-specific scope, and you can define new scope-specific beans local to a givenServletinstance
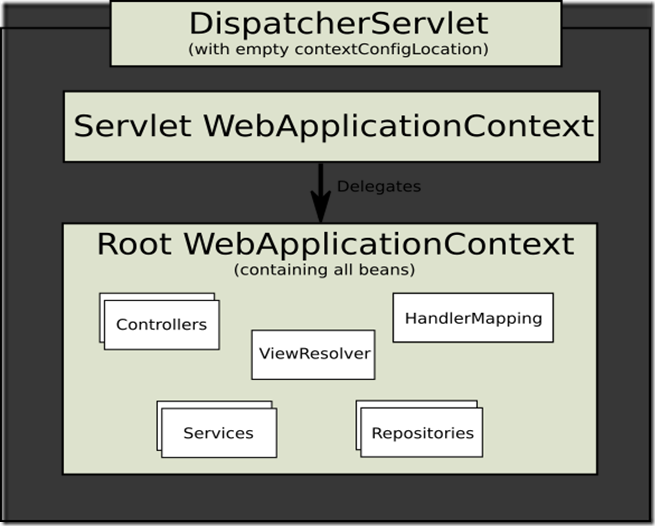
假如项目中只有一个DispatcherServlet , 那么我们可以把原来在 DispatcherServlet 的beans 全部移到父类Root WebApplicationContext中。
下面是一个实现了WebApplicationContext继承者的configuration。
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class<?>[] { RootConfig.class }; } @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class<?>[] { App1Config.class }; } @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[] { "/app1/*" }; } }
假如不需要 application context 是继承关系的(WebApplicationContext 和 child WebApplicationContext 的关系),那么可以返回所有的配置通过 getRootConfigClasses ( ) , getServletConfigClasses( )返回null 就行了。
在Servlet 3.0环境中, 容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类, 如果能发现的话, 就会用它来配置Servlet容器。Spring提供了这个接口的实现, 名为SpringServletContainerInitializer, 这个类反过来又会查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配置的任务交给它们来完成。 Spring 3.2引入了一个便利的WebApplicationInitializer基础实现, 也就是AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer。 因为我们的 SpittrWebAppInitializer 扩展了AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer(同时也就实现了WebApplicationInitializer) , 因此当部署到Servlet 3.0容器中的时候, 容器会自动发现它, 并用它来配置Servlet上下文。(简单地说就是继承了AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,就会形成一个child WebApplicationContext )
我们自己实现的MyWebAppInitializer 和下面用xml文件是同种效果的。
<web-app>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>app1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/app1-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>app1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/app1/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>同样,假如不需要 application context 是继承关系的(WebApplicationContext 和 child WebApplicationContext 的关系),那么可以返回所有的配置通过 “root context” , 而Servlet 中的参数 contextLocation 返回null 就行了。
实例理解DispatcherServlet
假如我使用Spring MVC, Spring Security 和Spring Data JPA 来构建我的应用,那么我需要知道三个 config files , WebConfig 包含了web 相关的配置, 例如 ViewResolvers , Controllers , ArgumentResolver ,代码如下:
@EnableWebMvc @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.so.web") public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Bean public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() { InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver(); viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/"); viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp"); return viewResolver; } @Override public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) { final boolean DO_NOT_USE_SUFFIX_PATTERN_MATCHING = false; configurer.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(DO_NOT_USE_SUFFIX_PATTERN_MATCHING); } }
这里我们定义了一个ViewResolver , 同时我们需要一个RepositoryConfig 配置数据有关的类,例如 DataSource 和 TransactionManager 等等。
@Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement @EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.so.repository") public class RepositoryConfig { @Bean public DataSource dataSource() { ... } @Bean public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory() { ... } @Bean public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() { ... } }
SecurityConfig 包含了安全相关的成员。
@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override @Autowired protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { ... } @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { ... } }
假如我们只有一个DispatcherServlet 下面我们有两种配置方法:
1 public class ServletInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { 2 @Override 3 protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { 4 return new Class<?>[] { RepositoryConfig.class, SecurityConfig.class }; 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { 9 return new Class<?>[] { WebConfig.class }; 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 protected String[] getServletMappings() { 14 return new String[] { "/" }; 15 } 16 }
或者是
1 public class ServletInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { 2 @Override 3 protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { 4 return new Class<?>[] { RepositoryConfig.class, SecurityConfig.class, WebConfig.class }; 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { 9 return null; 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 protected String[] getServletMappings() { 14 return new String[] { "/" }; 15 } 16 }
ContextLoaderListener
引导监听Spring 的 root WebApplicationContext 的启动和关闭,在 Spring 3.1 中,ContextLoaderListener 支持通过 ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)来初始化 root WebApplicationContext .
特殊的bean
DispatcherServlet 委托给一些特殊的bean去处理请求和返回对应的响应,这些