DefaultSecurityManager
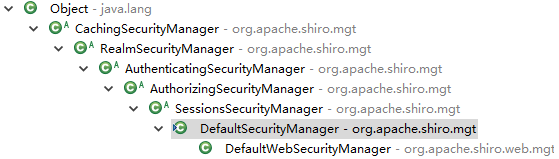
DefaultSecurityManager主要实现了SecurityManager的行为login()、logout()、createSubject()
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("username", "password");
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
currentUser.login(token);
DelegatingSubject的login()
Subject执行认证操作(成功为Subject设置会员信息) --> SecurityManager执行认证操作(成功创建Subject) --> Realm执行认证操作(认证及匹配逻辑、将认证信息加入缓存)
public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal(); Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token); PrincipalCollection principals; String host = null; if (subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) { DelegatingSubject delegating = (DelegatingSubject) subject; //we have to do this in case there are assumed identities - we don't want to lose the 'real' principals: principals = delegating.principals; host = delegating.host; } else { principals = subject.getPrincipals(); } if (principals == null || principals.isEmpty()) { String msg = "Principals returned from securityManager.login( token ) returned a null or " + "empty value. This value must be non null and populated with one or more elements."; throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } this.principals = principals; this.authenticated = true; if (token instanceof HostAuthenticationToken) { host = ((HostAuthenticationToken) token).getHost(); } if (host != null) { this.host = host; } Session session = subject.getSession(false); if (session != null) { this.session = decorate(session); } else { this.session = null; } }
DefaultSecurityManager的login()方法
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { AuthenticationInfo info; try {
// DefaultSecurityManager继承了AuthenticatingSecurityManager // AuthenticatingSecurityManager使用自己的Authenticator认证器进行会员信息认证,后文详解#1
info = authenticate(token); } catch (AuthenticationException ae) { try { onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " + "exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e); } } throw ae; //propagate } // 创建Subject,后文详解#2 Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject); // 启用了记住我功能时起作用 onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn); return loggedIn; }
书接前文#1
AuthenticatingSecurityManager使用自己的Authenticator认证器进行会员信息认证
public AuthenticatingSecurityManager() { super(); this.authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator(); } public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { return this.authenticator.authenticate(token); }
AbstractAuthenticator的公共认证逻辑,相同的行为抽取到父类了
public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { if (token == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Method argument (authentication token) cannot be null."); } log.trace("Authentication attempt received for token [{}]", token); AuthenticationInfo info; try {
// 具体的行为抽象出来了,ModularRealmAuthenticator负责具体实现 info = doAuthenticate(token); if (info == null) { String msg = "No account information found for authentication token [" + token + "] by this " + "Authenticator instance. Please check that it is configured correctly."; throw new AuthenticationException(msg); } } catch (Throwable t) { AuthenticationException ae = null; if (t instanceof AuthenticationException) { ae = (AuthenticationException) t; } if (ae == null) { //Exception thrown was not an expected AuthenticationException. Therefore it is probably a little more //severe or unexpected. So, wrap in an AuthenticationException, log to warn, and propagate: String msg = "Authentication failed for token submission [" + token + "]. Possible unexpected " + "error? (Typical or expected login exceptions should extend from AuthenticationException)."; ae = new AuthenticationException(msg, t); if (log.isWarnEnabled()) log.warn(msg, t); } try { notifyFailure(token, ae); } catch (Throwable t2) { if (log.isWarnEnabled()) { String msg = "Unable to send notification for failed authentication attempt - listener error?. " + "Please check your AuthenticationListener implementation(s). Logging sending exception " + "and propagating original AuthenticationException instead..."; log.warn(msg, t2); } } throw ae; } log.debug("Authentication successful for token [{}]. Returned account [{}]", token, info); // 如果有AuthenticationListener的实现类起作用 notifySuccess(token, info); return info; }
ModularRealmAuthenticator具体实现认证行为
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { assertRealmsConfigured(); Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms(); if (realms.size() == 1) {
// 单领域认证 return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken); } else { return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken); } }
单领域认证
protected AuthenticationInfo doSingleRealmAuthentication(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token) { if (!realm.supports(token)) { String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] does not support authentication token [" + token + "]. Please ensure that the appropriate Realm implementation is " + "configured correctly or that the realm accepts AuthenticationTokens of this type."; throw new UnsupportedTokenException(msg); }
// 获得认证信息的公共行为抽取出来到父类 AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token); if (info == null) { String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] was unable to find account data for the " + "submitted AuthenticationToken [" + token + "]."; throw new UnknownAccountException(msg); } return info; }
AuthenticatingRealm获得认证信息的公共行为抽取出来到父类
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { // 开启缓存功能起作用 AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token); if (info == null) { // 具体的认证行为抽象出来让程序员去继承AuthenticatingRealm具体实现 info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token); log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info); if (token != null && info != null) { cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info); } } else { log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info); } if (info != null) {
// token的登录信息和数据库查询出的会员信息进行比较,后文详解#3 assertCredentialsMatch(token, info); } else { log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token); } return info; }
程序员根据业务自定义的认证领域
package com.wjz.demo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthenticatingRealm; public class CustomRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm { @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("wjz", "123", getName()); } }
书接前文#2
SecurityManager的createSubject()
protected Subject createSubject(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info, Subject existing) { SubjectContext context = createSubjectContext(); context.setAuthenticated(true);
// 设置会员的登录信息UsernamePasswordToken(username, password)类 context.setAuthenticationToken(token);
// 设置认证成功的会员信息SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, password, username)类 context.setAuthenticationInfo(info); if (existing != null) { context.setSubject(existing); } return createSubject(context); }
公共逻辑抽取出来
public Subject createSubject(SubjectContext subjectContext) { // 创建一个备份对象 SubjectContext context = copy(subjectContext); // 确保有安全管理器 context = ensureSecurityManager(context); //Resolve an associated Session (usually based on a referenced session ID), and place it in the context before //sending to the SubjectFactory. The SubjectFactory should not need to know how to acquire sessions as the //process is often environment specific - better to shield the SF from these details: context = resolveSession(context); // 如果有必要的话从remeberme中获得会员信息 context = resolvePrincipals(context); // 使用SubjectFactory创建Subject Subject subject = doCreateSubject(context); //save this subject for future reference if necessary: //(this is needed here in case rememberMe principals were resolved and they need to be stored in the //session, so we don't constantly rehydrate the rememberMe PrincipalCollection on every operation). //Added in 1.2: save(subject); return subject; }
使用SubjectFactory(DefaultWebSubjectFactory)创建Subject(WebDelegatingSubject)
protected Subject doCreateSubject(SubjectContext context) { return getSubjectFactory().createSubject(context); }
public Subject createSubject(SubjectContext context) { if (!(context instanceof WebSubjectContext)) { return super.createSubject(context); } WebSubjectContext wsc = (WebSubjectContext) context; SecurityManager securityManager = wsc.resolveSecurityManager(); Session session = wsc.resolveSession(); boolean sessionEnabled = wsc.isSessionCreationEnabled(); PrincipalCollection principals = wsc.resolvePrincipals(); boolean authenticated = wsc.resolveAuthenticated(); String host = wsc.resolveHost(); ServletRequest request = wsc.resolveServletRequest(); ServletResponse response = wsc.resolveServletResponse(); return new WebDelegatingSubject(principals, authenticated, host, session, sessionEnabled, request, response, securityManager); }
DelegatingSubject执行login的逻辑
public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal();
// 调用了上面的一整套逻辑,以下是为Subject设置信息 Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token); PrincipalCollection principals; String host = null; if (subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) { DelegatingSubject delegating = (DelegatingSubject) subject; //we have to do this in case there are assumed identities - we don't want to lose the 'real' principals: principals = delegating.principals; host = delegating.host; } else { principals = subject.getPrincipals(); } if (principals == null || principals.isEmpty()) { String msg = "Principals returned from securityManager.login( token ) returned a null or " + "empty value. This value must be non null and populated with one or more elements."; throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } this.principals = principals; this.authenticated = true; if (token instanceof HostAuthenticationToken) { host = ((HostAuthenticationToken) token).getHost(); } if (host != null) { this.host = host; } Session session = subject.getSession(false); if (session != null) { this.session = decorate(session); } else { this.session = null; } }
书接前文#3
获得凭证匹配器(SimpleCredentialsMatcher)进行匹配
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException { CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher(); if (cm != null) {
// 执行匹配动作 if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) { //not successful - throw an exception to indicate this: String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials."; throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg); } } else { throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify " + "credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you " + "can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance."); } }
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) { Object tokenCredentials = getCredentials(token); Object accountCredentials = getCredentials(info); return equals(tokenCredentials, accountCredentials); }
SecurityManager的logout()
Subject执行退出操作(清空会员信息) --> SecurityManager执行退出操作(记住我退出、清空session) --> Realm执行退出操作(清空缓存如认证信息、授权信息)
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
currentUser.logout();
DelegatingSubject的logout行为,此为公共行为
public void logout() { try { clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal();
// 核心退出功能 this.securityManager.logout(this); } finally {
// 将以下Subject的信息置为null this.session = null; this.principals = null; this.authenticated = false; //Don't set securityManager to null here - the Subject can still be //used, it is just considered anonymous at this point. The SecurityManager instance is //necessary if the subject would log in again or acquire a new session. This is in response to //https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/JSEC-22 //this.securityManager = null; } }
安全管理器的公共退出逻辑
public void logout(Subject subject) { if (subject == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Subject method argument cannot be null."); } // 记住我退出,也就是清浏览器cookie beforeLogout(subject); PrincipalCollection principals = subject.getPrincipals(); if (principals != null && !principals.isEmpty()) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Logging out subject with primary principal {}", principals.getPrimaryPrincipal()); } Authenticator authc = getAuthenticator(); if (authc instanceof LogoutAware) {
// 认证器执行退出操作,后文详解#4 ((LogoutAware) authc).onLogout(principals); } } try {
// 清空shiro的session delete(subject); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { String msg = "Unable to cleanly unbind Subject. Ignoring (logging out)."; log.debug(msg, e); } } finally { try { stopSession(subject); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { String msg = "Unable to cleanly stop Session for Subject [" + subject.getPrincipal() + "] " + "Ignoring (logging out)."; log.debug(msg, e); } } } }
书接前文#4
public void onLogout(PrincipalCollection principals) {
// 如果有AuthenticationListener执行监听行为 super.onLogout(principals); Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms(); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(realms)) { for (Realm realm : realms) { if (realm instanceof LogoutAware) {
// 领域执行退出行为 ((LogoutAware) realm).onLogout(principals); } } } }