You are given a permutation p of numbers 1, 2, ..., n. Let's define f(p) as the following sum:
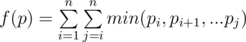
Find the lexicographically m-th permutation of length n in the set of permutations having the maximum possible value of f(p).
The single line of input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ m ≤ cntn), where cntn is the number of permutations of length n with maximum possible value of f(p).
The problem consists of two subproblems. The subproblems have different constraints on the input. You will get some score for the correct submission of the subproblem. The description of the subproblems follows.
- In subproblem B1 (3 points), the constraint 1 ≤ n ≤ 8 will hold.
- In subproblem B2 (4 points), the constraint 1 ≤ n ≤ 50 will hold.
Output n number forming the required permutation.
2 2
2 1
3 2
1 3 2
In the first example, both permutations of numbers {1, 2} yield maximum possible f(p) which is equal to 4. Among them, (2, 1) comes second in lexicographical order.
B1: 1<=n<=8;
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <cmath> 6 #include <cstdlib> 7 #include <string> 8 #include <vector> 9 #include <set> 10 #include <map> 11 #include <stack> 12 #include <queue> 13 using namespace std; 14 const int INF = 0x7fffffff; 15 const int MS = 100005; 16 const double EXP = 1e-8; 17 int a[55]; 18 int n, m; 19 int calc() 20 { 21 int res = 0; 22 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 23 for (int j = i; j < n; j++) 24 { 25 int maxv = n; 26 for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) 27 if (maxv>a[k]) 28 maxv = a[k]; 29 res += maxv; 30 } 31 return res; 32 } 33 void solve() 34 { 35 int i, j; 36 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) 37 a[i] = i + 1; 38 int maxv = -INF; 39 do 40 { 41 int s = calc(); 42 if (maxv < s) 43 maxv = s; 44 } while (next_permutation(a, a + n)); 45 46 sort(a, a + n); 47 do 48 { 49 int s = calc(); 50 if (maxv == s) 51 { 52 m--; 53 if (!m) 54 { 55 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) 56 { 57 if (i) 58 cout << " "; 59 cout << a[i]; 60 } 61 break; 62 } 63 } 64 65 } while (next_permutation(a, a + n)); 66 return; 67 } 68 69 int main() 70 { 71 cin >> n >> m; 72 solve(); 73 //void print(int, int *, int); 74 //print(n, a, 0); 75 return 0; 76 } 77 /* 78 void print(int n, int *a, int cur) 79 { 80 if (cur == n) 81 { 82 //print 83 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 84 { 85 if (i) 86 cout << " "; 87 cout << a[i]; 88 } 89 cout << endl; 90 } 91 else 92 { 93 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 94 { 95 int ok = 1; 96 for (int j = 0; j < cur&&ok; j++) 97 { 98 if (a[j] == i) 99 ok = 0; 100 } 101 if (ok) 102 { 103 a[cur] = i; 104 print(n, a, cur + 1); 105 } 106 } 107 } 108 return; 109 } 110 111 */
B2:1<=n<=50;
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 long long m, n, ans[50]; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 cin >> n >> m; 8 int l = 0, r = n - 1; 9 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 10 { 11 if(i == n) 12 { 13 if((m - 1) & ((1ll << n) - 1)) 14 ans[r--] = i; 15 else 16 ans[l++] = i; 17 } 18 else 19 { 20 if((m - 1) & (1ll << (n - i - 1))) 21 ans[r--] = i; 22 else 23 ans[l++] = i; 24 } 25 } 26 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 27 cout << ans[i] << ' '; 28 cout << endl; 29 }