#include<stdio.h> const int N = 3; int main(){ int a[N] = {1, 2, 3}; int i; for(i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("%d: %d ", &a[i], a[i]); printf("通过地址间接访问数组元素: "); for(i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("%d: %d ", a + i, *(a + i)); return 0;//通过冒号前面打印出的数组的地址,可以看出数组元素在内存中连续存放。 //2中的两个方法都是等价的。 }
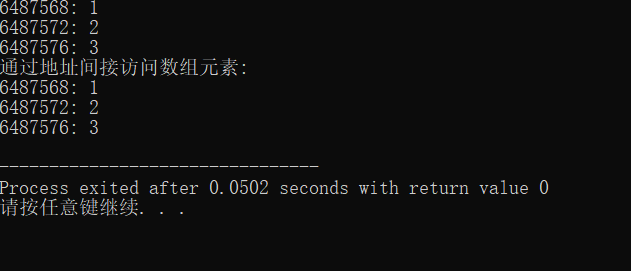
#include<stdio.h> const int LINE = 2; const int COL = 3; int main(){ int a[LINE][COL] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; int i, j; printf("通过数组名及下标直接访问数组元素: "); for(i = 0; i < LINE; i++) for(j = 0; j < COL; j++) printf("%d: %d ", &a[i][j], a[i][j]); printf("通过地址间接访问数组元素: "); for( i = 0; i < LINE ; i++) for( j = 0; j < COL ; j++) printf("%d: %d ", a[i]+j, *(a[i]+j)); printf("二维地址中a+i表示的地址: "); for(i = 0; i < LINE; i++) printf("a + %d: %d ", i, a+i); return 0; }
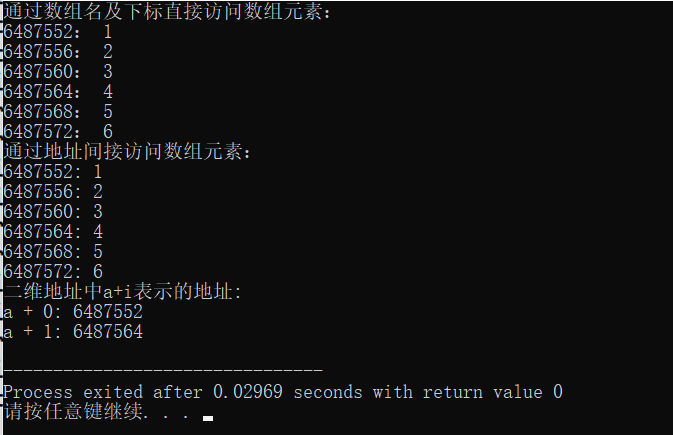
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> const int N = 3; int main(){ int a[N]; int *p,i; for(p = a; p<a+N; p++) scanf("%d",p);//p指向数组a最后一位的后一位 for(p = a; p<a+N; p++) printf("%d ", *p);//数组a最后一位的后一位 printf(" "); p = a; for(i = 0; i < N; i++) scanf("%d", p+i);//数组a的第一位 for(i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("%d ", *(p+i));//数组a的第一位 printf(" "); return 0; }
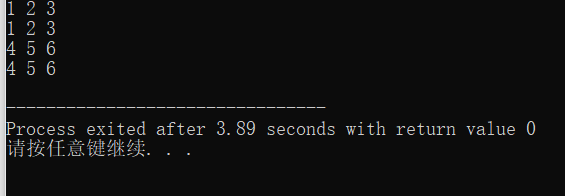
#include<stdio.h> int main(){ int a[2][3]{1,2,3,4,5,6}; int i, j; int *p; int (*q)[3]; #if(0) for(p = a[0]; p < a[0] + 6; p++)//由实践得这两句可以替换 #endif #if(1) for(p = &a[0][0];p < &a[0][0] + 6; p++)//需要运行哪段代码,哪段代码括号中改为1 #endif printf("%d",*p); printf(" "); for(q = a; q < a + 2; q++) for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) printf("%d",*(*q+j));//*q+j是第j行的首地址,*(*q+j)是第j行首个元素 printf(" "); return 0; } //p为指针,q为数组指针; #if(0) 都可以表示a[1][2]的地址 #endif
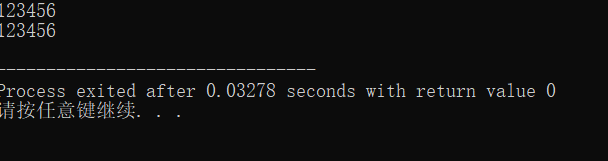
#include<stdio.h> const int N = 5; int binarySearch(int x[], int n, int item); int main(){ int a[N]={2,7,19,45,66}; int i, index, key; printf("数组a中的数据: "); for(i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]); printf(" "); printf("输入待查找的数据项:"); scanf("%d",&key); index = binarySearch(a, N, key); if(index >= 0) printf("%d在数组中,下标为%d ", key, index); else printf("%d不在数组中 ",key); return 0; } int binarySearch(int x[], int n, int item){ int low, high , mid; low = 0; high = n - 1; while(low <= high){ mid = (low + high) / 2; if(x[mid] == item) return mid; else if ( x[mid]> item) high = mid - 1; else low = mid + 1; } return -1; }
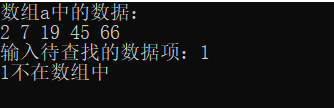
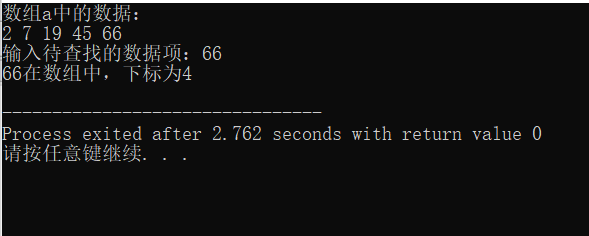
#include<stdio.h> const int N = 5; int binarySearch(int *x, int n, int item); int main(){ int a[N] = {2, 7, 19, 45, 66}; int i, index, key; printf("数组a中的数据: "); for(i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]); printf(" "); printf("输入待查找的数据: "); scanf("%d", &key); index = binarySearch(a, N, key); if(index >= 0) printf("%d在数组中,下标为%d", key, index); else printf("%d不再数组中"); return 0; } int binarySearch(int *x, int n, int item){ int low, high, mid; low = 0; high = n - 1; while(low <= high){ mid = (low + high) / 2; if ( item == *(x + mid)) return mid; else if (item < *(x + mid)) high = mid - 1; else low = mid - 1; } return -1; }
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> const int N = 5; void selectSort(char str[][20], int n); int main(){ char name[][20]={"Bob","Bill","Joseph","Taylor","George"}; int i ; printf("输出初始名单: "); for(i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("%s ",name[i]); selectSort(name, N); printf("按字典序输出名单: "); for(i = 0; i < N; i++) printf("%s ",name[i]); return 0; } void selectSort(char str[][20], int n){ int i , j; for(i = n - 1; i > 0;i--){ j = i - 1; char max[20]; strcpy(max,str[i]); for(;j >= 0; j--){ if(strcmp(max, str[j])<0){ strcpy(max,str[j]); strcpy(str[j], str[i]); strcpy(str[i], max); } } } }

实验一到四实验总结都在代码中打出,实验五的第一个代码的是数组的方法,第二个为指针的方法。