0前期调查
当我们需要购物时,我们需要搜索到平台上的商品,对其选择后知道其产品的各种属性比如说数量,单价,库存等等,再将其添加到购物车中。
0.1调查收获
在购物时,我们需要的产品需要通过搜索才能知道平台内各个产品的参数,所以我们可以创建一个动态数组来存放需要操作的商品名称。同时,我们可以利用这个数组来存放到时候需要删除的名单。
购物车内的物品名称和数量是一一对应的,我们可以通过调出商品名称来确定此商品在购物车内的数量。同样的,我也是打算用动态数组来存放各个商品的名称。
当我们将商品加入放进购物车时,平台中的库存也会相应的减少。
当我们要结算时,我们需要将各个商品的名单打印出,并再次询问顾客是否需要修改购物车内各个商品的属性。
当我们全部确定好后,我们便可以下单,并且清空购物车。
1功能设计
平台类:
商品的添加,
确定商品的名称,数量和单价。
个人类:
搜索商品,
将商品添加至购物车,
将商品从购物车移除,
对商品的重新调整。
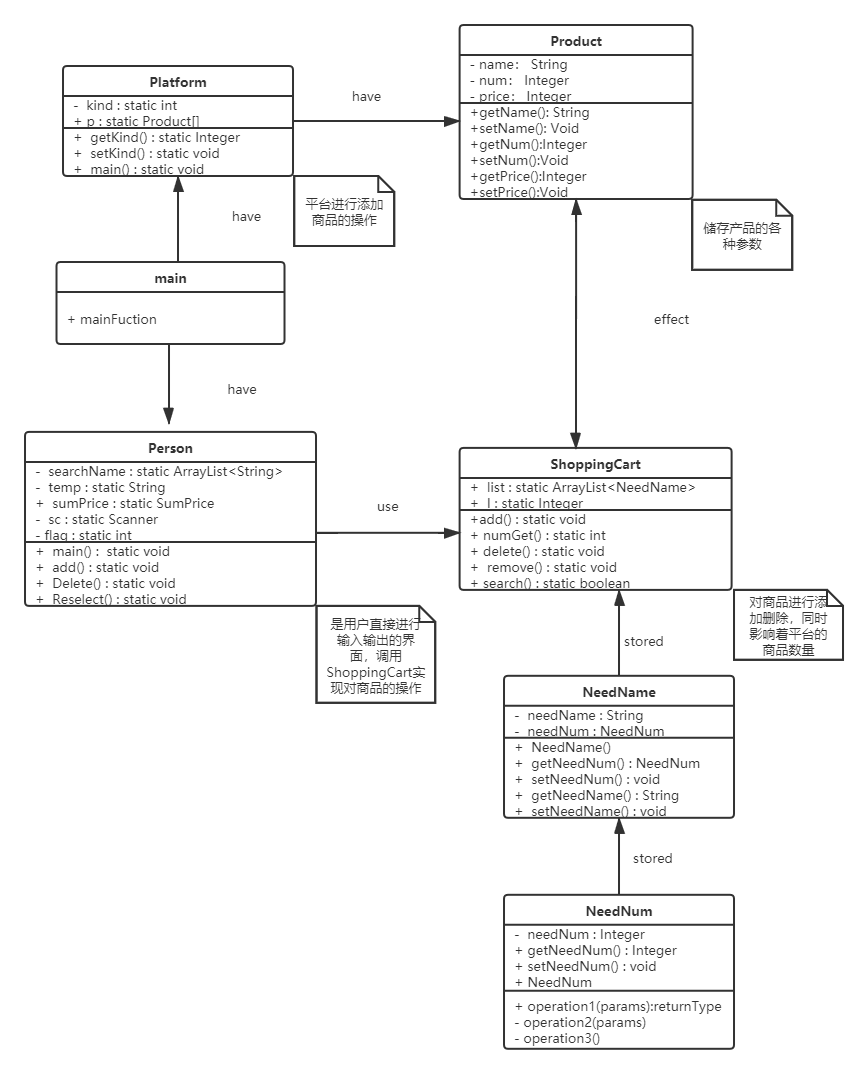
2.UML类图:

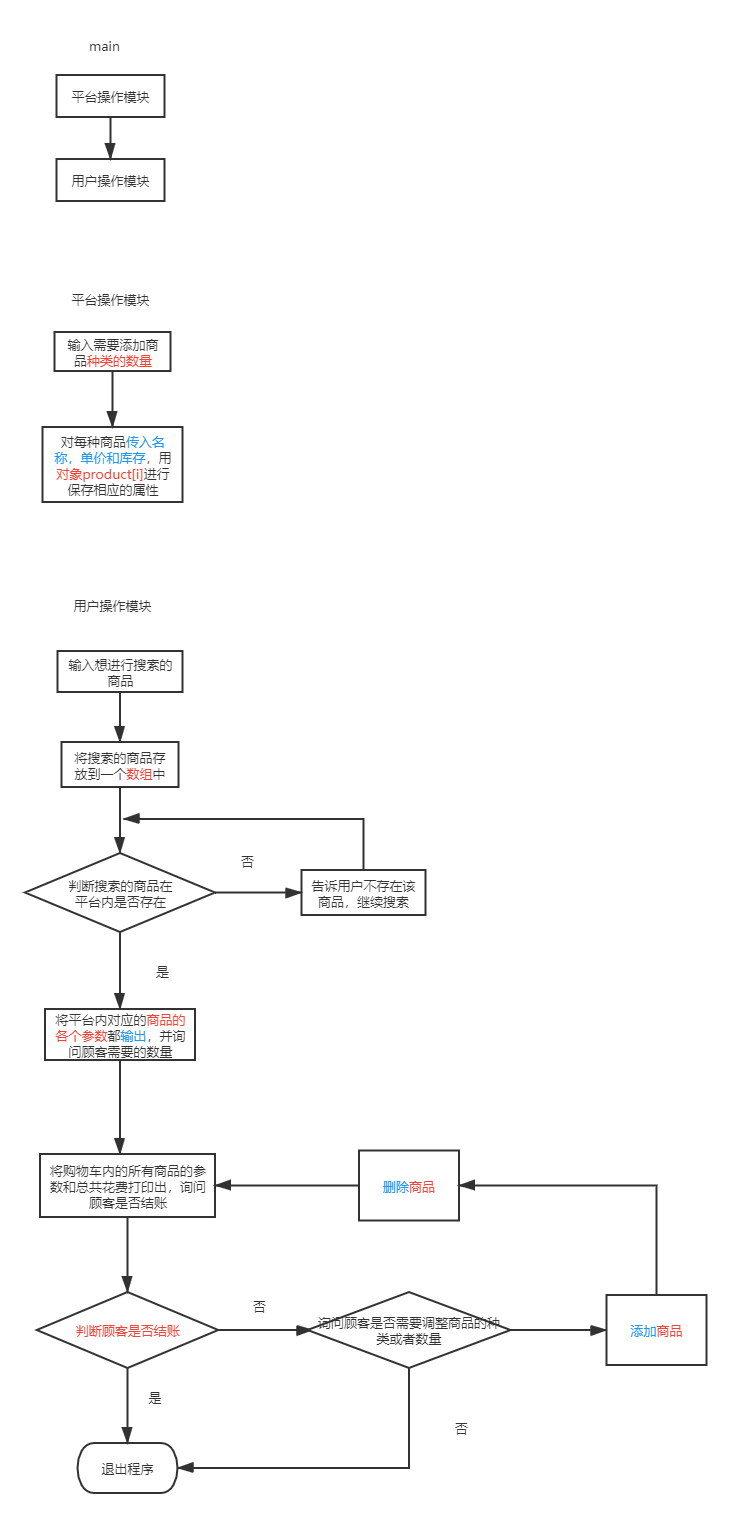
3.系统功能结构图及其系统描述
4.本系统哪里体现了面向对象的封装性
在 Product中
public class Product {
private String name;
private Integer price;
private Integer num;
private String model;
public Product(String name,Integer price,Integer num)
{
this.name=name;
this.price=price;
this.num=num;
}
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
public void setModel(String model) {
this.model = model;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Integer getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(Integer num) {
this.num = num;
}
}
将其各个属性设置成private,实现了保护当前类的某些属性和方法不被外部所见,用来实现该属性的get/set的方法,可以被外部访问。
5.项目的包结构和关键代码
项目的包结构:

在整个项目执行时,包的区分可以使各个类的对应联系更加明确。
关键代码
产品类
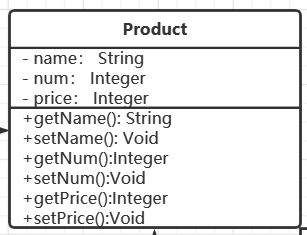
public class Product {
private String name;
private Integer price;
private Integer num;
private String model;
public Product(String name,Integer price,Integer num)
{
this.name=name;
this.price=price;
this.num=num;
}
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
public void setModel(String model) {
this.model = model;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price;
}
public Integer getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(Integer num) {
this.num = num;
}
}
购物车有关的类

public class ShoppingCart {
static ArrayList<NeedName> list=new ArrayList<>();
static Integer i = 0;
public static void add(String needName,Integer needNum){
Iterator<NeedName> iterator=list.iterator();
int flag = 0;
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
NeedName temp=iterator.next();
if(temp.getNeedName().equals(needName)) {
NeedNum num = new NeedNum(needNum+temp.getNeedNum().getNeedNum());
temp.setNeedNum(num);
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0) {
NeedName name=new NeedName(needName);
NeedNum num=new NeedNum(needNum);
name.setNeedNum(num);
list.add(name);
}
flag=0;
}
public static int numGet(String name) {
int num=0;
Iterator<NeedName> iterator=list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
NeedName temp = iterator.next();
if(temp.getNeedName().equals(name))
num=temp.getNeedNum().getNeedNum();
}
return num;
}
public static void delete(String name,Integer num) {
Iterator<NeedName> iterator=list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
NeedName temp = iterator.next();
if(temp.getNeedName().equals(name)) {
temp.getNeedNum().setNeedNum(temp.getNeedNum().getNeedNum()-num);
if(temp.getNeedNum().getNeedNum()==0)
iterator.remove();
break;
}
}
}
public static void remove(String name) {
Iterator<NeedName> iterator=list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
NeedName temp=iterator.next();
if(temp.getNeedName().equals(name)) {
for(int i=0;i<Platform.getKind();i++) {
if(name.equals(Platform.p[i].getName())) {
Platform.p[i].setNum(Platform.p[i].getNum()+temp.getNeedNum().getNeedNum());
Person.sumPrice.deleteSumPrice(ShoppingCart.numGet(name)*Platform.p[i].getPrice());
break;
}
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
平台有关的类

public class Platform {
private static int kind;
public static Product[] p;
public static int getKind() {
return kind;
}
public static void setKind(int kind) {
Platform.kind = kind;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("卖家您好,请输入您可以出售商品的种类数目");
Platform.kind=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请分别输入您所有商品的名称,单价和数量:");
p=new Product[kind];
for(int i=0;i<kind;i++)
{
p[i]=new Product(sc.next(),sc.nextInt(),sc.nextInt());
}
}
}