首先分析include头文件下的slamBase.h文件
# pragma once // 各种头文件 // C++标准库 #include <fstream> #include <vector> #include <map> using namespace std; // Eigen #include <Eigen/Core> #include <Eigen/Geometry> // OpenCV #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> // PCL #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/common/transforms.h> #include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> #include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h> //体素滤波器 进行降采样 #include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h> //统计滤波器 去除 孤立点 // 类型定义 typedef pcl::PointXYZRGBA PointT; typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud; // 相机内参结构 struct CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS { double cx, cy, fx, fy, scale; }; // 帧结构 struct FRAME { cv::Mat rgb, depth; //该帧对应的彩色图与深度图 cv::Mat desp; //特征描述子 vector<cv::KeyPoint> kp; //关键点 }; // PnP 结果 struct RESULT_OF_PNP { cv::Mat rvec, tvec; int inliers; }; // 函数接口 // image2PonitCloud 将rgb图转换为点云 PointCloud::Ptr image2PointCloud( cv::Mat& rgb, cv::Mat& depth, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ); // point2dTo3d 将单个点从图像坐标转换为空间坐标 // input: 3维点Point3f (u,v,d) cv::Point3f point2dTo3d( cv::Point3f& point, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ); // computeKeyPointsAndDesp 同时提取关键点与特征描述子 void computeKeyPointsAndDesp( FRAME& frame, string detector, string descriptor ); // estimateMotion 计算两个帧之间的运动 // 输入:帧1和帧2, 相机内参 RESULT_OF_PNP estimateMotion( FRAME& frame1, FRAME& frame2, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ); // cvMat2Eigen, 将cv的旋转矢量与位移矢量转换为变换矩阵,类型为Eigen::Isometry3d Eigen::Isometry3d cvMat2Eigen( cv::Mat& rvec, cv::Mat& tvec ); // joinPointCloud , 组合点云 PointCloud::Ptr joinPointCloud( PointCloud::Ptr original, FRAME& newFrame, Eigen::Isometry3d T, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) ; // 参数读取类 class ParameterReader { public: map<string, string> data; public: ParameterReader( string filename="./parameters.txt" ) { ifstream fin( filename.c_str() ); if (!fin) { cerr<<"parameter file does not exist."<<endl; return; } while(!fin.eof()) { string str; getline( fin, str ); if (str[0] == '#') { // 以‘#’开头的是注释 continue; } int pos = str.find("="); if (pos == -1) continue; string key = str.substr( 0, pos ); string value = str.substr( pos+1, str.length() ); data[key] = value; if ( !fin.good() ) break; } } string getData( string key ) { map<string, string>::iterator iter = data.find(key); if (iter == data.end()) { cerr<<"Parameter name "<<key<<" not found!"<<endl; return string("NOT_FOUND"); } return iter->second; } }; inline static CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS getDefaultCamera() { ParameterReader pd; CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS camera; camera.fx = atof( pd.getData( "camera.fx" ).c_str()); camera.fy = atof( pd.getData( "camera.fy" ).c_str()); camera.cx = atof( pd.getData( "camera.cx" ).c_str()); camera.cy = atof( pd.getData( "camera.cy" ).c_str()); camera.scale = atof( pd.getData( "camera.scale" ).c_str() ); return camera; }
从parameters.txt读取相机内参函数,参数不写进程序,修改时不需要重新编译,只需要修改参数文件。
inline static CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS getDefaultCamera() { ParameterReader pd; CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS camera; camera.fx = atof( pd.getData( "camera.fx" ).c_str()); camera.fy = atof( pd.getData( "camera.fy" ).c_str()); camera.cx = atof( pd.getData( "camera.cx" ).c_str()); camera.cy = atof( pd.getData( "camera.cy" ).c_str()); camera.scale = atof( pd.getData( "camera.scale" ).c_str() ); return camera; }
getDefaultCamera()函数返回的是CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS结构,获得所有相机内参(其中用到class ParameterReader类)。class ParameterReader类,成员函数为getData()。class ParameterReader类得到一个data(参数文件左边为key,右边为value),而成员函数为getData()根据key获得对应的value( 如camera.fx = atof( pd.getData( "camera.fx" ).c_str()) )。
以上slamBase.h中源函数在slamBase.cpp中的实现
#include "slamBase.h" PointCloud::Ptr image2PointCloud( cv::Mat& rgb, cv::Mat& depth, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { PointCloud::Ptr cloud ( new PointCloud ); for (int m = 0; m < depth.rows; m+=2) for (int n=0; n < depth.cols; n+=2) { // 获取深度图中(m,n)处的值 ushort d = depth.ptr<ushort>(m)[n]; // d 可能没有值,若如此,跳过此点 if (d == 0 || d>=4096) continue; // d 存在值,则向点云增加一个点 PointT p; // 计算这个点的空间坐标 p.z = double(d) / camera.scale; p.x = (n - camera.cx) * p.z / camera.fx; p.y = (m - camera.cy) * p.z / camera.fy; // 从rgb图像中获取它的颜色 // rgb是三通道的BGR格式图,所以按下面的顺序获取颜色 p.b = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3]; p.g = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3+1]; p.r = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3+2]; // 把p加入到点云中 cloud->points.push_back( p ); } // 设置并保存点云 cloud->height = 1; cloud->width = cloud->points.size(); cloud->is_dense = false; return cloud; } cv::Point3f point2dTo3d( cv::Point3f& point, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { cv::Point3f p; // 3D 点 p.z = double( point.z ) / camera.scale; p.x = ( point.x - camera.cx) * p.z / camera.fx; p.y = ( point.y - camera.cy) * p.z / camera.fy; return p; } // computeKeyPointsAndDesp 同时提取关键点与特征描述子 void computeKeyPointsAndDesp( FRAME& frame ) { cv::Ptr<cv::FeatureDetector> _detector; cv::Ptr<cv::DescriptorExtractor> _descriptor; _detector = cv::ORB::create(); _descriptor = cv::ORB::create(); /* if (!_detector || !_descriptor) { cerr<<"Unknown detector or discriptor type !"<<detector<<","<<descriptor<<endl; return; } */ _detector->detect( frame.rgb, frame.kp ); _descriptor->compute( frame.rgb, frame.kp, frame.desp ); return; } // estimateMotion 计算两个帧之间的运动 // 输入:帧1和帧2 // 输出:rvec 和 tvec RESULT_OF_PNP estimateMotion( FRAME& frame1, FRAME& frame2, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { static ParameterReader pd; vector< cv::DMatch > matches; cv::BFMatcher matcher; matcher.match( frame1.desp, frame2.desp, matches ); RESULT_OF_PNP result; vector< cv::DMatch > goodMatches; double minDis = 9999; double good_match_threshold = atof( pd.getData( "good_match_threshold" ).c_str() ); for ( size_t i=0; i<matches.size(); i++ ) { if ( matches[i].distance < minDis ) minDis = matches[i].distance; } cout<<"min dis = "<<minDis<<endl; if ( minDis < 10 ) minDis = 10; for ( size_t i=0; i<matches.size(); i++ ) { if (matches[i].distance < good_match_threshold*minDis ) goodMatches.push_back( matches[i] ); } cout<<"good matches: "<<goodMatches.size()<<endl; if (goodMatches.size() <= 5) { result.inliers = -1; return result; } // 第一个帧的三维点 vector<cv::Point3f> pts_obj; // 第二个帧的图像点 vector< cv::Point2f > pts_img; // 相机内参 for (size_t i=0; i<goodMatches.size(); i++) { // query 是第一个, train 是第二个 cv::Point2f p = frame1.kp[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt; // 获取d是要小心!x是向右的,y是向下的,所以y才是行,x是列! ushort d = frame1.depth.ptr<ushort>( int(p.y) )[ int(p.x) ]; if (d == 0 || d>=4096) continue; pts_img.push_back( cv::Point2f( frame2.kp[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt ) ); // 将(u,v,d)转成(x,y,z) cv::Point3f pt ( p.x, p.y, d ); cv::Point3f pd = point2dTo3d( pt, camera ); pts_obj.push_back( pd ); } if (pts_obj.size() ==0 || pts_img.size()==0) { result.inliers = -1; return result; } double camera_matrix_data[3][3] = { {camera.fx, 0, camera.cx}, {0, camera.fy, camera.cy}, {0, 0, 1} }; // 构建相机矩阵 cv::Mat cameraMatrix( 3, 3, CV_64F, camera_matrix_data ); cv::Mat rvec, tvec, inliers; // 求解pnp cv::solvePnPRansac( pts_obj, pts_img, cameraMatrix, cv::Mat(), rvec, tvec, false, 100, 1.0, 0.95, inliers ,cv::SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE); result.rvec = rvec; result.tvec = tvec; result.inliers = inliers.rows; return result; } // cvMat2Eigen (R,t -> T) ,将cv的旋转矢量与位移矢量转换为变换矩阵,类型为Eigen::Isometry3d Eigen::Isometry3d cvMat2Eigen( cv::Mat& rvec, cv::Mat& tvec ) { cv::Mat R; cv::Rodrigues( rvec, R ); Eigen::Matrix3d r; for ( int i=0; i<3; i++ ) for ( int j=0; j<3; j++ ) r(i,j) = R.at<double>(i,j); // 将平移向量和旋转矩阵转换成变换矩阵 Eigen::Isometry3d T = Eigen::Isometry3d::Identity(); Eigen::AngleAxisd angle(r); T = angle; T(0,3) = tvec.at<double>(0,0); T(1,3) = tvec.at<double>(1,0); T(2,3) = tvec.at<double>(2,0); return T; } // joinPointCloud // 输入:原始点云,新来的帧以及它的位姿 // 输出:将新来帧加到原始帧后的图像 PointCloud::Ptr joinPointCloud( PointCloud::Ptr original, FRAME& newFrame, Eigen::Isometry3d T, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { PointCloud::Ptr newCloud = image2PointCloud( newFrame.rgb, newFrame.depth, camera ); //新的点云 // depth filter and statistical removal PointCloud::Ptr df ( new PointCloud ); pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<PointT> statistical_filter; //newCloud -> df statistical_filter.setMeanK(50); statistical_filter.setStddevMulThresh(1.0); statistical_filter.setInputCloud(newCloud); statistical_filter.filter( *df ); // 合并点云 PointCloud::Ptr output (new PointCloud()); pcl::transformPointCloud( *original, *output, T.matrix() ); //将旧点云转到当前点云坐标系下 *df += *output; //新点云 + 之前的点云 //加入newCloud后,新的点云,进行滤波 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Voxel grid 滤波降采样 static pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> voxel; static ParameterReader pd; //参数读取 double gridsize = atof( pd.getData("voxel_grid").c_str() ); //分辨率 voxel.setLeafSize( gridsize, gridsize, gridsize ); //df -> tmp voxel.setInputCloud( df ); PointCloud::Ptr tmp( new PointCloud() ); voxel.filter( *tmp ); /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// return tmp; }
将rgb图和对应的深度图转为点云(包含相机内参结构)
PointCloud::Ptr image2PointCloud( cv::Mat& rgb, cv::Mat& depth, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { PointCloud::Ptr cloud ( new PointCloud ); for (int m = 0; m < depth.rows; m+=2) for (int n=0; n < depth.cols; n+=2) { // 获取深度图中(m,n)处的值 ushort d = depth.ptr<ushort>(m)[n]; // d 可能没有值,若如此,跳过此点 if (d == 0 || d>=4096) continue; // d 存在值,则向点云增加一个点 PointT p; // 计算这个点的空间坐标 p.z = double(d) / camera.scale; p.x = (n - camera.cx) * p.z / camera.fx; p.y = (m - camera.cy) * p.z / camera.fy; // 从rgb图像中获取它的颜色 // rgb是三通道的BGR格式图,所以按下面的顺序获取颜色 p.b = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3]; p.g = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3+1]; p.r = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3+2]; // 把p加入到点云中 cloud->points.push_back( p ); } // 设置并保存点云 cloud->height = 1; cloud->width = cloud->points.size(); cloud->is_dense = false; return cloud; }
// 获取深度图中(m,n)处的值
ushort d = depth.ptr<ushort>(m)[n]; depth是深度图
PointT p;一个点包含位置(p.x ,p.y ,p.z),和颜色RGB(p.b , p.g , p.r),将点p放入点云cloud中。
// computeKeyPointsAndDesp 同时提取关键点与特征描述子 void computeKeyPointsAndDesp( FRAME& frame ) { cv::Ptr<cv::FeatureDetector> _detector; //特征点提取 cv::Ptr<cv::DescriptorExtractor> _descriptor; //描述子 _detector = cv::ORB::create(); _descriptor = cv::ORB::create(); /* if (!_detector || !_descriptor) { cerr<<"Unknown detector or discriptor type !"<<detector<<","<<descriptor<<endl; return; } */ _detector->detect( frame.rgb, frame.kp ); //rgb图片frame.rgb, -> frame.kp特征点 _descriptor->compute( frame.rgb, frame.kp, frame.desp ); //(frame.rgb,frame.kp) -> frame.desp描述子 return; }
使用引用类型,不需要返回任何值。void computeKeyPointsAndDesp( FRAME& frame )传入的值为frame结构,包含rgb,depth,desp,kp,求得的frame.rgb,frame.desp,与frame.rgb(彩色图片)对应。
// estimateMotion 计算两个帧之间的运动 // 输入:帧1和帧2 // 输出:rvec 和 tvec RESULT_OF_PNP estimateMotion( FRAME& frame1, FRAME& frame2, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { static ParameterReader pd; vector< cv::DMatch > matches; cv::BFMatcher matcher; matcher.match( frame1.desp, frame2.desp, matches ); RESULT_OF_PNP result; vector< cv::DMatch > goodMatches; double minDis = 9999; double good_match_threshold = atof( pd.getData( "good_match_threshold" ).c_str() );
for ( size_t i=0; i<matches.size(); i++ )//输出最小匹配距离 { if ( matches[i].distance < minDis ) minDis = matches[i].distance; } cout<<"min dis = "<<minDis<<endl;
if ( minDis < 10 ) minDis = 10; for ( size_t i=0; i<matches.size(); i++ ) { if (matches[i].distance < good_match_threshold*minDis ) //小于最小距离的十倍,则将该匹配放入goodMatches中 goodMatches.push_back( matches[i] ); } cout<<"good matches: "<<goodMatches.size()<<endl; if (goodMatches.size() <= 5) //匹配点太少时,不进行之后计算 { result.inliers = -1; return result; } // 第一个帧的三维点 vector<cv::Point3f> pts_obj; // 第二个帧的图像点 vector< cv::Point2f > pts_img; // 相机内参,获得pts_img,pts_obj for (size_t i=0; i<goodMatches.size(); i++) { // query 是第一个, train 是第二个 cv::Point2f p = frame1.kp[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt; //取第一幅图最佳匹配点坐标 // 获取d是要小心!x是向右的,y是向下的,所以y才是行,x是列! ushort d = frame1.depth.ptr<ushort>( int(p.y) )[ int(p.x) ]; //取以上坐标的深度 if (d == 0 || d>=4096) continue; pts_img.push_back( cv::Point2f( frame2.kp[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt ) ); //取第二幅图最佳匹配点像素坐标 // 将(u,v,d)转成(x,y,z) cv::Point3f pt ( p.x, p.y, d ); cv::Point3f pd = point2dTo3d( pt, camera ); pts_obj.push_back( pd ); } if (pts_obj.size() ==0 || pts_img.size()==0) { result.inliers = -1; return result; } //数组,相机内参 double camera_matrix_data[3][3] =
{ {camera.fx, 0, camera.cx}, {0, camera.fy, camera.cy}, {0, 0, 1} }; // 构建相机矩阵 cv::Mat cameraMatrix( 3, 3, CV_64F, camera_matrix_data ); cv::Mat rvec, tvec, inliers; //rvec,旋转向量 tvec,位移向量 // 求解pnp cv::solvePnPRansac( pts_obj, pts_img, cameraMatrix, cv::Mat(), rvec, tvec, false, 100, 1.0, 0.95, inliers ,cv::SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE); result.rvec = rvec; result.tvec = tvec; result.inliers = inliers.rows; return result; }
RESULT_OF_PNP estimateMotion( FRAME& frame1, FRAME& frame2, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera )函数返回的类型是RESULT_OF_PNP结构包含数据为旋转向量rvec,位移向量tvec,inliers。其中用到的函数是cv::solvePnPRansac()https://blog.csdn.net/jay463261929/article/details/53818611
https://docs.opencv.org/master/d9/d0c/group__calib3d.html#ga50620f0e26e02caa2e9adc07b5fbf24e
其中最主要的程序为
// 相机内参,获得pts_img,pts_obj for (size_t i=0; i<goodMatches.size(); i++) { // query 是第一个, train 是第二个 cv::Point2f p = frame1.kp[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt; //取第一幅图最佳匹配点坐标 // 获取d是要小心!x是向右的,y是向下的,所以y才是行,x是列! ushort d = frame1.depth.ptr<ushort>( int(p.y) )[ int(p.x) ]; //取以上坐标的深度 if (d == 0 || d>=4096) continue; // 将(u,v,d)转成(x,y,z) cv::Point3f pt ( p.x, p.y, d ); cv::Point3f pd = point2dTo3d( pt, camera ); pts_obj.push_back( pd ); pts_img.push_back( cv::Point2f( frame2.kp[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt ) ); //取第二幅图最佳匹配点像素坐标 }
获得第一幅图特征点的3维点空间点坐标pts_obj,和对应第二幅图特征点的图像坐标pts_img。
frame1.kp[goodMatches[i].queryIdx]图像frame1特征点对应于frame2.kp[goodMatches[i].trainIdx]图像frame2特征点。frame1.kp[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt为特征点坐标。
点云合成
// joinPointCloud // 输入:原始点云,新来的帧以及它的位姿 // 输出:将新来帧加到原始帧后的图像 PointCloud::Ptr joinPointCloud( PointCloud::Ptr original, FRAME& newFrame, Eigen::Isometry3d T, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { PointCloud::Ptr newCloud = image2PointCloud( newFrame.rgb, newFrame.depth, camera ); //新的点云 // depth filter and statistical removal PointCloud::Ptr df ( new PointCloud ); pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<PointT> statistical_filter; //newCloud -> df statistical_filter.setMeanK(50); statistical_filter.setStddevMulThresh(1.0); statistical_filter.setInputCloud(newCloud); statistical_filter.filter( *df ); // 合并点云 PointCloud::Ptr output (new PointCloud()); pcl::transformPointCloud( *original, *output, T.matrix() ); //将旧点云转到当前点云坐标系下 *df += *output; //新点云 + 之前的点云 //加入newCloud后,新的点云,进行滤波 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Voxel grid 滤波降采样 static pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> voxel; static ParameterReader pd; //参数读取 double gridsize = atof( pd.getData("voxel_grid").c_str() ); //分辨率 voxel.setLeafSize( gridsize, gridsize, gridsize ); //df -> tmp voxel.setInputCloud( df ); PointCloud::Ptr tmp( new PointCloud() ); voxel.filter( *tmp ); /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// return tmp; }
其中包含两个滤波,一个是统计滤波器,用于去除孤立噪声点,另一个是体素滤波器,进行降采样,保证了在某个一定大小的立方体内仅有一个点。
视觉里程计visualOdometry.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <sstream> using namespace std; #include "slamBase.h" // 给定index,读取一帧数据 FRAME readFrame( int index, ParameterReader& pd ); // 度量运动的大小 double normofTransform( cv::Mat rvec, cv::Mat tvec ); int main( int argc, char** argv ) { ParameterReader pd; int startIndex = atoi( pd.getData( "start_index" ).c_str() ); int endIndex = atoi( pd.getData( "end_index" ).c_str() ); // initialize cout<<"Initializing ..."<<endl; int currIndex = startIndex; // 当前索引为currIndex FRAME lastFrame = readFrame( currIndex, pd ); // 上一帧数据 // 我们总是在比较currFrame和lastFrame /* string detector = pd.getData( "detector" ); string descriptor = pd.getData( "descriptor" ); */ CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS camera = getDefaultCamera(); //相机内参 computeKeyPointsAndDesp( lastFrame); PointCloud::Ptr cloud = image2PointCloud( lastFrame.rgb, lastFrame.depth, camera ); pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer("viewer"); // 是否显示点云 bool visualize = pd.getData("visualize_pointcloud")==string("yes"); int min_inliers = atoi( pd.getData("min_inliers").c_str() ); double max_norm = atof( pd.getData("max_norm").c_str() ); for ( currIndex=startIndex+1; currIndex<endIndex; currIndex++ ) { cout<<"Reading files "<<currIndex<<endl; FRAME currFrame = readFrame( currIndex,pd ); // 读取currFrame computeKeyPointsAndDesp( currFrame ); // 比较currFrame 和 lastFrame RESULT_OF_PNP result = estimateMotion( lastFrame, currFrame, camera ); if ( result.inliers < min_inliers ) //inliers不够,放弃该帧 continue; // 计算运动范围是否太大 double norm = normofTransform(result.rvec, result.tvec); cout<<"norm = "<<norm<<endl; if ( norm >= max_norm ) { cout<<"�33[41;36m move too much �33[0m "<<endl; continue; } Eigen::Isometry3d T = cvMat2Eigen( result.rvec, result.tvec ); cout<<"T="<<T.matrix()<<endl; cloud = joinPointCloud( cloud, currFrame, T, camera ); ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// PointCloud::Ptr Cloudreverse (new PointCloud()); Eigen::Isometry3d T1 = Eigen::Isometry3d::Identity();//x T1(0,0) = 1; T1(0,1) = 0; T1(1,0) = 0; T1(1,1) = -1; T1(2,2) = -1; pcl::transformPointCloud( *cloud, *Cloudreverse, (T1).matrix() ); ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// if ( visualize == true ) viewer.showCloud( Cloudreverse ); lastFrame = currFrame; } pcl::io::savePCDFile( "data/result.pcd", *cloud ); return 0; } FRAME readFrame( int index, ParameterReader& pd ) { FRAME f; string rgbDir = pd.getData("rgb_dir"); string depthDir = pd.getData("depth_dir"); string rgbExt = pd.getData("rgb_extension"); string depthExt = pd.getData("depth_extension"); stringstream ss; ss<<rgbDir<<index<<rgbExt; string filename; ss>>filename; f.rgb = cv::imread( filename ); ss.clear(); filename.clear(); ss<<depthDir<<index<<depthExt; ss>>filename; f.depth = cv::imread( filename, -1 ); return f; } double normofTransform( cv::Mat rvec, cv::Mat tvec ) { return fabs(min(cv::norm(rvec), 2*M_PI-cv::norm(rvec)))+ fabs(cv::norm(tvec)); }
参数文件(parameters.txt):
# 特征类型 detector=ORB descriptor=ORB # 筛选good match的倍数 good_match_threshold=10 # camera camera.cx=682.3; camera.cy=254.9; camera.fx=979.8; camera.fy=942.8; camera.scale=1000.0; # part 5 # 数据相关 # 起始与终止索引 start_index=1 end_index=300 # 数据所在目录 rgb_dir=./data/rgb_png/ rgb_extension=.png depth_dir=./data/depth_png/ depth_extension=.png # 点云分辨率 voxel_grid=0.005 # 是否实时可视化 visualize_pointcloud=yes # 最小匹配数量 min_good_match=10 # 最小内点 min_inliers=5 # 最大运动误差 max_norm=0.3
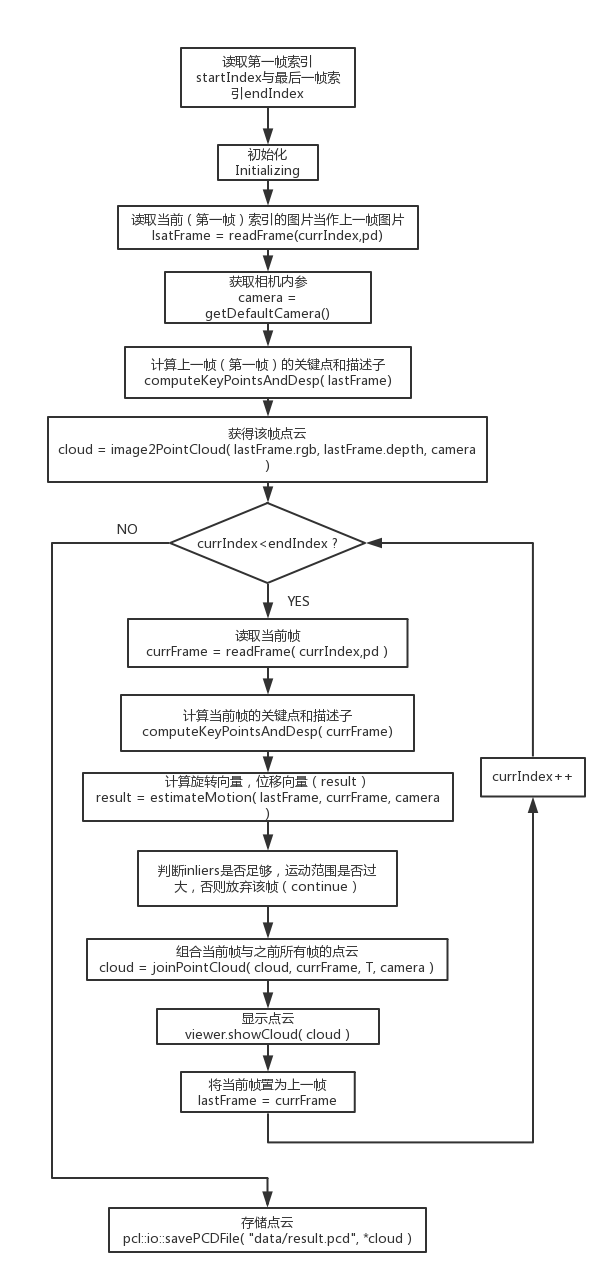
程序框图: