<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>定位</title>
<style media="screen">
.box1{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(184, 208, 162);
}
.box2{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(231, 223, 143);
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
.box3{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(188, 211, 213);
}
span{
background-color: rgb(209, 198, 209);
position:absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
</div>
<div class="box2">
</div>
<div class="box3">
</div>
<span>span元素</span>
</body>
</html>
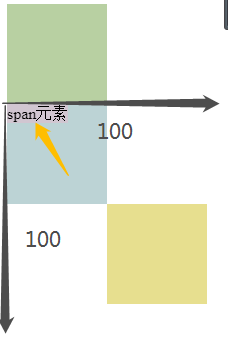
输出:
1.开启绝对定位,会使元素脱离文档流;
2、开启绝对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量,则元素的位置不会发生变化;
3、相对于浏览器窗口进行定位;

开启box3的定位并把box2作为box3的子元素:
.box2{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(231, 223, 143);
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
.box3{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(188, 211, 213);
position: absolute;
}
<div class="box3">
<div class="box2">
</div>
</div>
输出:
若有祖先元素开启了定位(一般情况,开启了子元素的绝对定位都会同时开启父元素的相对定位);
绝对定位是相对于离他最近的开启了定位的祖先元素进行定位的;
绝对定位会使元素提高一个层级;
改变元素的性质(块联元素变为内联元素);