There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
- (1) Every node is either red or black.
- (2) The root is black.
- (3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
- (4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
- (5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
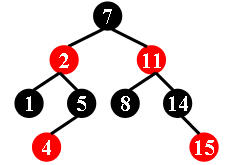 | 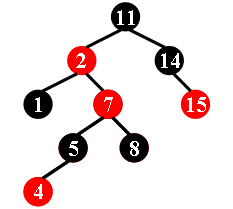 | 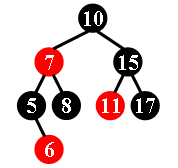 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤30) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the preorder traversal sequence of the tree. While all the keys in a tree are positive integers, we use negative signs to represent red nodes. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The sample input cases correspond to the trees shown in Figure 1, 2 and 3.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if the given tree is a red-black tree, or "No" if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
7 -2 1 5 -4 -11 8 14 -15
9
11 -2 1 -7 5 -4 8 14 -15
8
10 -7 5 -6 8 15 -11 17
Sample Output:
Yes No No
【注意,不用判断是不是平衡二叉树,因为红黑树不是严格的平衡二叉树】
分析:判断以下几点:
1.根结点是否为黑色
2.如果一个结点是红色,它的孩子节点是否都为黑色
3.从任意结点到叶子结点的路径中,黑色结点的个数是否相同
所以分为以下几步:
0. 根据先序建立一棵树,用链表表示
1. 判断根结点(题目所给先序的第一个点即根结点)是否是黑色
2. 根据建立的树,从根结点开始遍历,如果当前结点是红色,判断它的孩子节点是否为黑色,递归返回结果
3. 从根节点开始,递归遍历,检查每个结点的左子树的高度和右子树的高度(这里的高度指黑色结点的个数),比较左右孩子高度是否相等,递归返回结果
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 struct Node 7 { 8 int val; 9 Node *l, *r; 10 Node(int a) :val(a), l(nullptr), r(nullptr) {} 11 }; 12 int n, m; 13 int getHigh(Node *root)//是指黑节点个数哦 14 { 15 if (root == nullptr) 16 return 0; 17 int ln = getHigh(root->l); 18 int rn = getHigh(root->r); 19 return root->val > 0 ? max(ln, rn) + 1 : max(ln, rn);//计算黑节点个数 20 } 21 Node *Insert(Node *root, int x) 22 { 23 if (root == nullptr) 24 root = new Node(x); 25 else if (abs(x) < abs(root->val)) 26 root->l = Insert(root->l, x); 27 else 28 root->r = Insert(root->r, x); 29 return root; 30 } 31 bool redNode(Node *root) 32 { 33 if (root == nullptr) 34 return true; 35 if (root->val < 0)//红节点孩子一定要是黑节点 36 if (root->l != nullptr && root->l->val < 0 || 37 root->r != nullptr && root->r->val < 0) 38 return false; 39 return redNode(root->l) && redNode(root->r); 40 } 41 bool balanceTree(Node *root) 42 { 43 if (root == nullptr) return true; 44 if (getHigh(root->l) != getHigh(root->r))return false;//黑节点个数不同 45 return balanceTree(root->l) && balanceTree(root->r); 46 } 47 int main() 48 { 49 int n, m; 50 cin >> n; 51 while (n--) 52 { 53 cin >> m; 54 vector<int>v(m); 55 Node *root = nullptr; 56 for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) 57 { 58 cin >> v[i]; 59 root = Insert(root, v[i]); 60 } 61 if (v[0] >= 0 && balanceTree(root) && redNode(root)) 62 cout << "Yes" << endl; 63 else 64 cout << "No" << endl; 65 } 66 return 0; 67 }