安装
通过epel 源 yum 安装
[root@localhost varnish]# rpm -ql varnish /etc/logrotate.d/varnish /etc/varnish /etc/varnish/default.vcl /etc/varnish/varnish.params /run/varnish.pid /usr/bin/varnishadm /usr/bin/varnishhist /usr/bin/varnishlog /usr/bin/varnishncsa /usr/bin/varnishstat /usr/bin/varnishtest /usr/bin/varnishtop /usr/lib/systemd/system/varnish.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/varnishlog.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/varnishncsa.service /usr/sbin/varnish_reload_vcl /usr/sbin/varnishd /usr/share/doc/varnish-4.0.5 /usr/share/doc/varnish-4.0.5/LICENSE /usr/share/doc/varnish-4.0.5/README /usr/share/doc/varnish-4.0.5/builtin.vcl /usr/share/doc/varnish-4.0.5/changes.rst /usr/share/doc/varnish-4.0.5/example.vcl /usr/share/man/man1/varnishadm.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/varnishd.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/varnishhist.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/varnishlog.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/varnishncsa.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/varnishstat.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/varnishtest.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/varnishtop.1.gz /usr/share/man/man3/vmod_directors.3.gz /usr/share/man/man3/vmod_std.3.gz /usr/share/man/man7/varnish-cli.7.gz /usr/share/man/man7/varnish-counters.7.gz /usr/share/man/man7/vcl.7.gz /usr/share/man/man7/vsl-query.7.gz /usr/share/man/man7/vsl.7.gz /var/lib/varnish /var/log/varnish [root@localhost varnish]#
配置varnish的三种应用
1、varnishd应用程序的命令行参数; 监听的socket, 使用的存储类型等等;额外的配置参数; -p param=value -r param,param,... : 设定只读参数列表; /etc/varnish/varnish.params 2、-p选项指明的参数: 运行时参数: 也可在程序运行中,通过其CLI进行配置; 3、vcl:配置缓存系统的缓存机制; 通过vcl配置文件进行配置; 先编译,后应用; 依赖于c编译器;
启动varnish:
Starting Varnish(启动varnish) 假设varnishd在您的环境变量中,您可能需要运行pkill varnishd来确定varnish没有运行。然后使用root执行下面的命令。 varnishd -f /usr/local/etc/varnish/default.vcl -s malloc,1G -T 127.0.0.1:2000 -a 0.0.0.0:8080 我添加了一些选项,现在来详细分析他们: -f /usr/local/etc/varnish/default.vcl 这个 –f 选项指定varnishd使用哪个配置文件。 -s malloc,1G 这个 –s 选项用来确定varnish使用的存储类型和存储容量,我使用的是malloc类型(malloc是一个C函数,用于分配内存空间), 1G 定义多少内存被malloced,1G = 1gigabyte。 -T 127.0.0.1:2000 Varnish有一个基于文本的管理接口,启动它的话可以在不停止varnish的情况下来管理varnish。您可以指定管理软件监听哪个接口。当然您不能让全世界的人都能访问您的varnish管理接口,因为他们可以很轻松的通过访问varnish管理接口来获得您的root访问权限。我推荐只让它监听本机端口。如果您的系统里有您不完全信任的用户,您可以通过防火墙规则来限制他访问varnish的管理端口。 -a 0.0.0.0:8080 这一句的意思是制定varnish监听所有IP发给8080端口的http请求,如果在生产环境下,您应该让varnish监听80,这也是默认的。
*********#/etc/varnish/varnish.params 配置文件定义了默认的运行参数,可以直接通过命令行指定,也可以通过修改配置文件配置
*********#/etc/varnish/default.vcl 配置文件定义了缓存系统的配置
命令行工具: varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T IP:PORT Log: varnishlog varnishncsa Statistics varnishstat Top: varnishtop
数据处理流程:
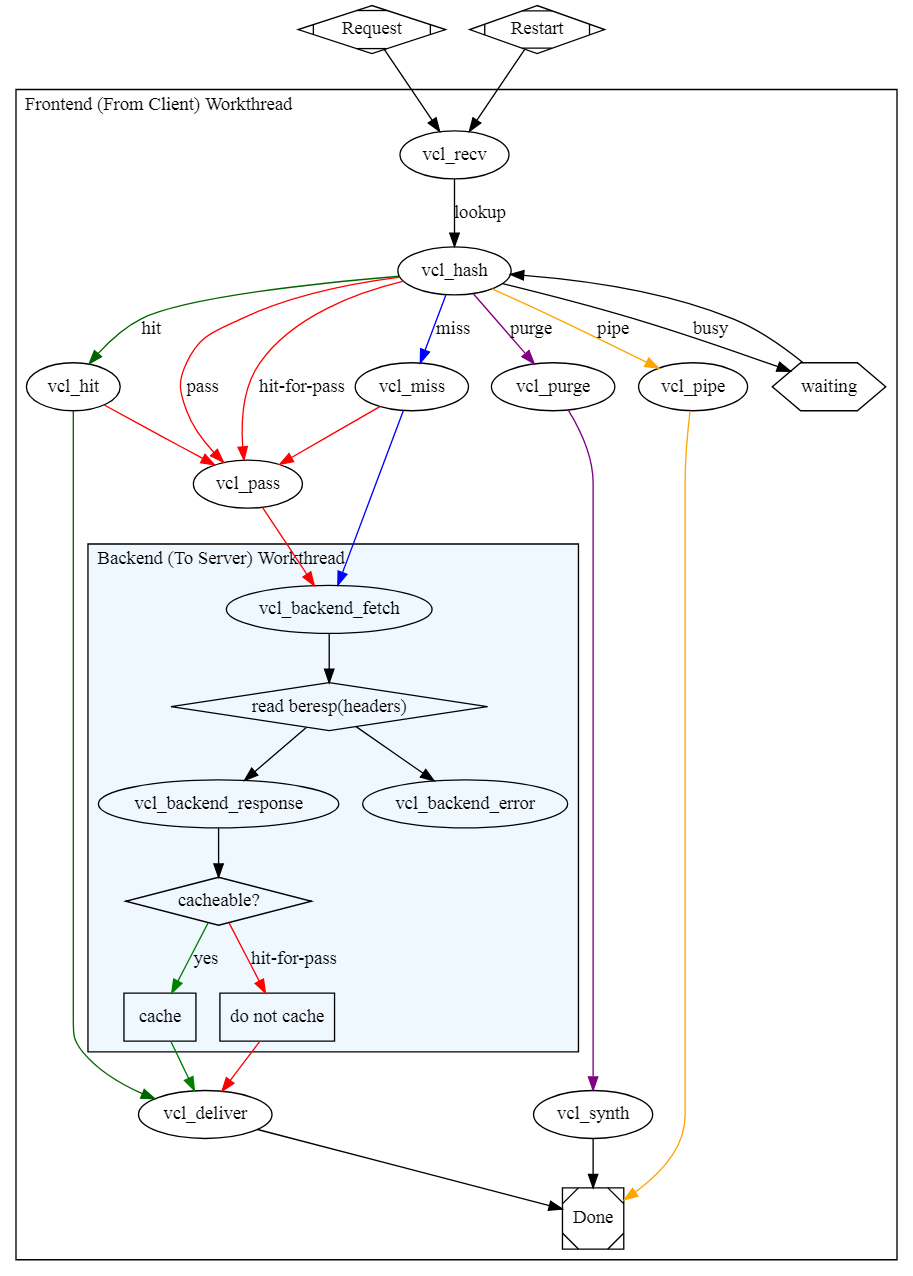
vcl各状态引擎的功用:
vcl_recv
vcl_fetch
vcl_pipe: 用于将请求直接发往后端主机;
vcl_hash: 自定义hash生成时的数据来源
vcl_pass: 用于将请求直接传递至后端主机;
vcl_hit: 从缓存中查找到缓存对象时要执行的操作;
vcl_miss: 从缓存中款查找到缓存对象时要执行的操作;
vcl_deliver: 将用户请求的内容响应给客户端时用到的方法;
vcl_error: 在varnish端合成错误响应而时;
配置文件介绍:
# # This is an example VCL file for Varnish. # # It does not do anything by default, delegating control to the # builtin VCL. The builtin VCL is called when there is no explicit # return statement. # # See the VCL chapters in the Users Guide at https://www.varnish-cache.org/docs/ # and http://varnish-cache.org/trac/wiki/VCLExamples for more examples. # Marker to tell the VCL compiler that this VCL has been adapted to the # new 4.0 format. vcl 4.0; # Default backend definition. Set this to point to your content server. backend default { #定义后端服务器主机 # .host = "127.0.0.1"; # .port = "8080"; .host = "192.168.100.103"; .port = "80"; } sub vcl_recv { # Happens before we check if we have this in cache already. # # Typically you clean up the request here, removing cookies you don't need, # rewriting the request, etc. if (req.method == "PRI") { #自己添加官网部分 /* We do not support SPDY or HTTP/2.0 */ return (synth(405)); } if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD" && req.method != "PUT" && req.method != "POST" && req.method != "TRACE" && req.method != "OPTIONS" && req.method != "DELETE") { /* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird. */ return (pipe); } if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD") { /* We only deal with GET and HEAD by default */ return (pass); } if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie) { /* Not cacheable by default */ return (pass); } return (hash); } sub vcl_backend_response { # Happens after we have read the response headers from the backend. # # Here you clean the response headers, removing silly Set-Cookie headers # and other mistakes your backend does. } sub vcl_deliver { # Happens when we have all the pieces we need, and are about to send the # response to the client. # # You can do accounting or modifying the final object here. if (obj.hits>0) { #定义在vcl_deliver中,向响应给客户端的报文添加一个自定义首部X-Cache; set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT"; } else { set resp.http.X-Cahce = "MISS"; } }
重新加载配置:
varnish> vcl.list 200 active 0 boot varnish> vcl.load test1 default.vcl 200 VCL compiled. varnish> vcl.use test1 200 VCL 'test1' now active varnish> vcl.list 200 available 0 boot active 0 test1
varnish中的内置变量: 变量种类: client server req resp bereq beresp obj storage bereq bereq.http.HEADERS: 由varnish发往backend server的请求报文的指定首部; bereq.request:请求方法; bereq.url: bereq.proto: bereq.backend:指明要调用的后端主机; beresp beresp.proto beresp.status:后端服务器的响应的状态码 beresp.reason:原因短语; beresp.backend.ip beresp.backend.name beresp.http.HEADER: 从backend server响应的报文的首部; beresp.ttl:后端服务器响应的内容的余下的生存时长; obj obj.ttl: 对象的ttl值; obj.hits:此对象从缓存中命中的次数; server server.ip server.hostname req resp
访问测试:
[root@localhost /]# curl -I http://192.168.100.100:6081/test1.html HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sun, 10 Mar 2019 16:26:59 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS) Last-Modified: Sun, 10 Mar 2019 16:26:16 GMT ETag: "8-583bfea477f63" Content-Length: 8 Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 X-Varnish: 327756 Age: 0 Via: 1.1 varnish-v4 X-Cahce: MISS192.168.100.100 Connection: keep-alive [root@localhost /]# curl -I http://192.168.100.100:6081/test1.html HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sun, 10 Mar 2019 16:26:59 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS) Last-Modified: Sun, 10 Mar 2019 16:26:16 GMT ETag: "8-583bfea477f63" Content-Length: 8 Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 X-Varnish: 131104 327757 Age: 2 Via: 1.1 varnish-v4 test-Cache: HIT192.168.100.100 Connection: keep-alive
定义vcl 集群:
vcl 4.0; backend b1 { .host = "..."; .port = "..."; } backend b2 { .host = "..."; .port = "..."; } sub vcl_init { new cluster1 = directors.round_robin(); cluster1.add_backend(b1, 1.0); cluster1.add_backend(b2, 1.0); } sub vcl_recv { set req.backend_hint = cluster1.backend(); }
backend server的定义: backend name { .attribute = "value"; } .host: BE主机的IP; .port:BE主机监听的PORT; .probe: 对BE做健康状态检测; .max_connections:并连接最大数量; 后端主机的健康状态检测方式: probe name { .attribute = "value"; } .url: 判定BE健康与否要请求的url; .expected_response:期望响应状态码;默认为200; 示例1: backend websrv1 { .host = "172.16.100.68"; .port = "80"; .probe = { .url = "/test1.html"; } } backend websrv2 { .host = "172.16.100.69"; .port = "80"; .probe = { .url = "/test1.html"; } }
配置文件详解:
[root@localhost varnish]# cat default.vcl # # This is an example VCL file for Varnish. # # It does not do anything by default, delegating control to the # builtin VCL. The builtin VCL is called when there is no explicit # return statement. # # See the VCL chapters in the Users Guide at https://www.varnish-cache.org/docs/ # and http://varnish-cache.org/trac/wiki/VCLExamples for more examples. # Marker to tell the VCL compiler that this VCL has been adapted to the # new 4.0 format. vcl 4.0; # Default backend definition. Set this to point to your content server. backend default { #定义后端服务器主机 # .host = "127.0.0.1"; # .port = "8080"; .host = "192.168.100.101"; .port = "80"; } backend web1 { .host = "192.168.100.101"; .port = "80"; .probe = { .url = "/tan.jpg"; } } backend web2 { .host = "192.168.100.103"; .port = "80"; .probe = { .url = "/tan.jpg"; } } import directors; sub vcl_init { #定义后端服务器集群 new cluster1 = directors.round_robin(); cluster1.add_backend(web1); cluster1.add_backend(web2); }
*******************************************************************************************
vcl_recv是在Varnish完成对请求报文的解码为基本数据结构后第一个要执行的子例程,它通常有四个主要用途:
(1)修改客户端数据以减少缓存对象差异性;比如删除URL中的www.等字符;
(2)基于客户端数据选用缓存策略;比如仅缓存特定的URL请求、不缓存POST请求等;
(3)为某web应用程序执行URL重写规则;
(4)挑选合适的后端Web服务器;
可以使用下面的终止语句,即通过return()向Varnish返回的指示操作:
pass:绕过缓存,即不从缓存中查询内容或不将内容存储至缓存中;
pipe:不对客户端进行检查或做出任何操作,而是在客户端与后端服务器之间建立专用“管道”,并直接将数据在二者之间进行传送;此时,keep-alive连接中后续传送的数据也都将通过此管道进行直接传送,并不会出现在任何日志中;
lookup:在缓存中查找用户请求的对象,如果缓存中没有其请求的对象,后续操作很可能会将其请求的对象进行缓存;
error:由Varnish自己合成一个响应报文,一般是响应一个错误类信息、重定向类信息或负载均衡器返回的后端web服务器健康状态检查类信息;
vcl_recv也可以通过精巧的策略完成一定意义上的安全功能,以将某些特定的攻击扼杀于摇篮中。同时,它也可以检查出一些拼写类的错误并将其进行修正等。
Varnish默认的vcl_recv专门设计用来实现安全的缓存策略,它主要完成两种功能:
(1)仅处理可以识别的HTTP方法,并且只缓存GET和HEAD方法;
(2)不缓存任何用户特有的数据;
安全起见,一般在自定义的vcl_recv中不要使用return()终止语句,而是再由默认vcl_recv进行处理,并由其做出相应的处理决策。
**********************************************************************************************************************************************
sub vcl_recv {
# Happens before we check if we have this in cache already. # # Typically you clean up the request here, removing cookies you don't need, # rewriting the request, etc. if (req.url ~ "(?i).(jpg|png|gif)$") { set req.backend_hint = web1; } else { set req.backend_hint = web2; } if (req.method == "PRI") { #如果是http 2.0 不缓存 /* We do not support SPDY or HTTP/2.0 */ return (synth(405)); } set req.backend_hint = cluster1.backend(); #设置默认的后端缓存集群 if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD" && req.method != "PUT" && req.method != "POST" && req.method != "TRACE" && req.method != "OPTIONS" && req.method != "DELETE") { /* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird. */ return (pipe); #如果请求方法都不是上面这些,就直接发到pipe,对客户端进行检查或做出任何操作,而是在客户端与后端服务器之间建立专用“管道”,并直接将数据在二者之间进行传送;此时,keep-alive连接中后续传送的数据也都将通过此管道进行直接传送,并不会出现在任何日志中; } if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD") { /* We only deal with GET and HEAD by default */ return (pass); #绕过缓存,即不从缓存中查询内容或不将内容存储至缓存中; } if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie) { /* Not cacheable by default */ return (pass); #绕过缓存,即不从缓存中查询内容或不将内容存储至缓存中;
}
return (hash); #交给hash 处理,判断是否能够缓存
}
sub vcl_backend_response {
# Happens after we have read the response headers from the backend.
#
# Here you clean the response headers, removing silly Set-Cookie headers
# and other mistakes your backend does.
if (beresp.http.cache-control !~ "s-maxage") { #定义varnish 定义对于特定资源的缓存时间
if (bereq.url ~ "(?i).jpg$") {
set beresp.ttl = 3600s;
unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie;
}
if (bereq.url ~ "(?i).css$") {
set beresp.ttl = 600s;
unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie;
}
}
}
*******************************************************************************************
5、vcl_fetch
如前面所述,相对于vcl_recv是根据客户端的请求作出缓存决策来说,vcl_fetch则是根据服务器端的响应作出缓存决策。在任何VCL状态引擎中返回的pass操作都将由vcl_fetch进行后续处理。vcl_fetch中有许多可用的内置变量,比如最常用的用于定义某对象缓存时长的beresp.ttl变量。通过return()返回给varnish的操作指示有:
(1)deliver:缓存此对象,并将其发送给客户端(经由vcl_deliver);
(2)hit_for_pass:不缓存此对象,但可以导致后续对此对象的请求直接送达到vcl_pass进行处理;
(3)restart:重启整个VCL,并增加重启计数;超出max_restarts限定的最大重启次数后将会返回错误信息;
(4)error code [reason]:返回指定的错误代码给客户端并丢弃此请求;
默认的vcl_fetch放弃了缓存任何使用了Set-Cookie首部的响应。
***************************************************************************************************************
sub vcl_deliver { # Happens when we have all the pieces we need, and are about to send the # response to the client. # # You can do accounting or modifying the final object here. if (obj.hits>0) { #判断在响应客户端时,如果命中缓存就响应HIT ,否则 MISS set resp.http.test-Cache = "HIT" + server.ip; } else { set resp.http.X-Cahce = "MISS" + server.ip; } } [root@localhost varnish]#