一、作用
(1)为各种“集合”的数据结构,提供一个统一的、简便的访问接口
(2)使得数据结构的成员能够按某种次序排列 (Object 正是因为无法确认属性的遍历的顺序,所以没有部署Iterator接口)
(3)使得“集合”数据结构能运用for....of循环遍历,Iterator 接口主要供for...of消费。
二、原理
创建一个遍历器对象(本质是一个指针对象),不断调用next方法,返回一个包含value和done的对象
var it = makeIterator(['a','b']); console.dir(it.next()); console.dir(it.next()); console.dir(it.next()); function makeIterator(arr){ let index = 0; return { next: function(){ return index < arr.length ? {value:arr[index++],done:false} : {value:undefined,done:true}; } }; }
三、具备Iterator接口的数据结构
(1)包括 : Array Map Set String TypedArray 函数的arguments对象 NodeList对象、部分类似数组的对象(并不是所有都可以,不行的对象,可以通过Array.from() 转化为数组)
let arrayLike = { length: 2, 0: 'a', 1: 'b' };
// 报错 for (let x of arrayLike) { console.log(x); } // 正确
//Array.from():从一个类似数组或可迭代对象创建一个新的,浅拷贝的数组实例
for (let x of Array.from(arrayLike)) { console.log(x); }
(2)特征:具有 Symbol.iterator 属性(本身是一个遍历器生成函数,一执行,返回一个遍历器)
const set = new Set("efe"); const it = set[Symbol.iterator](); console.dir(it.next()); console.dir(it.next()); console.dir(it.next());
四、调用场合
(1)解构赋值
const arr = ['a','b']; [x,y] = arr; console.log(x); //a console.log(y); //b
(2)扩展运算符 (注:任何部署了interator的数据结构,都可以通过扩展运算符转化为数组)
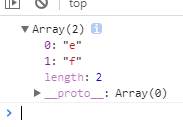
const set = new Set("efe"); console.dir([...set]);
(3)yield *
(4)for....of.....
五、还有方法return() 和 throw(),可选,不一定要部署
(1)return() : 遇到break或报错会调用,返回一个对象
六、与其他遍历语法的比较
(1)例子:数组
常用的遍历方法: for forEach for....in..... for....of.....
其中,forEach 缺点是:
即使使用break或return命令,还是不能跳出循环 (没有刹车系统~~)。
for.....in...... 缺点是:
1、键名的类型是字符串;
2、即使不是数字键名,同样进行遍历(所以for....in.....更适合在对象中使用,数组还是算了吧~~)
3、乱序遍历(先遍历数字键名,其他按加入顺序。到底还是因为所有键名都遍历造成的问题,也难怪Object部署不了遍历器~~)。
for....of....... 的优点是:
刚好弥补了上面两个的不足,既能随意暂停遍历,又能按顺序进行遍历
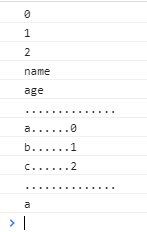
const arr = ['a','b']; arr.name = "zhengxiaona"; arr.push('c'); arr.age = "zhengxiaona"; for(let i in arr){ console.log(i); } console.log(".............."); arr.forEach((item,index) => { console.log(`${item}......${index}`); return; }); console.log(".............."); for(let value of arr){ console.log(value); break; }