Dreamoon likes to play with sets, integers and 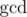 .
. 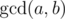 is defined as the largest positive integer that divides both a and b.
is defined as the largest positive integer that divides both a and b.
Let S be a set of exactly four distinct integers greater than 0. Define S to be of rank k if and only if for all pairs of distinct elements si, sjfrom S, 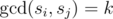 .
.
Given k and n, Dreamoon wants to make up n sets of rank k using integers from 1 to m such that no integer is used in two different sets (of course you can leave some integers without use). Calculate the minimum m that makes it possible and print one possible solution.
The single line of the input contains two space separated integers n, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 10 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 100).
On the first line print a single integer — the minimal possible m.
On each of the next n lines print four space separated integers representing the i-th set.
Neither the order of the sets nor the order of integers within a set is important. If there are multiple possible solutions with minimal m, print any one of them.
1 1
5
1 2 3 5
For the first example it's easy to see that set {1, 2, 3, 4} isn't a valid set of rank 1 since 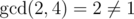 .
.
题意:求出n个集合均为4个元素,且每个集合内任意两两,元素的最大公约数为k,集合不允许有交集,当n*4个元素最大值最小时,输出所有n个集合,
题解:我是暴力水过去的,正解是:
两两元素之间是互质的,然后为了满足元素最大值最小,
在除掉k后,任意集合内肯定是由3个奇数,1个偶数组成,
因为若少一个奇数,就会有至少一对数不互质,
若多一个奇数,元素最大值就会变大。
所以,从1开始构建所有元素集合即可。

#include<iostream> #include<map> #include<string> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<queue> #include<vector> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int main() { int n,k; cin>>n>>k; cout<<(6*n-1)*k<<endl; while(n--) { cout<<(6*n+1)*k<<" "<<(6*n+2)*k<<" "<<(6*n+3)*k<<" "<<(6*n+5)*k<<endl; } }

///1085422276 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; typedef long long ll; #define mem(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a)) #define meminf(a) memset(a,127,sizeof(a)); #define TS printf("111111 "); #define FOR(i,a,b) for( int i=a;i<=b;i++) #define FORJ(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--) #define READ(a,b,c) scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c) #define inf 100000000 inline ll read() { ll x=0,f=1; char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') { if(ch=='-')f=-1; ch=getchar(); } while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') { x=x*10+ch-'0'; ch=getchar(); } return x*f; } //**************************************** ///**************************************************************** /// Miller_Rabin 算法进行素数测试 ///速度快,而且可以判断 <2^63的数 //**************************************************************** const int S=20;///随机算法判定次数,S越大,判错概率越小 ///计算 (a*b)%c. a,b都是long long的数,直接相乘可能溢出的 /// a,b,c <2^63 long long mult_mod(long long a,long long b,long long c) { a%=c; b%=c; long long ret=0; while(b) { if(b&1){ret+=a;ret%=c;} a<<=1; if(a>=c)a%=c; b>>=1; } return ret; } ///计算 x^n %c long long pow_mod(long long x,long long n,long long mod)//x^n%c { if(n==1)return x%mod; x%=mod; long long tmp=x; long long ret=1; while(n) { if(n&1) ret=mult_mod(ret,tmp,mod); tmp=mult_mod(tmp,tmp,mod); n>>=1; } return ret; } ///以a为基,n-1=x*2^t a^(n-1)=1(mod n) 验证n是不是合数 ///一定是合数返回true,不一定返回false bool check(long long a,long long n,long long x,long long t) { long long ret=pow_mod(a,x,n); long long last=ret; for(int i=1;i<=t;i++) { ret=mult_mod(ret,ret,n); if(ret==1&&last!=1&&last!=n-1) return true;//合数 last=ret; } if(ret!=1) return true; return false; } /// Miller_Rabin()算法素数判定 ///是素数返回true.(可能是伪素数,但概率极小) ///合数返回false; bool Miller_Rabin(long long n) { if(n<2)return false; if(n==2)return true; if((n&1)==0) return false;//偶数 long long x=n-1; long long t=0; while((x&1)==0){x>>=1;t++;} for(int i=0;i<S;i++) { long long a=rand()%(n-1)+1;///rand()需要stdlib.h头文件 if(check(a,n,x,t)) return false;//合数 } return true; } #define maxn 100000+5 int a[maxn],n,m; vector<int >G; int gcd(int M,int N ) { int Rem; while( N > 0 ) { Rem = M % N; M = N; N = Rem; } return M; } int main(){ n=read(),m=read(); int ans[maxn]; int k=0; int tmp=1; G.clear(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ while(G.size()!=4){ bool flag=1; for(int j=0;j<G.size();j++){ if(gcd(G[j],m*tmp)!=m)flag=0; } if(flag) G.push_back(tmp*m); tmp++; } for(int j=0;j<G.size();j++) a[++k]=G[j]; G.clear(); if(!Miller_Rabin(tmp))tmp++; } cout<<a[k]<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=k;i+=4){ cout<<a[i]<<" "<<a[i+1]<<" "<<a[i+2]<<" "<<a[i+3]<<endl; } return 0; }
