Bean基于XML和基于注解的装配
一、Bean基于XML的装配
1.生命周期接着day01_1来讲(了解)
Bean生命周期的如图所示:用红色框起来的都是我们要研究的!
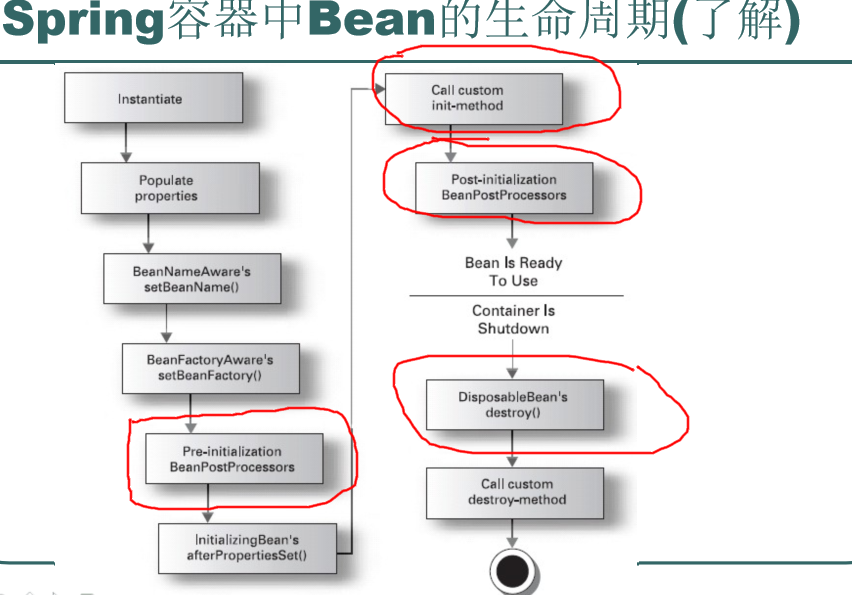
如图Bean is Ready To User 是bean实例的使用,当bean调用方法时会先调用初始化方法,在初始化方法前后又有两个方法分别是:预初始化方法,后初始化方法。当IOC容器关闭时将会自动调用销毁方法。
2.介绍初始和销毁方法
spring关于初始化和销毁方法的使用格式如下:前提你需要在配置的bean里面写入你想要初始化和销毁的代码
<bean id="" class="" init-method="初始化方法名称" destroy-method="销毁的方法名称">
spring配置如下:
<bean id="userService" class="cn.itcast.b_bean_xml.d_lifecycle.UserServiceImpl" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory"></bean>
关于配置bean的代码如下:配置了初始化方法和销毁方法
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { public void addUser() { System.out.println("添加用户成功!!!"); } public void myInit(){ System.out.println("初始化方法执行了"); } public void myDestory(){ System.out.println("销毁方法执行了"); } }
关于测试类的代码如下:
@Test public void fun01()throws Exception {//测试初始化方法和销毁方法 String xmlPath = "cn/itcast/b_bean_xml/d_lifecycle/applicationContext.xml"; ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); //使用默认构造创建的实例 UserService userService=(UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");//填写id名称 UserService userService2=(UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService"); //默认是单例的 System.out.println(userService==userService2); userService.addUser(); //关闭IOC容器时才会执行销毁方法,我们可以通过反射调用close但是没这个必要 //applicationContext.getClass().getMethod("close").invoke(applicationContext);这说明实现类含有close方法 applicationContext.close(); }
3. BeanPostProcessor 后处理Bean
① spring 提供一种机制,只要实现此接口BeanPostProcessor,并将实现类提供给spring容器,spring容器将自动执行,在初始化方法前执行before(),在初始化方法后执行after() 。 配置<bean class="">
②关于BeanPostProcessor接口的api解释如下:
Factory hook(勾子) that allows for custom modification of new bean instances, e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
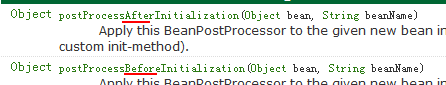
这个接口是spring提供工厂勾子,用于修改实例对象,可以生成代理对象,是AOP底层。
提供的这两个接口我们可以创建一个实现类来实现这两个方法,这个两个方法会将spring创建的bean进行包装在初始化方法前后执行如上面生命周期过程可知。
模拟spring所进行的过程:
A a =new A();
a = B.before(a) //返回一个包装bean --> 将a的实例对象传递给后处理bean,可以生成代理对象并返回。
a.init();
a = B.after(a);//返回出一个包装bean
a.addUser(); //生成代理对象,目的在目标方法前后执行(例如:开启事务、提交事务)
a.destroy()
关于上面的接口来实现上面的过程
BeanPostProcessor实现类:spring会自动去调用实现该接口的的实现类,并会将创建好的bean传进这个这个类的两个方法里面实现包装增强后返回

1 public class MyBeanPostprocessor implements BeanPostProcessor { 2 3 /* 4 * 在spring里面做了这样一件事当你在spring里面装配了<bean class="cn.itcast.b_bean_xml.f_lifecycle.MyBeanPostprocessor"></bean> 5 * 它会检查你放入IOC容器中的这个类是不是BeanPostProcessor的实现类 如果不是则不会走前后初始化方法,如果是就会进行下面操作 6 * A a =new A(); //spring会首先创建实例 7 * a = B.before(a) --> 将a的实例对象传递给后处理bean,可以生成代理对象并返回。 8 * a.init();代理对象调用初始化方法 9 * a = B.after(a);将代理对象再放入后初始化方法又会返回一个代理对象 10 * a.addUser(); //生成代理对象,目的在目标方法前后执行(例如:开启事务、提交事务) 11 * a.destroy() 12 * 13 */ 14 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 15 throws BeansException { 16 System.out.println("前处理方法" + beanName); 17 return bean; 18 } 19 20 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) 21 throws BeansException { 22 System.out.println("后处理方法" + beanName); 23 24 Object obj =Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(),bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { 25 26 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 27 throws Throwable { 28 System.out.println("开启事务......"); 29 Object obj = method.invoke(bean,args); 30 System.out.println("提交事务......"); 31 return obj; 32 } 33 } 34 35 36 ); 37 return obj; 38 } 39 40 41 42 }
需要将这个接口的实现类装入IOC容器这样spring才能调用:
<bean class="cn.itcast.b_bean_xml.f_lifecycle.MyBeanPostprocessor"></bean> <bean id="userService" class="cn.itcast.b_bean_xml.f_lifecycle.UserServiceImpl" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory"></bean>
需要包装的bean代码为:

1 package cn.itcast.b_bean_xml.f_lifecycle; 2 3 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { 4 5 public void addUser() { 6 System.out.println("添加用户成功!!!"); 7 8 } 9 10 public void myInit(){ 11 System.out.println("初始化方法执行了"); 12 13 } 14 public void myDestory(){ 15 System.out.println("销毁方法执行了"); 16 } 17 }
问题1:后处理bean作用某一个目标类,还是所有目标类?
所有
问题2:如何只作用一个?
通过“参数2”beanName进行控制
4.关于bean属性的属性依赖注入
①依赖注入方式:手动装配 和 自动装配
②属性手动依赖注入有两种基于:一般进行配置信息都采用手动 基于xml装配:构造方法、setter方法 基于注解装配:在注解里面注入value的值
构造方法注入的方式:需要给有参数的构造函数类
spring的配置如下:
1 <!--在bean里面有一个子元素 constructor-arg 是手动装配的一种 叫做构造方法注入 其中 2 index:代表构造函数中参数的索引值,而且这个index会默认匹配第一个构造函数 如果想指定准确用type和index一起指定 3 type:表示构造函数中参数的类型 4 constructor-arg元素的个数代表配配多少个参数的构造函数 5 --> 6 7 <bean id="user" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.a_constructInject.User"> 8 <constructor-arg index="0" type="Integer" value="2"></constructor-arg> 9 <constructor-arg index="1" type="String" value="1"></constructor-arg> 10 </bean>
给定的类代码为:

1 public class User { 2 private Integer uid; 3 private String name; 4 private Integer age; 5 6 7 public User(Integer uid,String name) { 8 super(); 9 this.uid = uid; 10 this.name=name; 11 } 12 13 14 public User(String name, Integer age) { 15 super(); 16 this.name = name; 17 this.age = age; 18 } 19 20 21 public Integer getUid() { 22 return uid; 23 } 24 public void setUid(Integer uid) { 25 this.uid = uid; 26 } 27 public String getName() { 28 return name; 29 } 30 public void setName(String name) { 31 this.name = name; 32 } 33 public Integer getAge() { 34 return age; 35 } 36 public void setAge(Integer age) { 37 this.age = age; 38 } 39 40 41 @Override 42 public String toString() { 43 return "User [uid=" + uid + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 44 } 45 46 }
测试代码:
public class Test01 { @Test public void fun01()throws Exception {//测试初始化方法和销毁方法 String xmlPath = "cn/itcast/c_bean_xml/a_constructInject/applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext applicationContext =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); User user=(User) applicationContext.getBean("user");//填写id名称 System.out.println(user); } }
使用setter方式注入:需要给属性提供setter方法
spring配置如下:

1 <!-- setter方法注入 2 * 普通数据 3 <property name="" value="值"> 4 等效 5 <property name=""> 6 <value>值 7 * 引用数据 8 <property name="" ref="另一个bean"> 9 等效 10 <property name=""> 11 <ref bean="另一个bean"/> 12 --> 13 14 15 <bean id="person" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.b_setterInject.Person"> 16 <property name="name" value="小西西"></property> 17 <property name="age" value="20"></property> 18 <property name="homeAddress" ref="homeAddress"></property> 19 <property name="companyAddress"><ref bean="companyAddress"/></property> 20 </bean> 21 22 <bean id="homeAddress" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.b_setterInject.Address"> 23 <property name="addr"><value>武汉职业技术学院</value></property> 24 <property name="tel" value="123456"></property> 25 </bean> 26 27 <bean id="companyAddress" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.b_setterInject.Address"> 28 <property name="addr"><value>武汉轻工大学</value></property> 29 <property name="tel"><value>12138</value></property> 30 </bean>
给定的类代码如下:

1 public class Person { 2 private String name; 3 private Integer age; 4 private Address homeAddress; 5 private Address companyAddress; 6 public String getName() { 7 return name; 8 } 9 public void setName(String name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 public Integer getAge() { 13 return age; 14 } 15 public void setAge(Integer age) { 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 public Address getHomeAddress() { 19 return homeAddress; 20 } 21 public void setHomeAddress(Address homeAddress) { 22 this.homeAddress = homeAddress; 23 } 24 public Address getCompanyAddress() { 25 return companyAddress; 26 } 27 public void setCompanyAddress(Address companyAddress) { 28 this.companyAddress = companyAddress; 29 } 30 @Override 31 public String toString() { 32 return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", homeAddress=" 33 + homeAddress + ", companyAddress=" + companyAddress + "]"; 34 } 35 36 37 }

1 public class Address { 2 private String addr; 3 private String tel; 4 5 6 public String getAddr() { 7 return addr; 8 } 9 public void setAddr(String addr) { 10 this.addr = addr; 11 } 12 public String getTel() { 13 return tel; 14 } 15 public void setTel(String tel) { 16 this.tel = tel; 17 } 18 @Override 19 public String toString() { 20 return "Address [addr=" + addr + ", tel=" + tel + "]"; 21 } 22 23 }
测试代码如下:

1 public class Test01 { 2 @Test 3 public void fun01() {//测试初始化方法和销毁方法 4 String xmlPath = "cn/itcast/c_bean_xml/b_setterInject/applicationContext.xml";//给定xml文件路径 5 ApplicationContext applicationContext =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);//加载spring配置文件 6 7 Person person=(Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");//填写id名称,使用IOC容器得到实例 8 System.out.println(person); 9 10 11 } 12 13 14 }
③自动装配:struts和spring 整合可以自动装配byType:按类型装配byName:按名称装配constructor构造装配, auto:不确定装配。
5.P命名空间(l了解)
①什么是P命名空间:p命名空间是用来简化setter注入的,替换<property name="属性名">,而是在 <bean p:属性名="普通值" p:属性名-ref="引用值">
②使用的前提是要加上命名空间

spring的配置文件如下:效果和上面的setter方式注入效果一样

1 <bean id="person" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.c_p_space.Person" 2 p:name="小君君" p:age="20" p:companyAddress-ref="companyAddress" p:homeAddress-ref="homeAddress" > 3 </bean> 4 5 <bean id="homeAddress" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.c_p_space.Address" p:addr="武汉职业技术学院" p:tel="123138"> 6 </bean> 7 8 <bean id="companyAddress" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.c_p_space.Address" p:addr="武汉轻工大学" p:tel="12138"> 9 </bean>
6.SpEL表达式(了解)
①什么是SpEL:SpEL是spring自己的一套表达式这个表达式也可以简化setter注入,使setter注入变得更加灵活
对<property>进行统一编程,所有的内容都使用value
<property name="" value="#{表达式}">
#{123}、#{'jack'} : 数字、字符串
#{beanId} :另一个bean引用
#{beanId.propName} :操作数据
#{beanId.toString()} :执行方法
#{T(类).字段|方法} :静态方法或字段
spring配置文件如下:

1 <!--SpEL表达式也是用来简化 setter注入的 2 使格式都变为<property name="" value=""> 3 <property name="cname" value="#{'jack'}"></property>这个是给实例注入赋值 4 <property name="cname" value="#{customer.cname}"></property>这个是的当属性有默认值时调用属性再注入进去(没人这么干多此一举但是我们要知道可以调用实例的属性值) 5 <property name="cname" value="#{customer.cname.toUpperCase()}"></property>我们可以调用方法进行操作和OGNL表达式有点像,但是这种方式如果没有默认值程序就会报控指针了 6 <property name="cname" value="#{customer.cname?.toUpperCase()}"></property>对引用类型的对象前加一个?判断是否是null如果是null则这个值就为null程序还是能走下去 7 格式:#{T(类).静态方法|字段} 8 <property name="pi" value="#{T(Math).PI}"></property>调用静态常量值赋值 9 --> 10 <bean id="customer" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.d_SPEL.Customer"> 11 <property name="cname" value="#{customer.cname?.toUpperCase()}"></property> 12 <property name="pi" value="#{T(Math).PI}"></property> 13 </bean> 14 </beans>
给定的类:

1 public class Customer { 2 private String cname="jack"; 3 private Double pi; //Math.PI; 4 public String getCname() { 5 return cname; 6 } 7 public void setCname(String cname) { 8 this.cname = cname; 9 } 10 public Double getPi() { 11 return pi; 12 } 13 public void setPi(Double pi) { 14 this.pi = pi; 15 } 16 @Override 17 public String toString() { 18 return "Customer [cname=" + cname + ", pi=" + pi + "]"; 19 } 20 21 22 23 24 25 }
测试代码:

1 public class Test01 { 2 @Test 3 public void fun01() {//测试初始化方法和销毁方法 4 String xmlPath = "cn/itcast/c_bean_xml/d_SPEL/applicationContext.xml";//给定xml文件路径 5 ApplicationContext applicationContext =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);//加载spring配置文件 6 7 Customer customer=(Customer) applicationContext.getBean("customer");//填写id名称,使用IOC容器得到实例 8 System.out.println(customer); 9 10 11 } 12 13 14 }
7.注入集合的方式:
一个类的属性是集合如何在配置文件中为这个集合赋值
spring配置文件代码如下:按照下面的方式来注入集合

1 <!-- 2 集合的注入都是给<property>添加子标签 3 数组:<array> 4 List:<list> 5 Set:<set> 6 Map:<map> ,map存放k/v 键值对,使用<entry>描述 7 Properties:<props> <prop key=""></prop> 【】 8 9 普通数据:<value> 10 引用数据:<ref> 11 --> 12 13 14 <bean id="collectionData" class="cn.itcast.c_bean_xml.e_arry_collection_Map.CollectionData"> 15 <property name="arrayData"> 16 <array> 17 <value>张三</value> 18 <value>李四</value> 19 </array> 20 </property> 21 <property name="listData"> 22 <list> 23 <value>王五</value> 24 <value>赵六</value> 25 </list> 26 </property> 27 28 <property name="setData"> 29 <set> 30 <value>小君君</value> 31 <value>小西西</value> 32 </set> 33 </property> 34 35 <property name="mapData"> 36 <map> 37 <entry key="Jack" value="杰克"></entry> 38 <entry> 39 <key><value>rose</value></key> 40 <value>肉丝</value> 41 </entry> 42 </map> 43 </property> 44 45 <property name="propertiesData"> 46 <props> 47 <prop key="高富帅">富</prop> 48 <prop key="白富美">美</prop> 49 </props> 50 51 </property> 52 </bean>
给定的类:类里面的属性包含集合

1 public class CollectionData { 2 private String[] arrayData; 3 private List<String> listData; 4 private Set<String> setData; 5 private Map<String,String> mapData; 6 private Properties propertiesData; 7 public String[] getArrayData() { 8 return arrayData; 9 } 10 public void setArrayData(String[] arrayData) { 11 this.arrayData = arrayData; 12 } 13 public List<String> getListData() { 14 return listData; 15 } 16 public void setListData(List<String> listData) { 17 this.listData = listData; 18 } 19 public Set<String> getSetData() { 20 return setData; 21 } 22 public void setSetData(Set<String> setData) { 23 this.setData = setData; 24 } 25 public Map<String, String> getMapData() { 26 return mapData; 27 } 28 public void setMapData(Map<String, String> mapData) { 29 this.mapData = mapData; 30 } 31 public Properties getPropertiesData() { 32 return propertiesData; 33 } 34 public void setPropertiesData(Properties propertiesData) { 35 this.propertiesData = propertiesData; 36 } 37 @Override 38 public String toString() { 39 return "CollectionData [arrayData=" + Arrays.toString(arrayData) 40 + ", listData=" + listData + ", setData=" + setData 41 + ", mapData=" + mapData + ", propertiesData=" + propertiesData 42 + "]"; 43 } 44 45
测试代码:

1 public class Test01 { 2 @Test 3 public void fun01() {//测试初始化方法和销毁方法 4 String xmlPath = "cn/itcast/c_bean_xml/e_arry_collection_Map/applicationContext.xml";//给定xml文件路径 5 ApplicationContext applicationContext =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);//加载spring配置文件 6 7 CollectionData conllectionData=(CollectionData) applicationContext.getBean("collectionData");//填写id名称,使用IOC容器得到实例 8 System.out.println(conllectionData); 9 10 11 } 12 13 14 }
二、基于注解进行bean的装配
1.注解的作用:主要是用来替代XML配置文件的,我们可以将在spring配置文件用注解的方式进行替换
2.注解使用前提:添加命名空间,让spring扫描含有注解类
添加命名空间的格式在:spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASEdocsspring-framework-referencehtmlxsd-config.html打开找到下图的地方将加粗的黑体加入spring配置文件
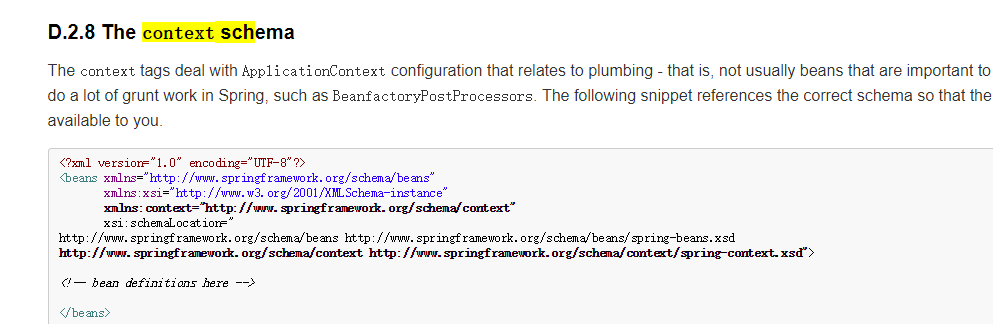
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.itcast.d_zhujie"></context:component-scan>在spring配置文件写入这个配置让spring去扫描这个包下所有类的注解
3.关于替代spring的注解分类
1. @Component取代<bean class="">
@Component("id") 取代 <bean id="" class="">
2.web开发,提供3个@Component注解衍生注解(功能一样)取代<bean class="">
@Repository :dao层
@Service:service层
@Controller:web层
3.依赖注入 :给私有字段在字段上面设置注解,也可以给setter方法上设置注解效果是一样的
普通值:@Value("")
引用值:
方式1:按照【类型】注入
@Autowired
方式2:按照【名称】注入1
@Autowired
@Qualifier("名称")
方式3:@Resource
4.生命周期
初始化:@PostConstruct
销毁:@PreDestroy
5.作用域
@Scope("prototype") 多例
4.模拟javaweb的三层架构来编写,将配置文件全部用注解代替
web层:

1 @Controller("userAction") 2 @Scope("prototype") 3 public class UserAction { 4 @Autowired//按照类型注入 5 private UserService userService; 6 7 public String execute(){ 8 userService.addUser(); 9 System.out.println("Action执行了"); 10 return "success"; 11 } 12 13 14 }
Service层:

1 @Service("userService")//使用注解的前提是要在xml文件中添加命名空间,还要加入扫描配置 2 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { 3 4 private UserDao userDao; 5 6 public void addUser() { 7 userDao.save(); 8 9 } 10 11 12 13 public UserDao getUserDao() { 14 return userDao; 15 } 16 17 18 // @Autowired单独写这个是第一种安装类型注入 19 // @Qualifier("userDao")//按名称注入这是第二种 20 21 @Resource//这个和按照类型有点类似这是第三种 22 public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { 23 this.userDao = userDao; 24 } 25 26 27 @PostConstruct//初始化方法 28 public void myInit(){ 29 System.out.println("初始化方法执行了"); 30 31 } 32 @PreDestroy//销毁方法 33 public void myDestory(){ 34 System.out.println("销毁方法执行了"); 35 } 36 }
Dao层:

1 @Repository("userDao") 2 public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { 3 4 public void save() { 5 System.out.println("添加用户成功!!!"); 6 7 } 8 9 }
测试代码:

1 public class Test01 { 2 @Test 3 public void fun01() {//测试初始化方法和销毁方法 4 String xmlPath = "cn/itcast/d_zhujie/applicationContext.xml"; 5 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); 6 //使用默认构造创建的实例 7 UserAction userAction=(UserAction) applicationContext.getBean("userAction");//填写id名称 8 UserAction userAction2=(UserAction) applicationContext.getBean("userAction");//填写id名称 9 //用来比对多例的配置有没有生效 10 System.out.println(userAction+" "+userAction2); 11 //执行方法并打印成功结果 12 System.out.println(userAction.execute()); 13 //关闭IOC容器可以看到销毁方法执行 14 applicationContext.close(); 15 16 }
三、注解和xml混合使用时
1.将所有的bean都配置xml中
<bean id="" class="">
2.将所有的依赖都使用注解
@Autowired
默认不生效。为了生效,需要在xml配置:<context:annotation-config>
总结:
注解1:<context:component-scan base-package=" ">
注解2:<context:annotation-config>
1.一般情况两个注解不一起使用,因为写了第一个第二个写了也没用,因为它会使注入注解自动生效
2. “注解1”扫描含有注解(@Component 等)类,注入注解自动生效。
“注解2”只在xml和注解(注入)混合使用时,使注入注解生效。
