目录:
一、TFRecord输入数据格式
1.1 TFrecord格式介绍
1.2 TFRecord样例程序
二、图像数据处理
2.1TensorFlow图像处理函数
2.2图像预处理完整样例
三、多线程数据输入处理框架
3.1 队列与多线程
3.2输入文件队列
3.3组合训练数据(batching)
3.4输入数据处理框架
一、TFRecord输入数据格式
TensorFlow提供了一种统一的格式来存储数据,这个格式就是TFRecord
1.1 TFrecord格式介绍
TFRecord文件中的数据都是通过tf.train.Example Protocol Buffer 的格式存储的。格式如下
message Example{ Features features=1; } message Features{ map<string Feature> feature = 1; } message Feature{ oneof kind { BytesList bytes_list = 1; FloatList float_list =2 ; Int64List int64_list =3; } }
1.2 TFRecord样例程序
将数据转化为TFRecord格式
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data import numpy as np #生成整数型的属性 def _int64_feature(value): return tf.train.Feature(int64_list = tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])) #生成字符串属性 def _byte_feature(value): return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list = tf.train.BytesList(value=[value])) mnsit = input_data.read_data_sets("mnist_set",one_hot=True) images = mnsit.train.images #训练数据所对应的正确答案,可以作为一个属性保存在TFRecord中。 labels = mnsit.train.labels #训练数据的图像分辨率,这可以作为Example中的一个属性。 pixels = images.shape[1] num_examples = mnsit.train.num_examples #输出TFRecord文件的地址。 filename = "path/to/output.tfrecords" #创建一个writer来写TFRecord文件。 writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(filename) for index in range(num_examples): #将图像矩阵转化为一个字符串。 image_raw = images[index].tostring() #将一个样例转化为Example Protocol Buffer ,并将所有信息写入这个数据结构。 example = tf.train.Example(features = tf.train.Features(feature={ "pixels":_int64_feature(pixels), "label":_int64_feature(np.argmax(labels[index])), 'image_raw':_byte_feature(image_raw) })) #将一个Example写入TFrecord中 writer.write(example.SerializeToString()) writer.close()
读取TFRecord文件
import tensorflow as tf #创建一个reader来读取TFRecord文件中的数据 reader = tf.TFRecordReader() #创建一个队列来维护输入文件列表 #tf.train.string_input_producer函数 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["path/to/output.tfrecords"]) #从文件中读出一个样例。也可以使用read_up_to函数一次性读取多个样例 _,serialed_example = reader.read(filename_queue) #解析读入的一个样例。如果需要解析多个样例,可以用parse_example函数 features = tf.parse_single_example(serialed_example,features={ 'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.string), 'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), 'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64) }) #tf.decode_raw可以将字符串解析成图像对应的像素数组 images = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'],tf.uint8) labels = tf.cast(features['label'],tf.int32) pixels = tf.cast(features['pixels'],tf.int32) #启动多线程处理数据 sess = tf.Session() coord = tf.train.Coordinator() thread = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord= coord) #每次运行可以读取Tfrecord文件中的一个样例。当所有的样例都读完之后,在此样例程序中会重头读取 for i in range(10): image,label,pixel = sess.run([images,labels,pixels])
二、图像数据处理
通过图像的预处理,可以尽量避免模型受到无关因素的干扰。
2.1TensorFlow图像处理函数
tensorflow提供了几类图像处理的函数。
图像编码处理
一个RGB模式的彩色模式的图像可以看作一个三维矩阵。然而图像的存储并不是记录这些矩阵中的数组,而是经过压缩编码之后的结果。TensorFlow提供了对图像的编码、解码函数。例如tf.image.decode_jpeg等
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf #读取图像的原始数据 image_raw_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile('path/to/picture.jpeg','rb').read() with tf.Session() as sess: #将图像解码,得到三维矩阵。解码为一个张量,在使用它的值之前需要明确调用运行的过程 img_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_raw_data) print(img_data.eval()) #使用pyplot工具可视化得到图像 plt.imshow(img_data.eval()) plt.show() #将数据的类型转化为实数,方便后面的程序对图像处理 img_data = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data,dtype=tf.uint8) #将表示一张图像的三维矩阵按照jpeg的格式重新编码并保存。可得到与原图一样的图像。 encode_image = tf.image.encode_jpeg(img_data) with tf.gfile.GFile("path/to/output_image.png","wb") as f: f.write(encode_image.eval())
图像大小调整
一般来说,网络上获取的图像大小是不固定的,但神经网络的节点的个数是固定的。TensorFlow提供了四种方法,并且将它们分装在tf.image.resize_images函数中。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf #读取图像的原始数据 image_raw_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile('path/to/picture.jpeg','rb').read() with tf.Session() as sess: #将图像解码,得到三维矩阵。解码为一个张量,在使用它的值之前需要明确调用运行的过程 img_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_raw_data) img_data = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data,dtype=tf.float32) #通过tf.image.resize_images调整图像大小。第一个参数为原始图像,第二和第三个参数为调整图像大小,method为调整图像大小的算法 resized = tf.image.resize_images(img_data,[300,300],method=0) print(resized.get_shape()) plt.imshow(resized.eval()) plt.show()
图像的剪裁和填充
#resize_image_with_crop_or_pad 超过原始图像的大小,自动填充,小于原始图像的大小自动裁剪 resized = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(img_data,1500,1800) print(resized.get_shape()) plt.imshow(resized.eval()) plt.show()
等比例裁剪
#通过tf.image.central_crop等比例调整图像大小。第一个参数为原始图像,第二个参数为调整图像大小的比例,范围(0,1】 resized = tf.image.central_crop(img_data,0.3) print(resized.get_shape()) plt.imshow(resized.eval()) plt.show()
上述函数都是截取或填充图像中间的部分,TF还提供了裁剪或填充指定区域的函数,如tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box或 tf.image.pad_to_bounding_box
图像翻转
#上下翻转 fliped_up_down = tf.image.flip_up_down(img_data) #左右翻转 fliped_l_r = tf.image.flip_left_right(img_data) #沿着对角线翻转 flip_transpose = tf.image.transpose_image(img_data) #随机翻转 ram_flip_up_dn = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(img_data) ram_flip_left_right = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(img_data)
图像色彩调整
#图像亮度调整 adjusted_down = tf.image.adjust_brightness(img_data,-0.5) adjusted_up = tf.image.adjust_brightness(img_data,0.5) #随机在【-0.5,0.5】之间调整 adjusted_random = tf.image.random_brightness(img_data,0.5)
类似的函数还有:对比度adjust_contrast、random_contrast,色相adjust_hue、random_hue,饱和度adjust_saturation、random_saturation
图像的标准化
所谓图像的标准化就是将图像上的亮度均值变为0,方差为1
adjusted_ = tf.image.per_image_whitening (img_data)
处理标注框
#缩小图像 image_data = tf.image.resize_images(img_data,[180,267],method=1) #图像矩阵转化为实数类型.tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes输入的是一个batch也就是多张图像组成的四维矩阵,所有需要在怎讲一维 batched = tf.expand_dims(tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image_data,dtype=tf.float32),0) #标注框需要四个数字【Ymin,Xmin,Ymax,Xmax】 boxes = tf.constant([[[0.05,0.05,0.97,0.7],[0.35,0.47,0.5,0.56]]]) #添加标注 result = tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes(batched,boxes)
2.2图像预处理完整样例
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def distort_color(image,color_ordering=0): if color_ordering == 0: image = tf.image.random_brightness(image,32.0/255.0) image = tf.image.random_saturation(image,lower=0.5,upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_hue(image,0.2) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image,lower=0.5,upper=1.5) elif color_ordering == 1: image = tf.image.random_saturation(image,lower=0.5,upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_brightness(image,32.0/255.0) image = tf.image.random_hue(image,0.2) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image,lower=0.5,upper=1.5) return tf.clip_by_value(image,0.0,1.0) def preprocess_for_train(image,height,width,bbox): #如果没有标注提示框,则认为整张图想是需要关注的部分 if bbox is None: bbox = tf.constant([0.0,0.0,1.0,1.0],dtype=tf.float32,shape=[1,1,4]) #转换图像张量的类型 if image.dtype != tf.float32: image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image,dtype=tf.float32) #随机截取的图像,减少需要关注的物体大小对图像识别的影响 bbox_begin,bbox_size,_ = tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(tf.shape(image),bounding_boxes=bbox) distorted_image = tf.slice(image,bbox_begin,bbox_size) #将截取的图像调整为神经网络输入层大小。大小调整的算法是随机的 distorted_image = tf.image.resize_images(distorted_image,[height,width],method=np.random.randint(4)) #随机左右翻转图像 distorted_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(distorted_image) #使用一种随机的顺序调整图像色彩 distorted_image = distort_color(distorted_image,np.random.randint(2)) return distorted_image image_raw_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile("path/to/picture.jpeg",'rb').read() with tf.Session() as sess: img_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_raw_data) boxes = tf.constant([[[0.05,0.05,0.97,0.7],[0.35,0.47,0.5,0.56]]]) for i in range(6): result = preprocess_for_train(img_data,299,299,boxes) plt.imshow(result.eval()) plt.show()
三、多线程数据输入处理框架
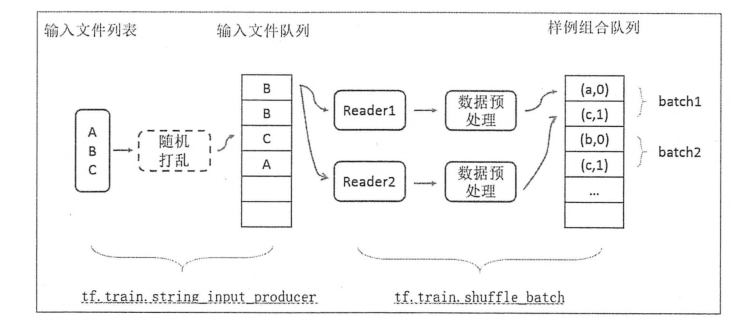
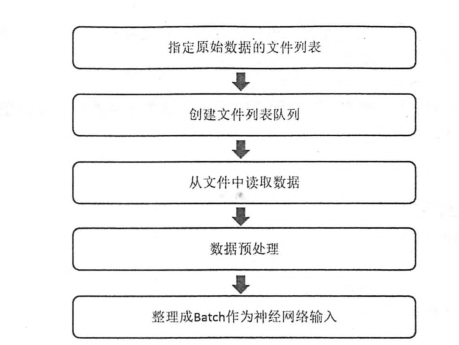
为了避免图像与处理成为神经网络模型训练效率的瓶颈,TensorFlow提供了一套多线程处理数据的框架。下面提供了一个经典的数据处理的流程图。
3.1 队列与多线程
在TF中,队列和变量类似,都是计算图上有状态的节点。对于队列,修改队列状态的操作主要有Enqueue、EnqueueMany和Dequeue。
import tensorflow as tf #创建一个先进先出的队列,指定队列最多可以保存连个元素,斌指定类型为整数。 q = tf.FIFOQueue(2,"int32") #使用enqueue_many函数来初始化队列中的元素。和变量初始化类似,在使用队列之前需要明确的调用这个初始化的过程 init = q.enqueue_many(([0,10],)) #使用Dequeue函数将队列中的第一个元素出队列。这个元素的值将被存在变量x中。 x = q.dequeue() #将得到的值加1 y = x + 1 #将加1 后的值重新加入队列 q_inc = q.enqueue([y]) with tf.Session() as sess: #运行初始化队列操作 init.run() for _ in range(5): #运行q_inc将执行数据出队列、出队列的元素 +1、重新加入队列的整个过程 v , _ = sess.run([x,q_inc]) print(v)
TF提供了FIFOQueue和RandomShufflerQueue两种队列。
TF提供了tf.coordinator和tf.QueueRunner两个类来完成多线程的协同功能。tf.coordinator 主要应用于多个线程协同停止,有request_stop 、should_stop、join三个函数。
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import threading import time #线程中运行的程序,这个程序每隔1S判断是否需要停止并且打印自己的ID def MyLoop(coord,worker_id): while not coord.should_stop(): #随机停止所有线程 if np.random.rand() < 0.1: print("stoping from id %d "%worker_id) #调用request_stop()函数来通知其他线程停止 coord.request_stop() else: print("working from id :%s "%worker_id) time.sleep(1) #声明一个Coordinator来协同多个线程 coord = tf.train.Coordinator() #创建5个线程 threads=[threading.Thread(target=MyLoop,args=(coord,i,)) for i in range(5)] #启动所有的线程 for t in threads: t.start() coord.join(threads)
tf.QueueRunner主要用于启动多个线程来操作同一个队列。
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np #声明一个先进先出的队列,队列中最多100个元素,类型为实数 queue = tf.FIFOQueue(100,"float") #定义队列的入队操作 enqueue_op = queue.enqueue([tf.random_normal([1])]) #tf.train.QueueRunner创建多个线程运行队列的入队操作 #参数1:需要操作的队列,参数2:需要启动的线程 qr = tf.train.QueueRunner(queue,[enqueue_op]*5) #将定义过的QueueRunner加入计算图指定的集合 tf.train.add_queue_runner(qr) #定义出队操作 out_queue = queue.dequeue() with tf.Session() as sess: coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess,coord) #获取队列中的取值 for _ in range(3): print(sess.run(out_queue)[0]) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads)
3.2输入文件队列
数据量较大的时候,可以将数据分成多个TFRecord文件来提高处理效率。TensorFlow提供了tf.train.match_filename_once函数来获取符合正则表达式的所有文件列表,得到的文件列表可通过tf.train.string_input_producer函数进行有效管理。
通过设置shuffle参数,tf.train.string_input_producer函数支持随机打乱文件列表中文件出队的顺序。
当一个输入队列中的文件都被处理完后,它会将初始化时提供的文件列表中的文件重新加入队列。tf.train.string_input_producer函数可以设置num_epochs参数来限制加载初始文件的最大轮数。
生成样例数据
import tensorflow as tf #创建TFRecord文件的帮助函数 def _int64_feature(value): return tf.train.Feature(int64_list = tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])) #模拟海量数据写入不同文件。num_shards定义有多少文件,instance_per_shard定义每个文件多少数据 num_shards = 2 instance_per_shard = 2 for i in range(num_shards): filename = "path/to/data.tfrecords-%.5d-of-%.5d"%(i,num_shards) writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(filename) #将数据封装成Example结构并写入TFRecord文件 for j in range(instance_per_shard): example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature = { "i":_int64_feature(i), "j":_int64_feature(value=j), })) writer.write(example.SerializeToString()) writer.close()
用tf.train.match_filename_once和tf.train.string_input_producer来处理生成的样例
import tensorflow as tf #使用tf.train.match_filename_once的正则表达式方式获取文件列表 files = tf.train.match_filenames_once("path/to/data.tfrecords-*") #通过tf.train.string_input_producer创建输入队列 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(files,shuffle=False) recorder = tf.TFRecordReader() _,serialize_example = recorder.read(filename_queue) features = tf.parse_single_example(serialize_example,features={ "i":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), "j":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), }) with tf.Session() as sess: #使用tf.train.string_input_producer函数也需要初始化变量,注意要初始化本地变量 tf.global_variables_initializer().run() tf.local_variables_initializer().run() #声明tf.train.Coordinator类来协同不同的线程,并启动线程 coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord=coord) for i in range(6): print(sess.run([features['i'],features['j']])) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads)
3.3组合训练数据(batching)
TF提供了tf.train.batch和tf.train.shuffle_batch函数来讲单个的样例组织成batch的形式输出。
import tensorflow as tf #使用tf.train.match_filename_once的正则表达式方式获取文件列表 files = tf.train.match_filenames_once("path/to/data.tfrecords-*") #通过tf.train.string_input_producer创建输入队列 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(files,shuffle=False) recorder = tf.TFRecordReader() _,serialize_example = recorder.read(filename_queue) features = tf.parse_single_example(serialize_example,features={ "i":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), "j":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), }) example,label = features['i'],features['j'] #一个batch中样例的个数 batch_size = 3 #组合样例的队列中最多可以存储的样例的个数。这个队列如果太大,消耗内存。如果太小,出队受阻。 capacity = 1000 +batch_size*3 #使用tf.train.batch来组合样例。【exmple,label】参数:需要组合样例的元素。 example_batch,label_batch = tf.train.batch([example,label],batch_size,capacity=capacity) with tf.Session() as sess: tf.global_variables_initializer().run() tf.local_variables_initializer().run() coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord=coord) for i in range(2): cur_example_batch,cur_label_batch = sess.run([example_batch,label_batch]) print((cur_example_batch,cur_label_batch)) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads)
打乱batch顺序,只需要将example_batch,label_batch = tf.train.batch([example,label],batch_size,capacity=capacity)改成example_batch,label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([example,label],batch_size,capacity=capacity,min_after_dequeue =30)min_after_dequeue限制了出队时队列中元素的最少个数,这个值应该不大于capacity
tf.train.batch和tf.train.shuffle_batch函数的参数num_threads,可指定多个线程同时执行入队操作
tf.train.batch_join和tf.train.shuffle_batch_join函数,从输入文件队列中获取不同文件中的样例分配给不同的线程
3.4输入数据处理框架
按照本节开头给出的流程图,用一个完整程序串联起来之前的步骤实现一个TF处理输入数据。在看一下流程图

import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np #创建文件列表,创建文件输入队列 files = tf.train.match_filenames_once("path/to/pattern-*") filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(files,shuffle=False) #解析TFRecord格式文件的数据 reader = tf.TFRecordReader() _,serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue) features = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example,features = tf.train.Features({ "image":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.string), "label":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), "height":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), "width":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), "channels":tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64), })) image,label = features['image'],features['label'] height,width = features['height'],features['weight'] channels = features['channels'] #从原始图像解析出像素矩阵,并根据图像尺寸还原图像 decoded_image = tf.decode_raw(image,tf.uint8) decoded_image.set_shape([height,width,channels]) #定义神经网络输入层图片的大小 image_size = 299 def distort_color(image,color_ordering=0): if color_ordering == 0: image = tf.image.random_brightness(image,32.0/255.0) image = tf.image.random_saturation(image,lower=0.5,upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_hue(image,0.2) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image,lower=0.5,upper=1.5) elif color_ordering == 1: image = tf.image.random_saturation(image,lower=0.5,upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_brightness(image,32.0/255.0) image = tf.image.random_hue(image,0.2) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image,lower=0.5,upper=1.5) return tf.clip_by_value(image,0.0,1.0) def preprocess_for_train(image,height,width,bbox): #如果没有标注提示框,则认为整张图想是需要关注的部分 if bbox is None: bbox = tf.constant([0.0,0.0,1.0,1.0],dtype=tf.float32,shape=[1,1,4]) #转换图像张量的类型 if image.dtype != tf.float32: image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image,dtype=tf.float32) #随机截取的图像,减少需要关注的物体大小对图像识别的影响 bbox_begin,bbox_size,_ = tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(tf.shape(image),bounding_boxes=bbox) distorted_image = tf.slice(image,bbox_begin,bbox_size) #将截取的图像调整为神经网络输入层大小。大小调整的算法是随机的 distorted_image = tf.image.resize_images(distorted_image,[height,width],method=np.random.randint(4)) #随机左右翻转图像 distorted_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(distorted_image) #使用一种随机的顺序调整图像色彩 distorted_image = distort_color(distorted_image,np.random.randint(2)) return distorted_image distorted_image = preprocess_for_train(decoded_image,image_size,image_size,None) #将样例组合batch min_after_dequeue = 10000 batch_size =100 capacity = min_after_dequeue+ batch_size *3 image_batch,label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([decoded_image,label],batch_size,capacity=capacity,min_after_dequeue=min_after_dequeue) #定义神经网络的结构及优化过程 def inference(image_data): """ 计算前向传播,参考前面的内容 :param image_data: :return: """ pass def calc_loss(logit,label): """ bp ,calc the loss,参考前面的内容 :param logit: :param label: :return: """ pass logit = inference(image_batch) loss = calc_loss(logit,label_batch) train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(loss) with tf.Session() as sess: tf.global_variables_initializer().run() tf.local_variables_initializer().run() coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord=coord) for i in range(10000): sess.run(train_step) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads)
整个数据处理的流程如下