http://openmaniak.com/quagga_case4.php
1. CASE PRINCIPLE  Some words about BGP.
Some words about BGP.
This tutorial is dedicated to the BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) dynamic routing protocol, for which the fourth and last version of BGP has been released in 1994.
BGP is mainly used by Service providers to perform the routing inside the Internet or to provide connectivity between the remote sites of a company with technologies like MPLS.
BGP is not scalable for a small to medium environment (up to 100 routers) because of its slow convergence time compared to the RIP or OSFP routing protocol. At the same time it can be very complex to configure and needs powerful (and very expensive) hardware
to be run comfortably.
This is why BGP should normally only be used by service providers or companies with a very large number of routers.
To give an example, in July 2007 more than 200'000
BGP entries were found on an internet router and are growing each day. Because of this high number of routes, the variation of the routing table will require a lot of resources and, as a consequence, the hardware must be very powerful.
Cisco Systems (with its 12000 series routers) and Juniper share this lucrative market.
For private networks, it is also possible to use BGP on "smaller" routers like the Cisco 7200 or 3800 series routers. Of course, Quagga supported by a good appliance can be comfortable in these environments too.
Two major BGP strong points are:
| - - |
Use of TCP. BGP communicates with the other BGP routers (called peers) through TCP which is the most reliable protocol.
The notion of Autonomous System (AS). It is a group of IP networks under common administration and common routing policies. It is composed of a variable number of BGP routers. |
Browse the web or buy a good book to find more details about this complex routing protocol.
Routing protocols comparison:
| RIP | OSPF | BGP | |
| Version: | v2 | v2 | v4 |
| RFC: | 2453 | 2328 | 1771 |
| Date: | 1998 | 1998 | 1994 |
| IGP - EGP: (1) | IGP | IGP | EGP |
| Type: | Distance vector | Link state | Path vector |
| Algorithm: | Bellman-Ford | Dijkstra | Best Path Selection |
| Convergence: (2) | Medium | Fast | Slow |
| Administrative distance: | 120 | 110 | 20 |
| OSI level / port: | UDP / 520 | IP / 89 | TCP / 179 |
| Configuration complexity: | Easy | Medium | Hard to very hard |
| Routing granularity: | Router | Router | Autonomous System (3) |
| Scalable for: | < 100 routers | < 100 routers | > 100 routers |
| Resource consumption: | Low | Low to Medium | High |
| (1) (2) (3) |
IGP stands for Interior Gateway Protocols, EGP for Exterior Gateway Protocols. EGPs are used between independent administrative entities, often called autonomous systems and IGPs are used inside them. Convergence time: time needed for the routers to update their routing table after a change in the network topology. When several paths are available for a specific network, BGP choose the route crossing the smallest number of autonomous systems. |
The BGP path selection process is used if there are several routes available for a network.You can see it with the "show ip bgp" command. This command must not be confounded with the "show ip route" command where only the best routes are displayed on the screen.
To get full details, you can read the Cisco webpage about the BGP path selection process.
Click on an attribute name to get an example.
| ATTRIBUTE NAME | PREFERENCE | VALUE TRANSMISSION | DESCRIPTION | |
| 1. | Weight (a) | Highest | Local to router | Cisco & Quagga specific |
| 2. | Local Preference | Highest | Global within AS | How to exit the AS if multiple paths |
| 3. | Path | Shortest | ||
| 4. | Origin Code | Lowest | IGP or "i" < EGP or "e" < Incomplete or "?" (b) | |
| 5. | MED (Metric) | Lowest | Transmitted to the neighbors AS only |
| (a) (b) |
By default, a directly connected route takes a weight of 32768. An origin code of incomplete is due to route redistribution into BGP. |
 Case study principle
Case study principleHere are the functionalities we will test in our BGP scenario:
| - - - - - - |
EBGP (external BGP): BGP between the autonomous systems. EBGP is running between Cisco 3750 L3 and Cisco 2651 A, Cisco 2651 A and Quagga B, Quagga B and Cisco 2651 C, Cisco 2651 and Quagga A. IBGP (Internal BGP): BGP inside an AS. IBGP is running between Cisco 3750 L3 and Quagga A. BGP to OSPF redistribution: On Cisco 3750 L3: BGP routes are injected into OSPF with a metric of 1000 and tagged as OE1. On Quagga A: BGP routes are injected into OSPF with a metric of 2000 and tagged as OE2 (default). OSPF to BGP redistribution: On Cisco 3750 L3 and Quagga A, the OSPF networks are injected into BGP with the default values. Local Preference: Cisco 3750 L3 is the preferred router to exit AS 65001 Customized local preferences are applied through route maps to the BGP incoming routes on Cisco 3750 L3 (333) and Quagga A (222). MED. Quagga B will prefer the path via AS 65003 rather than AS 65004 to reach AS 65001. Customized MEDs are applied through route maps to the outgoing BGP routes towards AS 65005on Cisco 2651 B (55) and Cisco 2651 C (99). |
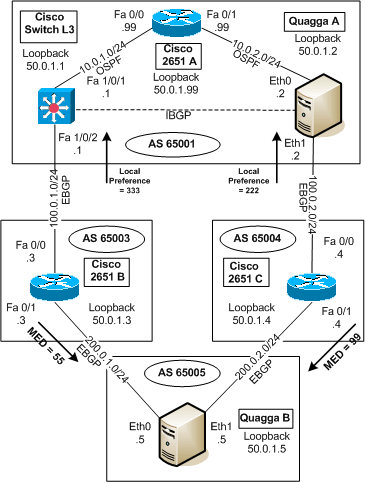 |
Functionalities tested: (click on the web links to have more details about a protocol)  Interface settings Interface settings OSPF - backbone area
OSPF - backbone area BGP
BGP Redistr. - BGP to OSPF Redistr. - BGP to OSPF Redistr. - OSPF to BGP Redistr. - OSPF to BGP Telnet access
Telnet access |
 Top of the page
Top of the page |
You must set your Linux system correctly to launch Quagga successfully. See the Quagga tutorial for help about this. |
 LINUX CONFIGURATIONS
LINUX CONFIGURATIONSCheck that the zebra, ospfd and bgpd daemons are activated on Quagga A:
| #vim /etc/quagga/daemons |
bgpd=yes
ospfd=yes
ospf6d=no
ripd=no
ripngd=no
isisd=no
Check that the zebra and bgpd daemons are activated on Quagga B:
| #vim /etc/quagga/daemons |
bgpd=yes
ospfd=no
ospf6d=no
ripd=no
ripngd=no
isisd=no
If you changed your daemons files, restart the quagga service:
| #vim /etc/init.d/quagga restart |
| #vim /etc/quagga/vtysh.conf |
! Sample
!
! service integrated-vtysh-config
hostname Quagga_A
username root nopassword
!
Set the Quagga B hostname in the /etc/quagga/vtysh.conf file:
| #vim /etc/quagga/vtysh.conf |
! Sample
!
! service integrated-vtysh-config
hostname Quagga_B
username root nopassword
!
Don't forget to activate the ip forwarding on the Quagga A and Quagga B routers!
 ROUTERS CONFIGURATIONS
ROUTERS CONFIGURATIONSROUTER 2651 A IOS: 12.2-23a  See the entire configuration See the entire configuration |
|
| interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 10.0.2.99 255.255.255.0 no shutdown |
|
| interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.1.99 255.255.255.0 no shutdown |
|
| interface Loopback 1 ip address 50.0.1.99 255.255.255.255 |
|
| Cisco_2651_A | |
| router ospf 1 network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 50.0.1.99 0.0.0.0 area 0 |
|
| line vty 0 4 no login |
|
| enable secret password | |
SWITCH L3 3750 IOS: 12.2-25.SEE2  See the entire configuration
See the entire configuration |
QUAGGA A 0.99.6  See the entire configuration
See the entire configuration |
| interface vlan 1 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface FastEthernet1/0/1 switchport access vlan 1 |
interface eth0 ip address 10.0.2.2/24 link-detect |
| interface vlan 2 ip address 100.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface FastEthernet1/0/2 switchport access vlan 2 |
interface eth1 ip address 100.0.2.2/24 link-detect |
| interface Loopback 1 ip address 50.0.1.1 255.255.255.255 |
interface lo ip address 50.0.1.2/32 link-detect |
| hostname Cisco_3750_L3 | |
| router ospf 1 redistribute connected metric 1000 metric-type 1 subnets redistribute bgp 65001 metric 1000 metric-type 1 subnets network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 |
router ospf redistribute connected metric 2000 redistribute bgp metric 2000 network 10.0.2.0/24 area 0.0.0.0 |
| router bgp 65001 no synchronization bgp router-id 50.0.1.1 network 50.0.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 redistribute connected redistribute ospf 1 neighbor 10.0.2.2 remote-as 65001 neighbor 100.0.1.3 remote-as 65003 neighbor 100.0.1.3 route-map r2 in no auto-summary |
bgp config-type cisco router bgp 65001 no synchronization bgp router-id 50.0.1.2 network 50.0.1.2 mask 255.255.255.255 redistribute connected redistribute ospf neighbor 10.0.1.1 remote-as 65001 neighbor 100.0.2.4 remote-as 65004 neighbor 100.0.2.4 route-map r2 in no auto-summary |
| route-map r2 permit 10 set local-preference 333 |
route-map r2 permit 10 set local-preference 222 |
| line vty 0 4 no login |
line vty no login |
| enable secret password |
enable password password |
| ip routing ip multicast-routing distributed |
|
ROUTER 2651 B IOS: 12.2-23a  See the entire configuration See the entire configuration |
QUAGGA B 0.99.6  See the entire configuration See the entire configuration |
| interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 100.0.1.3 255.255.255.0 no shutdown |
interface eth0 ip address 200.0.1.5/24 link-detect |
| interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 200.0.1.3 255.255.255.0 no shutdown |
interface eth1 ip address 200.0.2.5/24 link-detect |
| interface Loopback 1 ip address 50.0.1.3 255.255.255.255 |
interface lo ip address 50.0.1.5/32 link-detect |
| hostname Cisco_2651_B | |
| router bgp 65003 bgp router-id 50.0.1.3 network 50.0.1.3 mask 255.255.255.255 redistribute connected neighbor 100.0.1.1 remote-as 65001 neighbor 200.0.1.5 remote-as 65005 neighbor 200.0.1.5 route-map r3 out no auto-summary |
router bgp 65005 bgp router-id 50.0.1.5 network 50.0.1.5 mask 255.255.255.255 redistribute connected neighbor 200.0.1.3 remote-as 65003 neighbor 200.0.2.4 remote-as 65004 no auto-summary |
| route-map r3 permit 10 set metric 55 |
|
| line vty 0 4 no login |
line vty no login |
| enable secret password | enable password password |
ROUTER 2651 C IOS: 12.2-23a  See the entire configuration See the entire configuration |
|
| interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 100.0.2.4 255.255.255.0 no shutdown |
|
| interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 200.0.2.4 255.255.255.0 no shutdown |
|
| interface Loopback 1 ip address 50.0.1.4 255.255.255.255 |
|
| router bgp 65004 bgp router-id 50.0.1.4 network 50.0.1.4 mask 255.255.255.255 redistribute connected neighbor 100.0.2.2 remote-as 65001 neighbor 200.0.2.5 remote-as 65005 neighbor 200.0.2.5 route-map r99 out no auto-summary |
|
| hostname Cisco_2651_C | |
| route-map r99 permit 10 set metric 99 |
|
| line vty 0 4 no login |
|
| enable secret password |
 Top of the page
Top of the page| CISCO 2651 A | CISCO 3750 L3 | QUAGGA A | CISCO 2651 B | QUAGGA B | CISCO 2651 C |
 CISCO 2651 A
CISCO 2651 ACisco_2651_A#show ip int brief
| Interface | IP-Address | OK? | Method | Status | Protocol |
| FastEthernet0/0 | 10.0.1.99 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| FastEthernet0/1 | 10.0.2.99 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| Loopback1 | 50.0.1.99 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| Codes: | C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP | ||
| D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area | |||
| N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 | |||
| E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP | |||
| i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 | |||
| ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route | |||
| o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route | |||
| Gateway of last resort is not set | |||
| 50.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 6 subnets | |||
| O | E1 | 50.0.1.3 [110/1001] via 10.0.1.1, 00:37:09, FastEthernet0/0 | |
| O | E2 | 50.0.1.2 [110/2000] via 10.0.2.2, 00:37:15, FastEthernet0/1 | |
| O | E1 | 50.0.1.1 [110/1001] via 10.0.1.1, 00:37:15, FastEthernet0/0 | |
| O | E1 | 50.0.1.5 [110/1001] via 10.0.1.1, 00:36:22, FastEthernet0/0 | |
| O | E1 | 50.0.1.4 [110/1001] via 10.0.1.1, 00:35:56, FastEthernet0/0 | |
| C | 50.0.1.99 is directly connected, Loopback1 | ||
| 100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets | |||
| O | E1 | 100.0.1.0 [110/1001] via 10.0.1.1, 00:37:15, FastEthernet0/0 | |
| O | E2 | 100.0.2.0 [110/2000] via 10.0.2.2, 00:12:48, FastEthernet0/1 | |
| O | E1 | 200.0.1.0/24 [110/1001] via 10.0.1.1, 00:37:09, FastEthernet0/0 | |
| O | E1 | 200.0.2.0/24 [110/1001] via 10.0.1.1, 00:36:22, FastEthernet0/0 | |
| 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets | |||
| C | 10.0.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 | ||
| C | 10.0.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 | ||
| OSPF Router with ID (50.0.1.99) (Process ID 1) | ||||||
| Router Link States (Area 0) | ||||||
| Link ID | ADV Router | Age | Seq# | Checksum | Link count | |
| 50.0.1.1 | 50.0.1.1 | 357 | 0x80000004 | 0x003417 | 1 | |
| 50.0.1.2 | 50.0.1.2 | 555 | 0x80000004 | 0x00CC90 | 1 | |
| 50.0.1.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 404 | 0x80000005 | 0x00236B | 3 | |
| Net Link States (Area 0) | ||||||
| Link ID | ADV Router | Age | Seq# | Checksum | ||
| 10.0.1.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 404 | 0x80000002 | 0x009CCC | ||
| 10.0.2.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 404 | 0x80000002 | 0x009FC7 | ||
| Type-5 AS External Link States | ||||||
| Link ID | ADV Router | Age | Seq# | Checksum | Tag | |
| 50.0.1.1 | 50.0.1.1 | 357 | 0x80000002 | 0x005B84 | 0 | |
| 50.0.1.2 | 50.0.1.2 | 502 | 0x80000003 | 0x00C3CA | 0 | |
| 50.0.1.3 | 50.0.1.1 | 357 | 0x80000002 | 0x00BB38 | 65003 | |
| 50.0.1.4 | 50.0.1.1 | 357 | 0x80000002 | 0x00B141 | 65003 | |
| 50.0.1.5 | 50.0.1.1 | 357 | 0x80000002 | 0x00A74A | 65003 | |
| 100.0.1.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 357 | 0x80000002 | 0x00D8D5 | 0 | |
| 100.0.2.0 | 50.0.1.2 | 834 | 0x80000001 | 0x00441B | 0 | |
| 200.0.1.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 357 | 0x80000002 | 0x00342C | 65003 | |
| 200.0.2.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 357 | 0x80000002 | 0x002936 | 65003 | |
 CISCO 3750 L3
CISCO 3750 L3Cisco_3750_L3#show ip int brief
| Interface | IP-Address | OK? | Method | Status | Protocol |
| Vlan1 | 10.0.1.1 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| Vlan2 | 100.0.1.1 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| FastEthernet1/0/1 | unassigned | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| FastEthernet1/0/2 | unassigned | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Loopback1 | 50.0.1.1 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| Codes: | C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP | ||
| D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area | |||
| N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 | |||
| E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP | |||
| i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 | |||
| ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route | |||
| o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route | |||
| Gateway of last resort is not set | |||
| 50.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 6 subnets | |||
| B | 50.0.1.3 [20/0] via 100.0.1.3, 00:41:15 | ||
| O | E2 | 50.0.1.2 [110/2000] via 10.0.1.99, 00:41:20, Vlan1 | |
| C | 50.0.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback1 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.5 [20/0] via 100.0.1.3, 00:40:27 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.4 [20/0] via 100.0.1.3, 00:40:01 | ||
| O | 50.0.1.99 [110/2] via 10.0.1.99, 00:41:20, Vlan1 | ||
| 100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets | |||
| C | 100.0.1.0 is directly connected, Vlan2 | ||
| O | E2 | 100.0.2.0 [110/2000] via 10.0.1.99, 00:16:53, Vlan1 | |
| B | 200.0.1.0/24 [20/0] via 100.0.1.3, 00:41:15 | ||
| B | 200.0.2.0/24 [20/0] via 100.0.1.3, 00:40:27 | ||
| 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets | |||
| O | 10.0.2.0 [110/2] via 10.0.1.99, 00:41:20, Vlan1 | ||
| C | 10.0.1.0 is directly connected, Vlan1 | ||
| OSPF Router with ID (50.0.1.1) (Process ID 1) | ||||||
| Router Link States (Area 0) | ||||||
| Link ID | ADV Router | Age | Seq# | Checksum | Link count | |
| 50.0.1.1 | 50.0.1.1 | 631 | 0x80000004 | 0x003417 | 1 | |
| 50.0.1.2 | 50.0.1.2 | 832 | 0x80000004 | 0x00CC90 | 1 | |
| 50.0.1.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 680 | 0x80000005 | 0x00236B | 3 | |
| Net Link States (Area 0) | ||||||
| Link ID | ADV Router | Age | Seq# | Checksum | ||
| 10.0.1.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 680 | 0x80000002 | 0x009CCC | ||
| 10.0.2.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 680 | 0x80000002 | 0x009FC7 | ||
| Type-5 AS External Link States | ||||||
| Link ID | ADV Router | Age | Seq# | Checksum | Tag | |
| 50.0.1.1 | 50.0.1.1 | 631 | 0x80000002 | 0x005B84 | 0 | |
| 50.0.1.2 | 50.0.1.2 | 779 | 0x80000003 | 0x00C3CA | 0 | |
| 50.0.1.3 | 50.0.1.1 | 631 | 0x80000002 | 0x00BB38 | 65003 | |
| 50.0.1.4 | 50.0.1.1 | 631 | 0x80000002 | 0x00B141 | 65003 | |
| 50.0.1.5 | 50.0.1.1 | 631 | 0x80000002 | 0x00A74A | 65003 | |
| 100.0.1.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 631 | 0x80000002 | 0x00D8D5 | 0 | |
| 100.0.2.0 | 50.0.1.2 | 1111 | 0x80000001 | 0x00441B | 0 | |
| 200.0.1.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 632 | 0x80000002 | 0x00342C | 65003 | |
| 200.0.2.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 632 | 0x80000002 | 0x002936 | 65003 | |
| BGP router identifier 50.0.1.1, local AS number 65001 | |||||||||
| BGP table version is 16, main routing table version 16 | |||||||||
| 13 network entries using 1469 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 24 path entries using 1248 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 18/10 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 1944 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 3 BGP AS-PATH entries using 72 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| BGP using 4733 total bytes of memory | |||||||||
| BGP activity 13/0 prefixes, 24/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs | |||||||||
| Neighbor | V | AS | MsgRcvd | MsgSent | TblVer | InQ | OutQ | Up/Down | State/PfxRcd |
| 10.0.2.2 | 4 | 65001 | 58 | 64 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 00:44:16 | 13 |
| 100.0.1.3 | 4 | 65003 | 54 | 53 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 00:45:14 | 6 |
| BGP table version is 16, local router ID is 50.0.1.1 | ||||||||
| Status codes: | s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, | |||||||
| r RIB-failure, S Stale | ||||||||
| Origin codes: | i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete | |||||||
| Network | Next Hop | Metric | LocPrf | Weight | Path | |||
| * | i | 10.0.1.0/24 | 10.0.2.99 | 11 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 10.0.2.0/24 | 10.0.2.2 | 1 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 10.0.1.99 | 2 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 50.0.1.1/32 | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | i | ||||
| r> | i | 50.0.1.2/32 | 10.0.2.2 | 0 | 100 | 0 | i | |
| * | i | i50.0.1.3/32 | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 100.0.1.3 | 0 | 333 | 0 | 65003 i | |||
| * | i | 50.0.1.4/32 | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 100.0.1.3 | 333 | 0 | 65003 65005 65004 i | ||||
| * | i | 50.0.1.5/32 | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 100.0.1.3 | 333 | 0 | 65003 65005 i | ||||
| * | i | 50.0.1.99/32 | 10.0.2.99 | 11 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 10.0.1.99 | 2 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 100.0.1.0/24 | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| * | 100.0.1.3 | 0 | 333 | 0 | 65003 ? | |||
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| r> | i | 100.0.2.0/24 | 10.0.2.2 | 1 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| * | i | 200.0.1.0 | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 100.0.1.3 | 0 | 333 | 0 | 65003 ? | |||
| * | i | 200.0.2.0 | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 100.0.1.3 | 333 | 0 | 65003 65005 ? | ||||
 Top of the page Show Commands Menu
Top of the page Show Commands Menu QUAGGA A
QUAGGA AQuagga_A#show interface description
| Interface | Status | Protocol | Description |
| eth0 | up | up | |
| eth1 | up | up | |
| lo | up | up |
| Codes: | K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, | |
| I - ISIS, B - BGP, > - selected route, * - FIB route | ||
| O>* | 10.0.1.0/24 [110/11] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:11:01 | |
| O | 10.0.2.0/24 [110/10] is directly connected, eth0, 01:11:48 | |
| C>* | 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, eth0 | |
| O>* | 50.0.1.1/32 [110/1011] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:10:16 | |
| C>* | 50.0.1.2/32 is directly connected, lo | |
| O>* | 50.0.1.3/32 [110/1011] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:10:02 | |
| O>* | 50.0.1.4/32 [110/1011] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:08:48 | |
| O>* | 50.0.1.5/32 [110/1011] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:09:14 | |
| O>* | 50.0.1.99/32 [110/11] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:11:01 | |
| O>* | 100.0.1.0/24 [110/1011] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:10:16 | |
| C>* | 100.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, eth1 | |
| C>* | 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo | |
| O>* | 200.0.1.0/24 [110/1011] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:10:02 | |
| O>* | 200.0.2.0/24 [110/1011] via 10.0.2.99, eth0, 01:09:14 | |
| Destination | Gateway | Genmask | Flags | Metric | Ref | Use | Iface |
| 50.0.1.1 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.255 | UGH | 1011 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 50.0.1.99 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.255 | UGH | 11 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 50.0.1.3 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.255 | UGH | 1011 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 50.0.1.5 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.255 | UGH | 1011 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 50.0.1.4 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.255 | UGH | 1011 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 10.0.1.0 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.0 | UG | 11 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 10.0.2.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | U | 0 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 100.0.2.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 255.255.255.0 | U | 0 | 0 | 0 | eth1 |
| 200.0.1.0 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.0 | UG | 1011 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 200.0.2.0 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.0 | UG | 1011 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| 100.0.1.0 | 10.0.2.99 | 255.255.255.0 | UG | 1011 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
| OSPF Router with ID (50.0.1.2) | ||||||
| Router Link States (Area 0.0.0.0) | ||||||
| Link ID | ADV Router | Age | Seq# | CkSum | Link count | |
| 50.0.1.1 | 50.0.1.1 | 292 | 0x80000005 | 0x3218 | 1 | |
| 50.0.1.2 | 50.0.1.2 | 693 | 0x80000005 | 0xca91 | 1 | |
| 50.0.1.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 311 | 0x80000006 | 0x216c | 3 | |
| Net Link States (Area 0.0.0.0) | ||||||
| ADV Router | CkSum | |||||
| 10.0.1.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 0x80000003 | 0x9acd | |||
| 10.0.2.99 | 50.0.1.99 | 0x80000003 | 0x9dc8 | |||
| AS External Link States | ||||||
| Link ID | ADV Router | Age | Seq# | CkSum | Route | |
| 50.0.1.1 | 50.0.1.1 | 292 | 0x80000003 | 0x5985 | E1 50.0.1.1/32 [0x0] | |
| 50.0.1.2 | 50.0.1.2 | 611 | 0x80000004 | 0xc1cb | 50.0.1.2/32 [0x0] | |
| 50.0.1.3 | 50.0.1.1 | 292 | 0x80000003 | 0xb939 | 50.0.1.3/32 [0xfdeb] | |
| 50.0.1.4 | 50.0.1.1 | 292 | 0x80000003 | 0xaf42 | 50.0.1.4/32 [0xfdeb] | |
| 50.0.1.5 | 50.0.1.1 | 292 | 0x80000003 | 0xa54b | 50.0.1.5/32 [0xfdeb] | |
| 100.0.1.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 292 | 0x80000003 | 0xd6d6 | 100.0.1.0/24 [0x0] | |
| 100.0.2.0 | 50.0.1.2 | 1431 | 0x80000002 | 0x421c | 100.0.2.0/24 [0x0] | |
| 200.0.1.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 292 | 0x80000003 | 0x322d | 200.0.1.0/24 [0xfdeb] | |
| 200.0.2.0 | 50.0.1.1 | 292 | 0x80000003 | 0x2737 | 200.0.2.0/24 [0xfdeb] | |
| BGP router identifier 50.0.1.2, local AS number 65001 | |||||||||
| RIB entries 25, using 1600 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| Peers 2, using 5024 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| Neighbor | V | AS | MsgRcvd | MsgSent | TblVer | InQ | OutQ | Up/Down | State/PfxRcd |
| 10.0.1.1 | 4 | 65001 | 89 | 85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 01:11:27 | 10 |
| 100.0.2.4 | 4 | 65004 | 57 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 00:46:37 | 5 |
| Total number of neighbors 2 | |||||||||
| BGP table version is 0, local router ID is 50.0.1.2 | ||||||||
| Status codes: | s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, | |||||||
| r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed | ||||||||
| Origin codes: | i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete | |||||||
| Network | Next Hop | Metric | LocPrf | Weight | Path | |||
| * | i | 10.0.1.0/24 | 10.0.1.1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 10.0.2.99 | 11 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 10.0.2.0/24 | 10.0.1.99 | 2 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 1 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 50.0.1.1/32 | 10.0.1.1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | i | |
| *> | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | 50.0.1.2/32 | 0.0.0.0 | 1 | 32768 | ? | |||
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | i | ||||
| *> | 50.0.1.3/32 | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 32768 | ? | |||
| * | i | 100.0.1.3 | 0 | 333 | 0 | 65003 i | ||
| * | 50.0.1.4/32 | 100.0.2.4 | 0 | 222 | 0 | 65004 i | ||
| *> | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 100.0.1.3 | 0 | 333 | 0 | 65003 65005 65004 i | ||
| * | 50.0.1.5/32 | 100.0.2.4 | 222 | 0 | 65004 65005 i | |||
| * | i | 100.0.1.3 | 0 | 333 | 0 | 65003 65005 i | ||
| *> | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 50.0.1.99/32 | 10.0.1.99 | 2 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 10.0.2.99 | 11 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 100.0.1.0/24 | 10.0.1.1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | ? | |
| *> | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | 100.0.2.0/24 | 100.0.2.4 | 0 | 222 | 0 | 65004 ? | ||
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 1 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | 200.0.1.0 | 100.0.2.4 | 222 | 0 | 65004 65005 ? | |||
| *> | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 100.0.1.3 | 0 | 333 | 0 | 65003 ? | ||
| * | 200.0.2.0 | 100.0.2.4 | 0 | 222 | 0 | 65004 ? | ||
| *> | 10.0.2.99 | 1011 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | i | 100.0.1.3 | 0 | 333 | 0 | 65003 65005 ? | ||
There are two routes for 50.0.1.3; which one will be chosen?
The weights are different so the elected route (indicated with the ">" character) will have the highest weight (32768).
Let's look at the local preference effect on the 50.1.0.5 network (see above):
There are two routes for 50.0.1.5; which one will be chosen?
The weights are equals -> the local preferences are different so the route (indicated with the ">" character) with the highest local preference (333) will be chosen.
See details about the BGP path selection process.
Quagga_A#show route-map r2
| OSPF: | ||
| route-map r2, permit, sequence 10 | ||
| Match clauses: | ||
| Set clauses: | ||
| Call clause: | ||
| Action: | ||
| Exit routemap | ||
| BGP: | ||
| route-map r2, permit, sequence 10 | ||
| Match clauses: | ||
| Set clauses: | ||
| local-preference 222 | ||
| Call clause: | ||
| Action: | ||
| Exit routemap | ||
 Top of the page Show Commands Menu
Top of the page Show Commands Menu CISCO 2651 B
CISCO 2651 BCisco_2651_B#show ip interface brief
| Interface | IP-Address | OK? | Method | Status | Protocol |
| FastEthernet0/1 | 100.0.1.3 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| FastEthernet0/1 | 200.0.1.3 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| Loopback1 | 50.0.1.3 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| Codes: | C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP | ||
| D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area | |||
| N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 | |||
| E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP | |||
| i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 | |||
| ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route | |||
| o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route | |||
| Gateway of last resort is not set | |||
| 50.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 6 subnets | |||
| C | 50.0.1.3 is directly connected, Loopback1 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.2 [20/0] via 100.0.1.1, 00:46:33 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.1 [20/0] via 100.0.1.1, 00:47:02 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.5 [20/0] via 200.0.1.5, 00:46:30 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.4 [20/0] via 200.0.1.5, 00:46:00 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.99 [20/2] via 100.0.1.1, 00:47:02 | ||
| 100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets | |||
| C | 100.0.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 | ||
| B | 100.0.2.0 [20/0] via 100.0.1.1, 00:22:34 | ||
| C | 200.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 | ||
| B | 200.0.2.0/24 [20/1] via 200.0.1.5, 00:46:30 | ||
| 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets | |||
| B | 10.0.2.0 [20/2] via 100.0.1.1, 00:47:02 | ||
| B | 10.0.1.0 [20/0] via 100.0.1.1, 00:47:03 | ||
| BGP router identifier 50.0.1.3, local AS number 65003 | |||||||||
| BGP table version is 14, main routing table version 14 | |||||||||
| 13 network entries using 1261 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 16 path entries using 576 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 11 BGP path attribute entries using 660 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 3 BGP AS-PATH entries using 72 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| BGP using 2569 total bytes of memory | |||||||||
| BGP activity 13/0 prefixes, 16/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs | |||||||||
| Neighbor | V | AS | MsgRcvd | MsgSent | TblVer | InQ | OutQ | Up/Down | State/PfxRcd |
| 100.0.1.1 | 4 | 65001 | 56 | 57 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 00:48:56 | 8 |
| 200.0.1.5 | 4 | 65005 | 57 | 58 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 00:47:26 | 5 |
| BGP table version is 16, local router ID is 50.0.1.3 | ||||||||
| Status codes: | s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, | |||||||
| r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed | ||||||||
| Origin codes: | i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete | |||||||
| Network | Next Hop | Metric | LocPrf | Weight | Path | |||
| *> | 10.0.1.0/24 | 100.0.1.1 | 0 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.1.5 | 0 | 65005 65004 65001 ? | |||||
| *> | 10.0.2.0/24 | 100.0.1.1 | 2 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.1.5 | 0 | 65005 65004 65001 ? | |||||
| *> | 50.0.1.1/32 | 100.0.1.1 | 0 | 0 | 65001 i | |||
| *> | 50.0.1.2/32 | 100.0.1.1 | 0 | 65001 i | ||||
| * | 200.0.1.5 | 0 | 65005 65004 65001 i | |||||
| *> | 50.0.1.3/32 | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | i | |||
| *> | 50.0.1.4/32 | 100.0.1.1 | 0 | 65001 65004 i | ||||
| * | 200.0.1.5 | 0 | 65005 65004 i | |||||
| *> | 50.0.1.5/32 | 200.0.1.5 | 0 | 0 | 65005 i | |||
| *> | 50.0.1.99/32 | 100.0.1.1 | 2 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.1.5 | 0 | 65005 65004 65001 ? | |||||
| *> | 100.0.1.0/24 | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | ? | |||
| * | 100.0.1.1 | 0 | 0 | 65001 ? | ||||
| *> | 100.0.2.0/24 | 100.0.1.1 | 0 | 65001 ? | ||||
| * | 200.0.1.5 | 0 | 65005 65004 ? | |||||
| *> | 200.0.1.0 | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | ? | |||
| * | 200.0.1.5 | 1 | 0 | 65005 ? | ||||
| *> | 200.0.2.0 | 200.0.1.5 | 1 | 0 | 65005 ? | |||
There are two routes for 10.0.2.0; which one will be chosen?
The weights are equals (0) -> the local preferences are not set -> The path lengths are different. This means that the elected route (indicated with the ">" character) will have the shortest path (1).
See details about the BGP path selection process.
 Top of the page Show Commands Menu
Top of the page Show Commands Menu QUAGGA B
QUAGGA BQuagga_B#show interface description
| Interface | Status | Protocol | Description |
| eth0 | up | up | |
| eth1 | up | up | |
| lo | up | up |
| Codes: | K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, | |
| I - ISIS, B - BGP, > - selected route, * - FIB route | ||
| B>* | 10.0.1.0/24 [20/55] via 200.0.1.3, eth0, 01:14:47 | |
| B>* | 10.0.2.0/24 [20/55] via 200.0.1.3, eth0, 01:14:47 | |
| B>* | 50.0.1.1/32 [20/55] via 200.0.1.3, eth0, 01:14:47 | |
| B>* | 50.0.1.2/32 [20/55] via 200.0.1.3, eth0, 01:14:47 | |
| B>* | 50.0.1.3/32 [20/55] via 200.0.1.3, eth0, 01:14:47 | |
| B>* | 50.0.1.4/32 [20/99] via 200.0.2.4, eth1, 01:14:45 | |
| C>* | 50.0.1.5/32 is directly connected, lo | |
| B>* | 50.0.1.99/32 [20/55] via 200.0.1.3, eth0, 01:14:47 | |
| B>* | 100.0.1.0/24 [20/55] via 200.0.1.3, eth0, 01:14:47 | |
| B>* | 100.0.2.0/24 [20/99] via 200.0.2.4, eth1, 00:50:45 | |
| C>* | 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo | |
| C>* | 200.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, eth0 | |
| C>* | 200.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, eth1 | |
| BGP router identifier 50.0.1.5, local AS number 65005 | |||||||||
| RIB entries 25, using 1600 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| Peers 2, using 5024 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| Neighbor | V | AS | MsgRcvd | MsgSent | TblVer | InQ | OutQ | Up/Down | State/PfxRcd |
| 200.0.1.3 | 4 | 65003 | 85 | 85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 01:16:00 | 10 |
| 200.0.2.4 | 4 | 65004 | 84 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 01:15:59 | 11 |
| Total number of neighbors 2 | |||||||||
| BGP table version is 0, local router ID is 50.0.1.5 | ||||||||
| Status codes: | s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, | |||||||
| r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed | ||||||||
| Origin codes: | i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete | |||||||
| Network | Next Hop | Metric | LocPrf | Weight | Path | |||
| * | 10.0.1.0/24 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 65001 ? | ||||
| * | 10.0.2.0/24 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 65001 ? | ||||
| * | 50.0.1.1/32 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 65001 i | ||||
| * | 50.0.1.2/32 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 65001 i | |||
| *> | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 65001 i | ||||
| * | 50.0.1.3/32 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 i | ||||
| *> | 50.0.1.4/32 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 i | |||
| * | 50.0.1.5/32 | 0.0.0.0 | 1 | 32768 | ? | |||
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | i | ||||
| * | 50.0.1.99/32 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 65001 ? | ||||
| * | 100.0.1.0/24 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 ? | ||||
| *> | 100.0.2.0/24 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 65001 ? | ||||
| * | 200.0.1.0 | 200.0.1.3 | 55 | 0 | 65003 ? | |||
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 1 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | 200.0.2.0 | 200.0.2.4 | 99 | 0 | 65004 ? | |||
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 1 | 32768 | ? | ||||
There are two routes for 10.0.1.0; which one will be chosen?
The weights are equal (0) -> the local preferences are not set -> The path lengthsare equal (2) -> The origine codes are equal ("?" character) -> the MED are differrent. It means that the elected route (indicated with the ">" character) will have the lowest MED (55).
See details about the BGP path selection process.
 Top of the page Show Commands Menu
Top of the page Show Commands Menu CISCO 2651 C
CISCO 2651 CCisco_2651_C#show ip interface brief
| Interface | IP-Address | OK? | Method | Status | Protocol |
| FastEthernet0/1 | 100.0.2.4 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| FastEthernet0/1 | 200.0.2.4 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| Loopback1 | 50.0.1.4 | YES | NVRAM | up | up |
| Codes: | C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP | ||
| D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area | |||
| N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 | |||
| E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP | |||
| i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 | |||
| ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route | |||
| o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route | |||
| Gateway of last resort is not set | |||
| 50.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 6 subnets | |||
| B | 50.0.1.3 [20/1011] via 100.0.2.2, 00:41:28 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.2 [20/0] via 100.0.2.2, 00:41:28 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.1 [20/1011] via 100.0.2.2, 00:41:28 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.5 [20/0] via 200.0.2.5, 01:05:46 | ||
| C | 50.0.1.4 is directly connected, Loopback1 | ||
| B | 50.0.1.99 [20/11] via 100.0.2.2, 00:41:29 | ||
| 100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets | |||
| B | 100.0.1.0 [20/1011] via 100.0.2.2, 00:41:28 | ||
| C | 100.0.2.0 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 | ||
| B | 200.0.1.0/24 [20/1] via 200.0.2.5, 01:05:46 | ||
| C | 200.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1 | ||
| 10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets | |||
| B | 10.0.2.0 [20/1] via 100.0.2.2, 00:41:28 | ||
| B | 10.0.1.0 [20/11] via 100.0.2.2, 00:41:30 | ||
| BGP router identifier 50.0.1.4, local AS number 65004 | |||||||||
| BGP table version is 24, main routing table version 24 | |||||||||
| 13 network entries and 26 paths using 2197 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 12 BGP path attribute entries using 624 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 4 BGP AS-PATH entries using 96 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory | |||||||||
| BGP activity 16/26 prefixes, 31/2 paths, scan interval 15 secs | |||||||||
| Neighbor | V | AS | MsgRcvd | MsgSent | TblVer | InQ | OutQ | Up/Down | State/PfxRcd |
| 100.0.2.2 | 4 | 65001 | 49 | 54 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 00:42:26 | 12 |
| 200.0.2.5 | 4 | 65005 | 81 | 76 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 01:06:44 | 11 |
| BGP table version is 0, local router ID is 50.0.1.5 | ||||||||
| Status codes: | s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, | |||||||
| r RIB-failure, S Stale, R Removed | ||||||||
| Origin codes: | i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete | |||||||
| Network | Next Hop | Metric | LocPrf | Weight | Path | |||
| *> | 10.0.1.0/24 | 100.0.2.2 | 11 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 65005 65003 65001 ? | |||||
| *> | 10.0.2.0/24 | 100.0.2.2 | 0 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 65005 65003 65001 ? | |||||
| *> | 50.0.1.1/32 | 100.0.2.2 | 1011 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 65005 65003 65001 i | |||||
| *> | 50.0.1.2/32 | 100.0.2.2 | 0 | 0 | 65001 i | |||
| * | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 65005 65003 65001 i | |||||
| *> | 50.0.1.3/32 | 100.0.2.2 | 1011 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 65005 65003 i | |||||
| *> | 50.0.1.4/32 | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | i | |||
| * | 50.0.1.5/32 | 100.0.2.2 | 1011 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 0 | 65005 i | ||||
| *> | 50.0.1.99/32 | 100.0.2.2 | 11 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 65005 65003 65001 ? | |||||
| *> | 100.0.1.0/24 | 100.0.2.2 | 1011 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 65005 65003 ? | |||||
| * | 100.0.2.0/24 | 100.0.2.2 | 1 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.2.5 | 0 | 32768 | ? | ||||
| * | 200.0.1.0 | 100.0.2.2 | 1011 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| *> | 200.0.2.5 | 1 | 0 | 65005 ? | ||||
| * | 200.0.2.0 | 100.0.2.2 | 1011 | 0 | 65001 ? | |||
| * | 200.0.2.5 | 1 | 0 | 65005 ? | ||||
| *> | 0.0.0.0 | 0 | 32768 | ? | ||||
There are two routes for 50.0.1.5; which one will be chosen?
The weights are equal (0) -> the local preferences are not set -> The path lengths are equal (1) -> The origin codes are different. It means that the elected route (indicated with the ">" character) will have the lowest origin code (i).
See details about the BGP path selection process.
Cisco_2651_C#show route-map
| route-map r99, permit, sequence 10 | ||
| Match clauses: | ||
| Set clauses: | ||
| metric 99 | ||
| Policy routing matches: 0 packets, 0 bytes | ||
 Top of the page Show Commands Menu
Top of the page Show Commands Menu 5. FAILOVER SCENARIO
5. FAILOVER SCENARIO
The goal is to power off Switch 3750 L3 and see the routing tables changes on Cisco 2651 A and Quagga A.
Cisco 2651 A should always be able to reach Quagga B but via Quagga A instead of Switch 3750 L3.
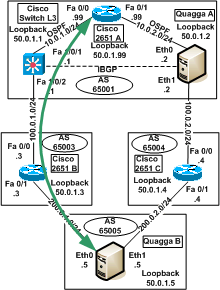 |
 |
 |
Paths comparison from Cisco 2651 A to Quagga B:
(recursive ping from Cisco 2651 A to Quagga B)
| 10.0.1.99 100.0.1.1 200.0.1.3 50.0.1.5 50.0.1.5 100.0.1.3 10.0.1.1 10.0.1.99 |
 |
10.0.2.99 100.0.2.2 200.0.2.4 50.0.1.5 50.0.1.5 100.0.2.4 10.0.2.2 10.0.2.99 |
|
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||