原文by无悔铭
- 居中布局
水平居中
1)使用display:inline-block+text-align:center(display问题1 2)
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:先将子框由块级元素改变为行内块元素,再通过设置行内块元素居中以达到水平居中。
- 用法:对子框设置display:inline-block,对父框设置text-align:center。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.child{ display:inline-block; } .parent{ text-align:center; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:兼容性好,甚至可以兼容ie6、ie7
- 缺点:child里的文字也会水平居中,可以在.child添加text-align:left;还原
2)使用table+margin
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:先将子框设置为块级表格来显示(类似 <table>),再设置子框居中以达到水平居中。
- 用法:对子框设置display:table,再设置margin:0 auto。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.child { display:table; margin:0 auto; }
(3)优缺点:
- 优点:只设置了child,ie8以上都支持
- 缺点:不支持ie6、ie7,将div换成table
3)使用absolute+transform
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:将子框设置为绝对定位,移动子框,使子框左侧距离相对框左侧边框的距离为相对框宽度的一半,再通过向左移动子框的一半宽度以达到水平居中。当然,在此之前,我们需要设置父框为相对定位,使父框成为子框的相对框。
- 用法:对父框设置position:relative,对子框设置position:absolute,left:50%,transform:translateX(-50%)。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { position:relative; } .child { position:absolute; left:50%; transform:translateX(-50%); }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:居中元素不会对其他的产生影响
- 缺点:transform属于css3内容,兼容性存在一定问题,高版本浏览器需要添加一些前缀
4)使用flex+margin
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过CSS3中的布局利器flex将子框转换为flex item,再设置子框居中以达到居中。
- 用法:先将父框设置为display:flex,再设置子框margin:0 auto。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { display:flex; } .child { margin:0 auto; }
(3)优缺点
- 缺点:低版本浏览器(ie6 ie7 ie8)不支持
5)使用flex+justify-content
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过CSS3中的布局利器flex中的justify-content属性来达到水平居中。
- 用法:先将父框设置为display:flex,再设置justify-content:center。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { display:flex; justify-content:center; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:设置parent即可
- 缺点:低版本浏览器(ie6 ie7 ie8)不支持
垂直居中
1)使用table-cell+vertical-align
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过将父框转化为一个表格单元格显示(类似 <td> 和 <th>),再通过设置属性,使表格单元格内容垂直居中以达到垂直居中。
- 用法:先将父框设置为display:table-cell,再设置vertical-align:middle。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { display:table-cell; vertical-align:middle; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:兼容性较好,ie8以上均支持
2)使用absolute+transform
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:类似于水平居中时的absolute+transform原理。将子框设置为绝对定位,移动子框,使子框上边距离相对框上边边框的距离为相对框高度的一半,再通过向上移动子框的一半高度以达到垂直居中。当然,在此之前,我们需要设置父框为相对定位,使父框成为子框的相对框。
- 用法:先将父框设置为position:relative,再设置子框position:absolute,top:50%,transform:translateY(-50%)。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { position:relative; } .child { position:absolute; top:50%; transform:translateY(-50%); }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:居中元素不会对其他的产生影响
- 缺点:transform属于css3内容,兼容性存在一定问题,高版本浏览器需要添加一些前缀
3)使用flex+align-items
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过设置CSS3中的布局利器flex中的属性align-times,使子框垂直居中。
- 用法:先将父框设置为position:flex,再设置align-items:center。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { position:flex; align-items:center; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:只设置parent
- 缺点:兼容性存在一定问题
水平垂直居中
1)使用absolute+transform
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:将水平居中时的absolute+transform和垂直居中时的absolute+transform相结合。详见:水平居中的3)和垂直居中的2)。
- 见水平居中的3)和垂直居中的2)。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { position:relative; } .child { position:absolute; left:50%; top:50%; transform:tranplate(-50%,-50%); }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:child元素不会对其他元素产生影响
- 缺点:兼容性存在一定问题,注意:CSS的transform属性
2)使用inline-block+text-align+table-cell+vertical-align
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:使用inline-block+text-align水平居中,再用table-cell+vertical-align垂直居中,将二者结合起来。详见:水平居中的1)和垂直居中的1)。
- 见水平居中的1)和垂直居中的1)。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { text-align:center; display:table-cell; vertical-align:middle; } .child { display:inline-block; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:兼容性较好
3)使用flex+justify-content+align-items
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过设置CSS3布局利器flex中的justify-content和align-items,从而达到水平垂直居中。详见:水平居中的4)和垂直居中的3)。
- 见水平居中的4)和垂直居中的3)。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="child>DEMO</div> </div>
.parent { display:flex; justify-content:center; align-items:center; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:只设置了parent
- 缺点:兼容性存在一定问题 ,另有
- 多列布局
定宽+自适应
1)使用float+overflow
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过将左边框脱离文本流,设置右边规定当内容溢出元素框时发生的事情以达到多列布局。
- 用法:先将左框设置为float:left、width、margin-left,再设置实际的右框overflow:hidden。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.left { float:left; width:100px; margin-right:20px; } .right { overflow:hidden; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:简单
- 缺点:不支持ie6
2)使用float+margin
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过将左框脱离文本流,加上右框向右移动一定的距离,以达到视觉上的多列布局。
- 用法:先将左框设置为float:left、margin-left,再设置右框margin-left。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.left { float:left; width:100px; } .right { margin-left:120px; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:简单,易理解
- 缺点:兼容性存在一定问题,ie6下有3px的bug。right下的p清除浮动将产生bug
3)使用float+margin(改良版)
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:在1)的基础之上,通过向右框添加一个父框,再加上设置左、右父框属性使之产生BFC以去除bug。
- 用法:先将左框设置为float:left、margin-left、position:relative,再设置右父框float:right、100%、margin-left,最后设置实际的右框margin-left。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="rigth-fix"> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div> </div>
.left { float:left; 100px; position:relative; } .right-fix { float:right; width:100%; margin-left:-100px; } .right { margin-left:120px; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:简单,易理解
4)使用table
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过将父框设置为表格,将左右边框转化为类似于同一行的td,从而达到多列布局。
- 用法:先将父框设置为display:table、100%、table-layout:fixed,再设置左右框display:table-cell,最后设置左框width、padding-right。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.parent { display:table; width:100%; table-layout:fixed; } .left { width:100px; padding-right:20px; } .right,.left { display:table-cell; }
5)使用flex
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过设置CSS3布局利器flex中的flex属性以达到多列布局。(注意:flex属性)
- 用法:先将父框设置为display:flex,再设置左框flex:1,最后设置左框width、margin-right。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.parent { display:flex; } .left { width:100px; margin-right:20px; } .right { flex:1; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:flex很强大
- 缺点:兼容性存在一定问题,性能存在一定问题
两列定宽+一列自适应
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:这种情况与两列定宽查不多。
- 用法:先将左、中框设置为float:left、width、margin-right,再设置右框overflow:hidden。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="center"> <p>center</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.left,.center { float:left; width:100px; margin-right:20px; } .right { overflow:hidden; }
不定宽+自适应
1)使用float+overflow
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:这种情况与两列定宽查不多。
- 用法:先将左框设置为float:left、margin-right,再设置右框overflow: hidden,最后设置左框中的内容width。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.left{ float: left; margin-right: 20px; } .right{ overflow: hidden; } .left p{ width: 200px; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:简单
- 缺点:ie6下兼容性存在一定问题
2)使用table
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过将父框改变为表格,将左右框转换为类似于同一行的td以达到多列布局,设置父框宽度100%,给左框子元素一个固定宽度从而达到自适应。
- 用法:先将父框设置为display: table、 100%,再设置左、右框display: table-cell,最后设置左框 0.1%、padding-right以及左框中的内容width。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.parent{ display: table;
width: 100%; } .left,.right{ display: table-cell; } .left{ width: 0.1%; padding-right: 20px; } .left p{ width:200px; }
(3)优缺点
- 缺点:ie6 ie7不支持
3)使用flex
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过设置CSS3布局利器flex中的flex属性以达到多列布局,加上给左框中的内容定宽、给右框设置flex达到不定款+自适应。
- 用法:先将父框设置为display:flex,再设置右框flex:1,最后设置左框margin-right:20px、左框中的内容width。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.parent { display:flex; } .left { margin-right:20px; } .right { flex:1; } .left p{ width: 200px; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:flex很强大
- 缺点:兼容性存在一定问题,性能存在一定问题
两列不定宽+一列自适应
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:这个情况与一列不定宽+一列自适应查不多。
- 用法:先将左、中框设置为float:left、margin-right,再设置右框overflow:hidden,最后给左中框中的内容设置width。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="center"> <p>center</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.left,.center{ float: left; margin-right: 20px; } .right{ overflow: hidden; } .left p,.center p{ width: 100px; }
等分布局
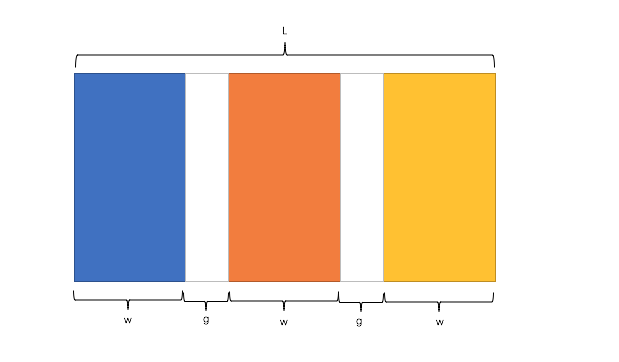
公式转化:
l = w * n + g * (n-1) -> l = w * n + g * n - g -> l + g = (w + g) * n
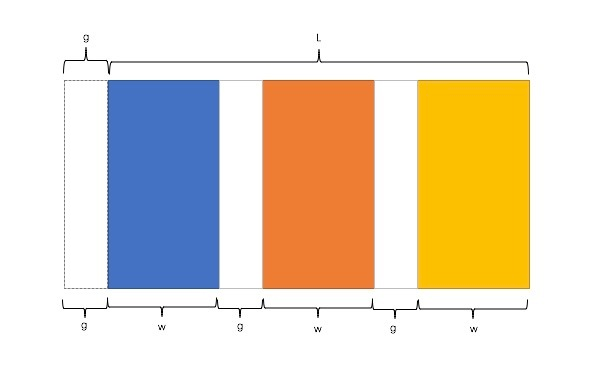
因此,我们需要解决两个问题:
- 如何让总宽度增加g(即:L+g)
- 如何让每个宽包含g(即:w+g)
1)使用float
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:增大父框的实际宽度后,使用CSS3属性box-sizing进行布局的辅助。
- 用法:先将父框设置为margin-left: -*px,再设置子框float: left、 25%、padding-left、box-sizing: border-box。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="column"><p>1</p></div> <div class="column"><p>2</p></div> <div class="column"><p>3</p></div> <div class="column"><p>4</p></div> </div>
.parent{ margin-left: -20px;//l增加g } .column{ float: left; width: 25%; padding-left: 20px; box-sizing: border-box;//包含padding区域 w+g }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:兼容性较好
- 缺点:ie6 ie7百分比兼容存在一定问题
2)使用table
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过增加一个父框的修正框,增大其宽度,并将父框转换为table,将子框转换为tabel-cell进行布局。
- 用法:先将父框的修正框设置为margin-left: -*px,再设置父框display: table、100%、table-layout: fixed,设置子框display: table-cell、padding-left。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent-fix"> <div class="parent"> <div class="column"><p>1</p></div> <div class="column"><p>2</p></div> <div class="column"><p>3</p></div> <div class="column"><p>4</p></div> </div> </div>
.parent-fix{ margin-left: -20px;//l+g } .parent{ display: table; width:100%; table-layout: fixed; } .column{ display: table-cell; padding-left: 20px;//w+g }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:结构和块数无关联
- 缺点:增加了一层
3)使用flex
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过设置CSS3布局利器flex中的flex属性以达到等分布局。
- 用法:将父框设置为display: flex,再设置子框flex: 1,最后设置子框与子框的间距margin-left。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="column"><p>1</p></div> <div class="column"><p>2</p></div> <div class="column"><p>3</p></div> <div class="column"><p>4</p></div> </div>
.parent{ display: flex; } .column{ flex: 1; } .column+.column{ margin-left:20px; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:代码量少,与块数无关
- 缺点:兼容性存在一定问题
定宽+自适应+两块高度一样高
1)使用float
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过过分加大左右子框的高度,辅助超出隐藏,以达到视觉上的等高。
- 用法:将父框设置overflow: hidden,再设置左右子框padding-bottom: 9999px、margin-bottom: -9999px,最后设置左框float: left、width、margin-right,右框overflow: hidden。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
p{ background: none!important; } .left,.right{ background: #444; } .parent{ overflow: hidden; } .left,.right{ padding-bottom: 9999px; margin-bottom: -9999px; } .left{ float: left; width: 100px; margin-right: 20px; } .right{ overflow: hidden; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:兼容性好
- 缺点:伪等高,不是真正意义上的等高
2)使用table
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:将父框转化为tabel,将子框转化为tabel-cell布局,以达到定宽+自适应+两块高度一样高。
- 用法:先将父框设置为display:table、100%、table-layout:fixed,再设置左右框为display:table-cell,最后设置左框width、padding-right。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.parent { display:table; width:100%; table-layout:fixed; } .left { width:100px; padding-right:20px; } .right,.left { display:table-cell; }
3)使用flex
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过设置CSS3布局利器flex中的flex属性以达到定宽+自适应+两块高度一样高。
- 用法:将父框设置为display: flex,再设置左框width、margin-right,最后设置右框flex:1。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left"> <p>left</p> </div> <div class="right"> <p>right</p> <p>right</p> </div> </div>
.parent { display:flex; } .left { width:100px; margin-right:20px; } .right { flex:1; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:代码少,flex很强大
- 缺点:兼容性存在一定问题
4)使用display
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过设置display中的CSS3的-webkit-box属性以达到定宽+自适应+两块高度一样高。
- 用法:将父框设置为display: -webkit-box、 100%,再设置左框width、margin-right,最后设置右框-webkit-box-flex: 1。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="left">left</div> <div class="right">right </div> </div>
.parent { width: 100%; display: -webkit-box; } .left { width:100px; margin-right: 20px; } .right { -webkit-box-flex: 1; }
(3)优缺点
- 缺点:兼容性存在较大的问题
-
全屏布局
全屏布局
全屏布局的特点
- 滚动条不是全局滚动条,而是出现在内容区域里,往往是主内容区域
- 浏览器变大时,撑满窗口
全屏布局的方法

1)使用position
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:将上下部分固定,中间部分使用定宽+自适应+两块高度一样高。
- 用法:见实例。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="top">top</div> <div class="left">left</div> <div class="right"> <div class="inner">right</div> </div> <div class="bottom">bottom</div> </div>
html,body,.parent{ margin:0; height:100%; overflow:hidden; } body{ color:white; } .top{ position:absolute; top:0; left:0; right:0; height:100px; background:blue; } .left{ position:absolute; left:0; top:100px; bottom:50px; width:200px; background:red; } .right{ position:absolute; left:200px; top:100px; bottom:50px; right:0; background:pink; overflow: auto; } .right .inner{ min-height: 1000px; } .bottom{ position:absolute; left:0; right:0; bottom:0; height:50px; background: black; }
(3)优缺点
- 优点:兼容性好,ie6下不支持
2)使用flex
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过灵活使用CSS3布局利器flex中的flex属性和flex-direction属性以达到全屏布局。
- 用法:见实例。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="top">top</div> <div class="middle"> <div class="left">left</div> <div class="right"> <div class="inner">right</div> </div> </div> <div class="bottom">bottom</div> </div>
html,body,.parent{ margin:0; height:100%; overflow:hidden; } body{ color: white; } .parent{ display: flex; flex-direction: column; } .top{ height:100px; background: blue; } .bottom{ height:50px; background: black; } .middle{ flex:1; display:flex; } .left{ width:200px; background: red; } .right{ flex: 1; overflow: auto; background:pink; } .right .inner{ min-height: 1000px; }
(3)优缺点
- 缺点:兼容性差,ie9及ie9以下不兼容
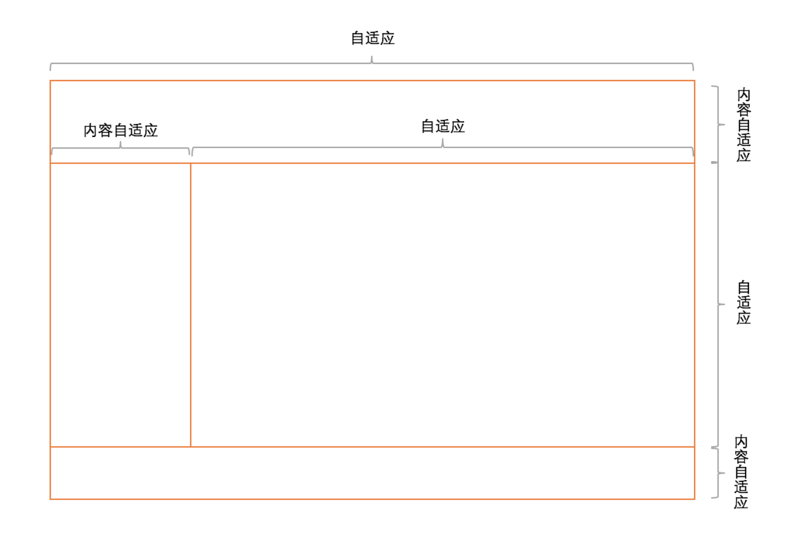
1)使用flex
(1)原理、用法
- 原理:通过灵活使用CSS3布局利器flex中的flex属性和flex-direction属性以达到全屏布局。
- 用法:见实例。
(2)代码实例
<div class="parent"> <div class="top">top</div> <div class="middle"> <div class="left">left</div> <div class="right"> <div class="inner">right</div> </div> </div> <div class="bottom">bottom</div> </div>
html,body,.parent{ margin:0; height:100%; overflow:hidden; } body{ color:white; } .parent{ display:flex; flex-direction:column; } .top{ background:blue; } .bottom{ background:black; } .middle{ flex:1; display:flex; } .left{ background: red; } .right{ flex:1; overflow:auto; background: pink; } .right .inner{ min-height:1000px; }
全屏布局相关方案的兼容性、性能和自适应一览表
| 方案 | 兼容性 | 性能 | 是否自适应 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | 好 | 好 | 部分自适应 |
| Flex | 较差 | 差 | 可自适应 |
| Grid | 差 | 较好 | 可自适应 |