1.选择排序
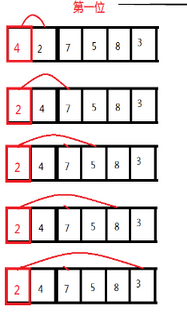
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){//n-1趟 int k=i;//令第一个数为最小值 for(j=i+1;j<n;j++){ if(a[k]>a[j]){ t = a[k]; a[k] = a[j]; a[j] = t; } } }
2.冒泡排序
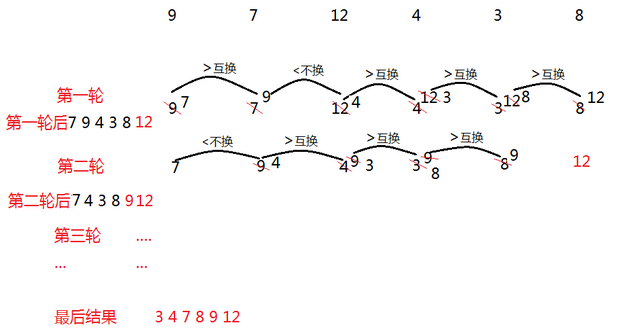
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){//n-1趟冒泡 for(j=0;j<n-i-1;j++){ if(a[j]>a[j+1]){ t = a[j]; a[j] = a[j+1]; a[j+1] = t; } } }
3.快速排序(排序不稳定)

void quick_sort(int a[],int low,int high){ int pivot = a[low]; int i = low+1; int j = high;int temp; while(i<j){ while((i<j)&&pivot<=a[j]){ --j; } while((i<j)&&pivot>=a[i]){ ++i; } if(i<j){ temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } } if(a[low]>a[j]){ temp = a[low]; a[low] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } if(i-low>1) quick_sort(a,low,i-1); if(high-j>1) quick_sort(a,j+1,high); }
4.插入排序

for(i=1;i<n;i++){ if(a[i]<a[i-1]){ //两部分,有序区最后一位元素和无序区第一位元素大小比较 int temp = a[i]; //将有序区元素向后移动,为待插入元素留出位置 for(j=i-1;j>=0&&temp<a[j];j--){ a[j+1] = a[j]; } //j跳出来的是比新元素小的前一位标识,直接插入有序区的位置上 a[j+1] = temp; } }
5.合并排序
public class hebin{ public static void merge(int[]a,int low,int mid,int high){//对两组已经排序的数组进行合并 int[]b=new int[high-low+1]; //临时数组,存储个数为high - low + 1个数据 int s=low; int t=mid+1; int k=0; while(s<=mid&&t<=high){ //直至前半部或后半部数据完全录入暂存 if(a[s]<=a[t]) //如果前半部的数据小于后半部的,前半部数据暂存 b[k++]=a[s++]; else //否则后半部数据暂存,并下标自加 b[k++]=a[t++]; } while(s<=mid) b[k++]=a[s++]; while(t<=high) b[k++]=a[t++]; for(int i=0;i<b.length;i++){ //将暂存的数据重新填充至array[low]--array[high]中 a[low+i]=b[i]; } } public static void mergesort(int a[],int low,int high){//对数组进行递归排序 int mid; if(low<high){ mid=(low+high)/2; mergesort(a,low,mid); mergesort(a,mid+1,high); merge(a,low,mid,high); } } public static void main(String[]args){ int[]a={4,34,2,56,5,9,6,45,8,3}; System.out.println("排序前数组为:"); for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ System.out.print(a[i]+" "); } mergesort(a,0,a.length-1); System.out.println(" 排序后数组为:"); for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){ System.out.print(a[i]+" ");} } }