Nginx安装
参考:
- 学习视频
- https://www.cnblogs.com/EasonJim/p/7806879.html
- http://www.cnblogs.com/piscesLoveCc/p/5794926.html
- http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-08/134080.htm
- https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002797601
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/99aac00aa3b7
各种环境的nginx的关于安装的汇总...有点乱
Nginx版本
- Mainline version-开发版
- Stable version-稳定版
- Legacy version-历史稳定版本
可以到 http://nginx.org/en/download.html 下载需要的版本
win
Nginx+Tomcat的集群配置:
1、2步骤解压java/Nginx中的window集群就可以使用了;
3要使用单独的Nginx压缩包;
1)在一台电脑上安装两个tomcat
需要在一台电脑模拟:在E盘解压两个tomcat,分别命名为tomcat1,tomcat2.
2)修改tomcat的配置文件,将端口进行修改:
分别完成如下配置:(需要将tomcat带有端口号的地方改成不同的端口即可.)分别打开两个tomcat的conf下的server.xml
- tomcat1/conf/server.xml
<Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<!--端口号8080-->
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" />
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
- tomcat2/conf/server.xml:所有端口+10
<Server port="8015" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<!--端口号8090-->
<Connector port="8090" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8453" />
<Connector port="8019" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8453" />
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
3)将项目分别发布到两个tomcat中:
- 打开eclipse;
- 选中项目,右键export--war file--选择位置;
- 复制项目到Tomcat的webapps下;
测试:
a.启动Tomcat:bin/startup.bat
b.浏览器:localhost:8080/项目名;
4)安装Nginx:
1.解压nginx-1.8.0;
2.双击nginx.exe
启动完以后访问http://localhost
 5)配置Nginx:
5)配置Nginx:
修改nginx-1.8.0/conf/nginx.conf文件:
1.需要在http节点上添加一个:
upstream servlet_yujia{ //upstream后跟自己起的名称
server 127.0.0.1:8080; //代理的服务器的接口
server 127.0.0.1:8090;
}
2.修改location /下的反向代理 :
proxy_pass http://servlet_yujia //http:后跟名称
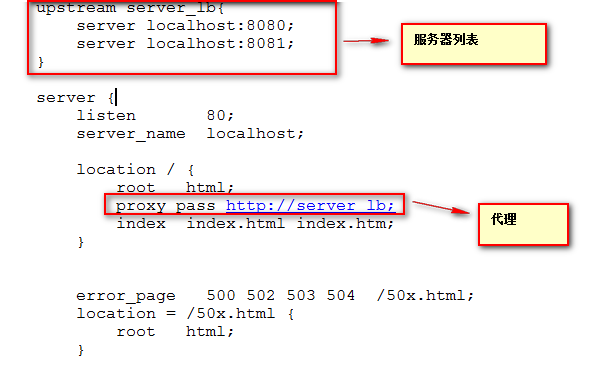
6)Tomcat集群的session共享:
1.一种解决办法:一个用户进来以后只在tomcat1上进行操作,另一个用户进行只在tomcat2上进行操作.
2.session的共享
一种使用tomcat广播机制完成session的共享(不推荐的方式)
一种使用redis服务器的方式完成session的共享(推荐的方式)
- 解决方式1:只能在window下好使(下方有7)
web服务器解决(广播机制)
注意:tomcat下性能低,但是在weblogic上很好
修改两个地方:
1.修改每个tomcat的server.xml 支持共享
将引擎标签下的
<Cluster className="org.apache.catalina.ha.tcp.SimpleTcpCluster"/>
注释去掉
2.修改每个项目的配置文件 web.xml(/tomcat/webapps/项目/WEB-INF/web.xml)中添加一个节点
<distributable/>
3.重启Tomcat

现在再访问项目,在不同Tomcat中的项目的id不变;
- 解决方式2:
可以将session的id放入redis中 - 解决方式3:在linux使用多
保证一个ip地址永远的访问一台web服务器,就不存在session共享问题了
在nginx的配置文件中upstream中添加ip_hash;
linux
环境确认:可能会有影响
1、确认系统网络
2、确认yum可用
3、确认关闭iptables规则
4、确认停用selinux
ubuntu安装nginx
方法1:基于APT源安装
sudo apt-get install nginx
- /usr/sbin/nginx:主程序
- /etc/nginx:存放配置文件
- /usr/share/nginx:存放静态文件
- /var/log/nginx:存放日志
Linux系统的配置文件一般放在
/etc,日志一般放在/var/log,运行的程序一般放在/usr/sbin或者/usr/bin。
如果要更清楚Nginx的配置项放在什么地方,可以打开/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
通过这种方式安装的,会自动创建服务,会自动在/etc/init.d/nginx新建服务脚本
- 查看加载的是哪个配置文件
sudo nginx -t或者ps -ef | grep nginx
- 启动/停用服务
sudo service nginx {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|status|configtest|rotate|upgrade}
方法2:命令行+压缩文件安装
- 官方下载页面:http://nginx.org/en/download.html
- configure配置文件详解:http://nginx.org/en/docs/configure.html
- 检查Linux内核
# inux的内核版本要在2.6以上
uname -a
- 安装依赖
#1.安装gcc g++的依赖库
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt-get install libtool
#2.安装pcre依赖库([http://www.pcre.org/](http://www.pcre.org/))
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libpcre3 libpcre3-dev
#3.安装zlib依赖库([http://www.zlib.net](http://www.zlib.net/))
sudo apt-get install zlib1g-dev
#4.安装SSL依赖库(16.04默认已经安装了)
sudo apt-get install openssl
- 安装Nginx
Nginx的官网下载地址是:http://nginx.org/en/download.html ,点击进入,

#下载最新版本:复制上面的Linux的下载链接,wget下载(我当时是1.13.6版本) 进入到想要放置文件的目录
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.13.6.tar.gz
#解压:
tar -zxvf nginx-1.13.6.tar.gz
#进入解压目录:
cd nginx-1.13.6
#配置:
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx
# --with-http_stub_status_module 加入http_stub_status(用来做连接数检测)模块
# --with-http_ssl_module http_ssl(https协议)模块
# --with-debug 打开debug开关
#编译:
make
#安装:安装在/usr/local/nginx
sudo make install
#启动:
sudo /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
注意:-c 指定配置文件的路径,不加的话,nginx会自动加载默认路径的配置文件,可以通过-h查看帮助命令。
#查看进程:
ps -ef | grep nginx
配置
- 配置软链接:就可以不用路径直接输入nginx启动
sudo ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/bin/nginx
- 配置开机启动服务
在/etc/init.d/下创建nginx文件,sudo vim /etc/init.d/nginx,内容如下:
#!/bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: nginx
# Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $syslog $named
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $syslog $named
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: starts the nginx web server
# Description: starts nginx using start-stop-daemon
### END INIT INFO
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
DAEMON=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
NAME=nginx
DESC=nginx
# Include nginx defaults if available
if [ -r /etc/default/nginx ]; then
. /etc/default/nginx
fi
STOP_SCHEDULE="${STOP_SCHEDULE:-QUIT/5/TERM/5/KILL/5}"
test -x $DAEMON || exit 0
. /lib/init/vars.sh
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
# Try to extract nginx pidfile
PID=$(cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf | grep -Ev '^s*#' | awk 'BEGIN { RS="[;{}]" } { if ($1 == "pid") print $2 }' | head -n1)
if [ -z "$PID" ]; then
PID=/run/nginx.pid
fi
if [ -n "$ULIMIT" ]; then
# Set ulimit if it is set in /etc/default/nginx
ulimit $ULIMIT
fi
start_nginx() {
# Start the daemon/service
#
# Returns:
# 0 if daemon has been started
# 1 if daemon was already running
# 2 if daemon could not be started
start-stop-daemon --start --quiet --pidfile $PID --exec $DAEMON --test > /dev/null
|| return 1
start-stop-daemon --start --quiet --pidfile $PID --exec $DAEMON --
$DAEMON_OPTS 2>/dev/null
|| return 2
}
test_config() {
# Test the nginx configuration
$DAEMON -t $DAEMON_OPTS >/dev/null 2>&1
}
stop_nginx() {
# Stops the daemon/service
#
# Return
# 0 if daemon has been stopped
# 1 if daemon was already stopped
# 2 if daemon could not be stopped
# other if a failure occurred
start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet --retry=$STOP_SCHEDULE --pidfile $PID --name $NAME
RETVAL="$?"
sleep 1
return "$RETVAL"
}
reload_nginx() {
# Function that sends a SIGHUP to the daemon/service
start-stop-daemon --stop --signal HUP --quiet --pidfile $PID --name $NAME
return 0
}
rotate_logs() {
# Rotate log files
start-stop-daemon --stop --signal USR1 --quiet --pidfile $PID --name $NAME
return 0
}
upgrade_nginx() {
# Online upgrade nginx executable
# http://nginx.org/en/docs/control.html
#
# Return
# 0 if nginx has been successfully upgraded
# 1 if nginx is not running
# 2 if the pid files were not created on time
# 3 if the old master could not be killed
if start-stop-daemon --stop --signal USR2 --quiet --pidfile $PID --name $NAME; then
# Wait for both old and new master to write their pid file
while [ ! -s "${PID}.oldbin" ] || [ ! -s "${PID}" ]; do
cnt=`expr $cnt + 1`
if [ $cnt -gt 10 ]; then
return 2
fi
sleep 1
done
# Everything is ready, gracefully stop the old master
if start-stop-daemon --stop --signal QUIT --quiet --pidfile "${PID}.oldbin" --name $NAME; then
return 0
else
return 3
fi
else
return 1
fi
}
case "$1" in
start)
log_daemon_msg "Starting $DESC" "$NAME"
start_nginx
case "$?" in
0|1) log_end_msg 0 ;;
2) log_end_msg 1 ;;
esac
;;
stop)
log_daemon_msg "Stopping $DESC" "$NAME"
stop_nginx
case "$?" in
0|1) log_end_msg 0 ;;
2) log_end_msg 1 ;;
esac
;;
restart)
log_daemon_msg "Restarting $DESC" "$NAME"
# Check configuration before stopping nginx
if ! test_config; then
log_end_msg 1 # Configuration error
exit $?
fi
stop_nginx
case "$?" in
0|1)
start_nginx
case "$?" in
0) log_end_msg 0 ;;
1) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Old process is still running
*) log_end_msg 1 ;; # Failed to start
esac
;;
*)
# Failed to stop
log_end_msg 1
;;
esac
;;
reload|force-reload)
log_daemon_msg "Reloading $DESC configuration" "$NAME"
# Check configuration before stopping nginx
#
# This is not entirely correct since the on-disk nginx binary
# may differ from the in-memory one, but that's not common.
# We prefer to check the configuration and return an error
# to the administrator.
if ! test_config; then
log_end_msg 1 # Configuration error
exit $?
fi
reload_nginx
log_end_msg $?
;;
configtest|testconfig)
log_daemon_msg "Testing $DESC configuration"
test_config
log_end_msg $?
;;
status)
status_of_proc -p $PID "$DAEMON" "$NAME" && exit 0 || exit $?
;;
upgrade)
log_daemon_msg "Upgrading binary" "$NAME"
upgrade_nginx
log_end_msg $?
;;
rotate)
log_daemon_msg "Re-opening $DESC log files" "$NAME"
rotate_logs
log_end_msg $?
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $NAME {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|status|configtest|rotate|upgrade}" >&2
exit 3
;;
esac
- 设置服务脚本有执行权限
sudo chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
- 注册服务
cd /etc/init.d/
sudo update-rc.d nginx defaults
- 启动/停用服务
sudo service nginx {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|status|configtest|rotate|upgrade}
修改端口
nginx默认使用的端口是80,如果端口已经被占据,那么需要修改默认端口!默认的配置在安装文件夹下的conf文件夹下的ngixn.conf文件中,目录为 /usr/local/nginx/conf
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/ngixn.conf
# 将 server中的listen 中对应的就是端口号了
比如,改为8080

常用命令
- 启动方式
#默认方式启动:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
#指定配置文件启动
/usr/local/nginx/sbing/nginx -c /tmp/nginx.conf
##-c 指定配置文件的路径,不加的话,nginx会自动加载默认路径的配置文件,可以通过-h查看帮助命令。
#指定nginx程序目录启动
/usr/local/nginx /sbin/nginx -p /usr/local/nginx/
- 停止方式
#快速停止
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
#优雅停止
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
- 热装载配置文件 ,不用停止可以刷新配置
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
- 重新打开日志文件
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reopen
- 检测当前使用的是哪个配置文件,配置是否正确
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #可以在配置文件加点乱码测试一下
日志切割备份
默认日志是在/usr/local/nginx/logs/文件夹中,默认写在access.log 中
mv access.log access.log.bak
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reopen # 重新打开日志文件,写入新文件中(若是不运行一下,写入的还是旧文件,就是上面的.bat的文件)
centos安装
预处理:
关闭iptables:
iptables -L #查看是否开启
iptables -F #关闭
iptables -t nat -L #查看net中是否有规则
iptables -t nat -F #关闭nat规则
停用selinux:
getenforce #查看是否关闭 disabled 代表关闭了
setenforce 0 #关闭
安装
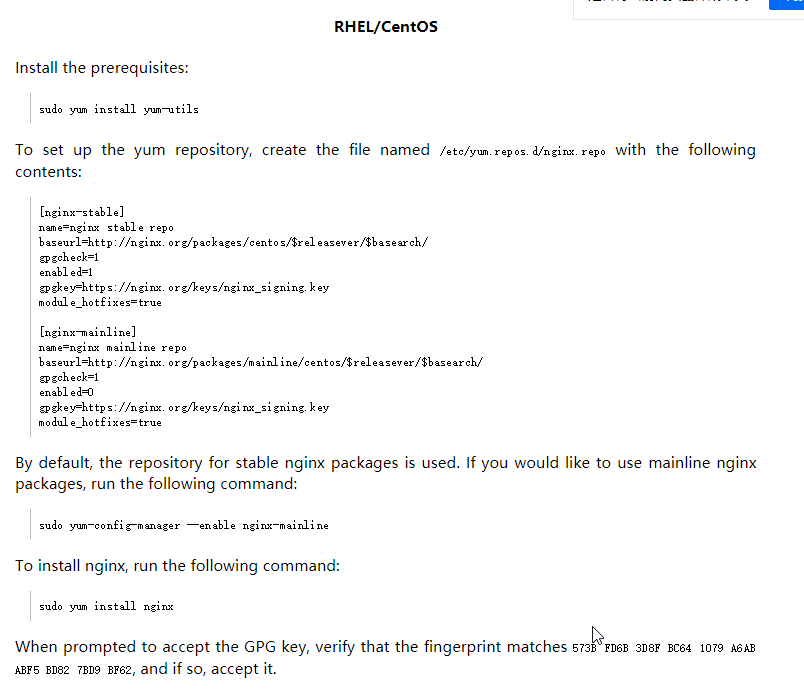
在http://nginx.org/en/download.html 的Pre-Built Packages的stable and mainline连接进入就可以看到官方提供的yum的安装方法.此处使用的是RHEL/CentOS的安装方法
#yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ autoconf pcre pcre-devel make automake
# yum -y install wget httpd-tools vim
# 首先运行
sudo yum install yum-utils
# 创建一个nginx的配置文件
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
# 配置
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
[nginx-mainline]
name=nginx mainline repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/centos/$releasever/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
# 获取所有的版本
sudo yum list | grep nginx
# 下载最新稳定版
sudo yum install nginx
# 查看安装版本
nginx -v
# 查看编译参数
nginx -V

Linux上搭建Nginx+Tomcat集群:
在Linux上安装多个Tomcat:
- 解压tomcat
分别解压tomcat到/usr/local/tomcat1 和 tomcat2 - 修改tomcat2中server.xml:
将修改后的端口添加到防火墙中. - Linux上安装Nginx:
1.先将 nginx上传到linux上
2.解压nginx(放在usr/local中 或放在自己建立的software中)
tar -xvf 文件;
3.进入目录 cd xxx
4.安装依赖包
yum install gcc-c++
yum install -y pcre pcre-devel
yum install -y zlib zlib-devel
yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
5.执行编译
先进入 nginx的目录
执行 ./configure
可以通过在upstream下设置一个ip_hash解决session共享问题
ip_hash指令能够将某个客户端IP的请求通过哈希算法定位到同一台后端服务器上
启动
在nginx目录下有一个sbin目录,sbin目录下有一个nginx可执行程序。
./nginx


关闭nginx
关闭命令:相当于找到nginx进程kill。
./nginx -s stop
退出命令:等程序执行完毕后关闭,建议使用此命令。
./nginx -s quit
动态加载配置文件
可以不关闭nginx的情况下更新配置文件。
./nginx -s reload
docker安装nginx
version: '3.6'
services:
nginx:
restart: always
image: daocloud.io/library/nginx:latest #镜像
container_name: nginx # 容器名
ports:
- 80:80
- 进入文件夹
/opt/docker_nginx/docker-compose.yml,将上面的内容复制进去 - 运行
docker-compose up -d - 打开浏览器,访问这个服务器的80端口,就能进入docker的首页
nginx配置
默认在容器的
/etc/nginx中
- 进入nginx容器:
docker exec -it nginx bash - 进入:
cd /etc/nginx - 打开配置文件:
cat nginx.conf
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf文件
user nginx;
worker_processes 1; # worker_processes的值越大,Nginx的并发能力越强
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn; # 代表nginx的错误日志存放的位置
pid /var/run/nginx.pid; # nginx运行的标志
# 以上统称为全局块,
events { # events块
worker_connections 1024; # worker_connections数值越大,nginx并发能力越强
}
http { # http块
include /etc/nginx/mime.types; #include代表引入一个外部的文件 ->mime.types中放着大量的媒体类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; # 引入了conf.d目录下的以.conf为结尾的配置文件,在整个http块中,主要关注这个就够了,后期主要就是在编写这个目录下的配置文件
}
/etc/nginx/conf.d/defualt.conf文件
这个文件是在http快中引入的,相当于在nginx.conf文件中替换了http中的include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {# server块
listen 80; # 代表nginx监听的端口号
listen [::]:80;
server_name localhost;
location / { # 代表nginx接收请求的ip
root /usr/share/nginx/html; # 将接收到的请求根据/usr/share/nginx/html去查找静态资源
index index.html index.htm; # 默认去上述的路径中找到index.html 或index.htm文件
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
}
真正要关注的是nginx.conf中http块中的include中的/etc/nginx/conf.d/中的所有的conf文件的server块
修改安装nginx的docker-compose.yml文件
version: '3.6'
services:
nginx:
restart: always
image: daocloud.io/library/nginx:latest #镜像
container_name: nginx # 容器名
ports:
- 80:80
volumes: #映射文件,
- /opt/docker_nginx/conf.d/:/etc/nginx/conf.d/ # 将配置文件映射到宿主机上...我个人是在/data/dockerdata/docker-compose-data/docker_nginx/conf.d
操作
exit # 退出nginx容器
#进入nginx的docker-compose.yml的路径
docker-compose down
vim docker-compose.yml 修改docker-compose.yml
# 将上面的配置写入
#保存文件
docker-compose build #重新构建
docker-compose up -d
# 启动之后,在当前路径下就创建了一个conf.d文件夹
现在访问nginx页面,会进不去,因为在conf.d文件夹下没有默认配置,找不到对应的配置
创建默认conf配置
进入conf.d文件夹
运行 vi defualt.conf,编写文件 # 默认没有vim
server {# server块
listen 80; # 代表nginx监听的端口号
server_name localhost;
location / { # 代表nginx接收请求的ip
root /usr/share/nginx/html; # 将接收到的请求根据/usr/share/nginx/html去查找静态资源
index index.html index.htm; # 默认去上述的路径中找到index.html 或index.htm文件
}
}
保存文件
返回 docker-compose.yml文件夹
运行 docker-compose restart