1.在配置文件里配置Bean时,有时需要在Bean的配置里混入系统部署的细节信息(如:文件路径,数据源配置信息等)。而这些部署细节实际上需要和Bean配置相分离。
2.Spring提供了一个PropertyPlacehoiderConfigurer的BeanFactory后置处理器,这个处理器允许用户将Bean配置的部分内容外移到属性文件中。可以在Bean配置文件里使用形式为${var}的变量,PropertyPlacehoiderConfigurer从属性文件里加载属性,并使用这些属性来替换变量。
3.Spring还允许在属性文件中使用${propName},以实现属性之间的相互引用。
如:
beans-properties.xml:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> 7 8 <!-- 导入属性文件 --> 9 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> 10 11 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"> 12 <!-- 使用外部化属性文件的属性 --> 13 <property name="user" value="${user}"></property> 14 <property name="password" value="${password}"></property> 15 <property name="driverClass" value="${driverClass}"></property> 16 <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbcUrl}"></property> 17 </bean> 18 </beans>
注意:要导入context命名空间。
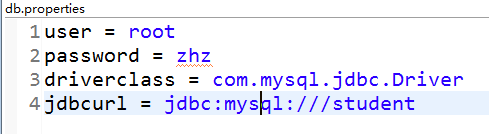
db.properties: