spark架构原理

原理图:

创建RDD
一是使用程序中的集合创建RDD,主要用于进行测试,可以实际部署到集群运行之前,
自己使用集合构造测试数据,来测试后面的spark应用的流程;
二是使用本地文件创建RDD,主要用于的场景为在本地临时性地处理一些存储了大量数据的文件;
三是使用HDFS文件创建RDD,主要用于针对HDFS上存储的大数据,进行离线批处理操作
操作RDD
转化操作:

行为操作:

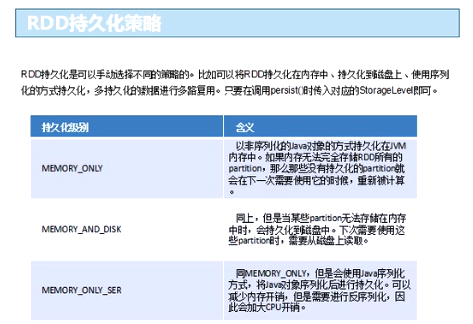
RDD持久化
为什么要执行RDD持久化?

RDD持久化策略是什么?
Spark内核源码深度剖析

原理图:
宽依赖和窄依赖
基于yarn的两种提交模式
sparkcontext原理剖析

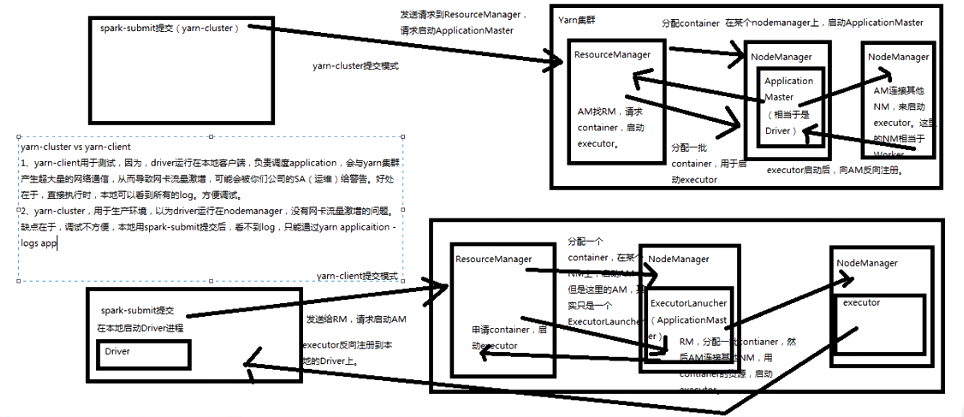
master原理剖析与源码分析

资源调度机制十分重要(两种资源调度机制)
主备切换机制原理图:

注册机制原理图:
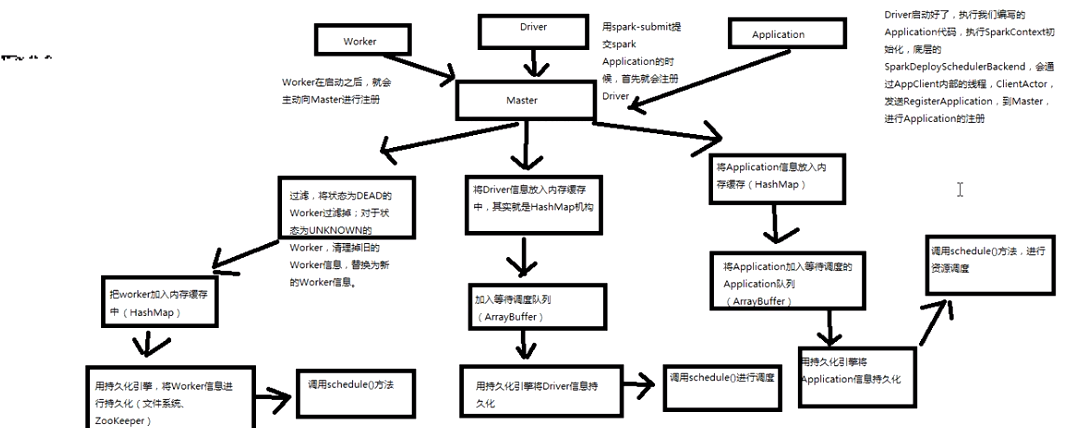
master资源调度算法原理:
master是通过schedule方法进行资源调度,告知worker启动executor,,,
1,schedule方法

2,startExecutorOnWorkers在woker上开启executor进程

3, scheduleExecutorsOnWorker在每一个worker上调度资源
判断该worker能否分配一个或者多个executor,能则分配相应的executor所需要的CPU核数;
4, allocateWorkerResourceToExecutor在worker上分配的具体资源

五、launchDriver发起driver
六、launchExecutor发起executor
worker原理剖析:

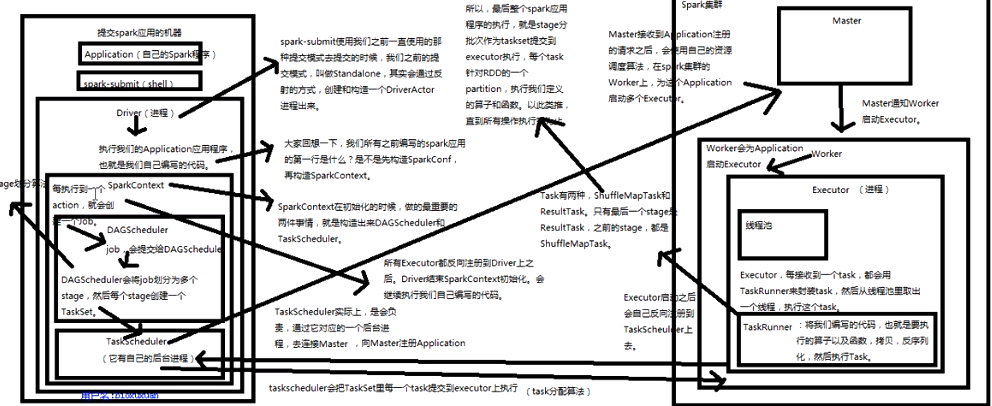
job触发流程原理剖析:
其实最终是调用了SparkContext之前初始化时创建的DAGSchdule的runjob方法;
DAGSchdule原理剖析:
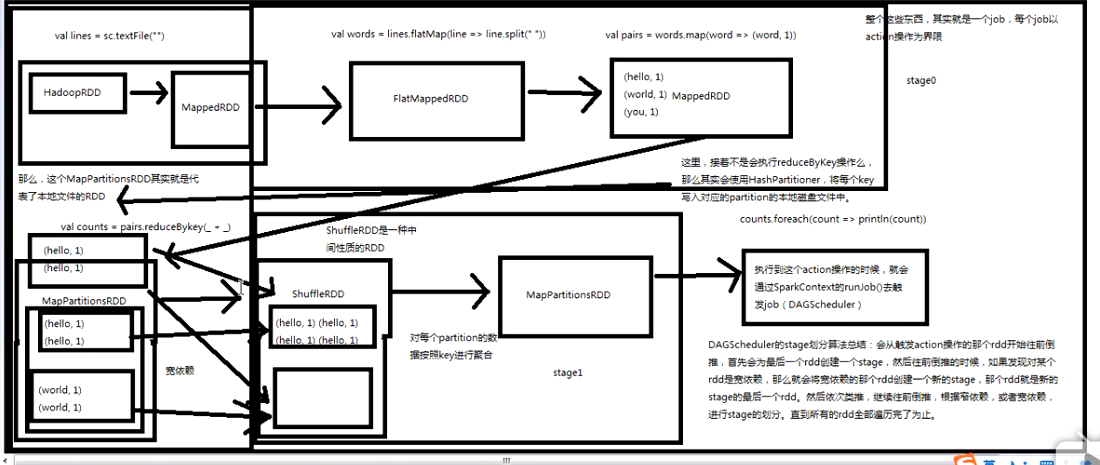
注:reduceByKey的作用就是对相同key的数据进行处理,最终每个key只保留一条记录;
其作用对象是(key, value)形式的RDD;
Taskschedule原理分析

注:本地化级别种类:
PROCESS_LOCAL:进程本地化,rdd和partition和task在同一个executor中;
NODE_LOCAL:rdd的parttion和task,不在一个同一个executor中,但在同一个节点中;
NO_PREF:没有本地化级别;
RACK_LOCAL:机架本地化,至少rdd的parttion和task在一盒机架中;
ANY:任意本地化级别;
Executor原理剖析与源码分析
1、work为application启动的executor,实际上是启动了CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend进程;

2、获取driver的actor,向driver发送RegisterExecutor信息

3、dirver注册executor成功之后,会发送RegisteredExecutor信息
(此时CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend会创建Executor执行句柄,大部分功能都是通过Executor实现的)

4、启动task,反序列化task,调用Executor执行器的launchTask()启动一个task;

5、对每个task都会创建一个TaskRunner,将TaskRunner放入内存缓存中;
(将task封装在一个线程TaskRunner),将线程丢入线程池中,然后执行线程池是自动实现了排队机制的

Task原理剖析

1、task是封装在一个线程中(taskRunner)

2、调用run(),对序列化的task数据进行反序列化,然后通过通络通信,将需要的文件,资源,jar文件拷贝过来,
通过反序列化操作,调用updateDependencies() 将整个Task数据反序列化回来;
1 <span style="font-size:14px;">override def run(): Unit = { 2 val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean 3 val taskMemoryManager = new TaskMemoryManager(env.memoryManager, taskId) 4 val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis() 5 val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { 6 threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime 7 } else 0L 8 Thread.currentThread.setContextClassLoader(replClassLoader) 9 val ser = env.closureSerializer.newInstance() 10 logInfo(s"Running $taskName (TID $taskId)") 11 execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.RUNNING, EMPTY_BYTE_BUFFER) 12 var taskStart: Long = 0 13 var taskStartCpu: Long = 0 14 startGCTime = computeTotalGcTime() 15 16 try { 17 //对序列化的task数据进行反序列化 18 val (taskFiles, taskJars, taskProps, taskBytes) = 19 Task.deserializeWithDependencies(serializedTask) 20 21 // Must be set before <span style="color:#ff0000;">updateDependencies</span>() is called, in case fetching dependencies 22 // requires access to properties contained within (e.g. for access control). 23 Executor.taskDeserializationProps.set(taskProps) 24 //然后通过网络通信,将需要的文件,资源呢、jar拷贝过来 25 updateDependencies(taskFiles, taskJars) 26 //通过反序列化操作,将整个Task的数据反序列化回来 27 task = ser.deserialize[Task[Any]](taskBytes, Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) 28 task.localProperties = taskProps 29 task.setTaskMemoryManager(taskMemoryManager) 30 31 // If this task has been killed before we deserialized it, let's quit now. Otherwise, 32 // continue executing the task. 33 if (killed) { 34 // Throw an exception rather than returning, because returning within a try{} block 35 // causes a NonLocalReturnControl exception to be thrown. The NonLocalReturnControl 36 // exception will be caught by the catch block, leading to an incorrect ExceptionFailure 37 // for the task. 38 throw new TaskKilledException 39 } 40 41 logDebug("Task " + taskId + "'s epoch is " + task.epoch) 42 env.mapOutputTracker.updateEpoch(task.epoch) 43 44 // Run the actual task and measure its runtime. 45 //计算task的开始时间 46 taskStart = System.currentTimeMillis() 47 taskStartCpu = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { 48 threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime 49 } else 0L 50 var threwException = true 51 val value = try { 52 调用task的run() 53 val res = task.run( 54 taskAttemptId = taskId, 55 attemptNumber = attemptNumber, 56 metricsSystem = env.metricsSystem) 57 threwException = false 58 res 59 } finally { 60 val releasedLocks = env.blockManager.releaseAllLocksForTask(taskId) 61 val freedMemory = taskMemoryManager.cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory() 62 63 if (freedMemory > 0 && !threwException) { 64 val errMsg = s"Managed memory leak detected; size = $freedMemory bytes, TID = $taskId" 65 if (conf.getBoolean("spark.unsafe.exceptionOnMemoryLeak", false)) { 66 throw new SparkException(errMsg) 67 } else { 68 logWarning(errMsg) 69 } 70 } 71 72 if (releasedLocks.nonEmpty && !threwException) { 73 val errMsg = 74 s"${releasedLocks.size} block locks were not released by TID = $taskId: " + 75 releasedLocks.mkString("[", ", ", "]") 76 if (conf.getBoolean("spark.storage.exceptionOnPinLeak", false)) { 77 throw new SparkException(errMsg) 78 } else { 79 logWarning(errMsg) 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 val taskFinish = System.currentTimeMillis() 84 val taskFinishCpu = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { 85 threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime 86 } else 0L 87 88 // If the task has been killed, let's fail it. 89 if (task.killed) { 90 throw new TaskKilledException 91 } </span> 92
3、updateDependencies() 主要是获取hadoop的配置文件,使用了java的synchronized多线程访问方式,
task是以java线程的方式,在一个CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend进程内并发运行的,因此在执行一些业务逻辑
的时候,需要访问一些共享资源,就会出现多线程并发访问的安全问题;
1 <span style="font-size:14px;"> private def updateDependencies(newFiles: HashMap[String, Long], newJars: HashMap[String, Long]) { 2 //获取hadoop的配置文件 3 lazy val hadoopConf = SparkHadoopUtil.get.newConfiguration(conf) 4 //使用了java的synchronized多线程并发访问方式 5 //task是以java线程的方式,在一个CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend进程内并发运行的 6 //因此在执行一些业务逻辑的时候,需要访问一些共享资源,就会出现多线程并发访问安全问题 7 synchronized { 8 // Fetch missing dependencies 9 //遍历要拉取的文件 10 for ((name, timestamp) <- newFiles if currentFiles.getOrElse(name, -1L) < timestamp) { 11 logInfo("Fetching " + name + " with timestamp " + timestamp) 12 // Fetch file with useCache mode, close cache for local mode. 13 //通过Utils的fetchFile(),通过网络通信,从远程拉取文件 14 Utils.fetchFile(name, new File(SparkFiles.getRootDirectory()), conf, 15 env.securityManager, hadoopConf, timestamp, useCache = !isLocal) 16 currentFiles(name) = timestamp 17 } 18 //遍历要拉取得jar 19 for ((name, timestamp) <- newJars) { 20 val localName = name.split("/").last 21 val currentTimeStamp = currentJars.get(name) 22 .orElse(currentJars.get(localName)) 23 .getOrElse(-1L) 24 if (currentTimeStamp < timestamp) { 25 logInfo("Fetching " + name + " with timestamp " + timestamp) 26 // Fetch file with useCache mode, close cache for local mode. 27 Utils.fetchFile(name, new File(SparkFiles.getRootDirectory()), conf, 28 env.securityManager, hadoopConf, timestamp, useCache = !isLocal) 29 currentJars(name) = timestamp 30 // Add it to our class loader 31 val url = new File(SparkFiles.getRootDirectory(), localName).toURI.toURL 32 if (!urlClassLoader.getURLs().contains(url)) { 33 logInfo("Adding " + url + " to class loader") 34 urlClassLoader.addURL(url) 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 } </span> 40
4、task的run方法,创建了Taskcontext,里面记录了task的一些全局性的数据,还包括task重试了几次,task属于
哪个stage,task处理的是rdd的哪个parttion,然后调用抽象方法runTask();
1 <span style="font-size:14px;">final def run( 2 taskAttemptId: Long, 3 attemptNumber: Int, 4 metricsSystem: MetricsSystem): T = { 5 SparkEnv.get.blockManager.registerTask(taskAttemptId) 6 //创建了Taskcontext,里面记录了task的一些全局性的数据 7 //包括task重试了几次,task属于哪个stage,task处理的是rdd的哪个partition 8 context = new TaskContextImpl( 9 stageId, 10 partitionId, 11 taskAttemptId, 12 attemptNumber, 13 taskMemoryManager, 14 localProperties, 15 metricsSystem, 16 metrics) 17 TaskContext.setTaskContext(context) 18 taskThread = Thread.currentThread() 19 20 if (_killed) { 21 kill(interruptThread = false) 22 } 23 24 new CallerContext("TASK", appId, appAttemptId, jobId, Option(stageId), Option(stageAttemptId), 25 Option(taskAttemptId), Option(attemptNumber)).setCurrentContext() 26 27 try { 28 //调用抽象方法runTask() 29 runTask(context) 30 } catch { 31 case e: Throwable => 32 // Catch all errors; run task failure callbacks, and rethrow the exception. 33 try { 34 context.markTaskFailed(e) 35 } catch { 36 case t: Throwable => 37 e.addSuppressed(t) 38 } 39 throw e 40 } finally { 41 // Call the task completion callbacks. 42 context.markTaskCompleted() 43 try { 44 Utils.tryLogNonFatalError { 45 // Release memory used by this thread for unrolling blocks 46 SparkEnv.get.blockManager.memoryStore.releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask(MemoryMode.ON_HEAP) 47 SparkEnv.get.blockManager.memoryStore.releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask(MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP) 48 // Notify any tasks waiting for execution memory to be freed to wake up and try to 49 // acquire memory again. This makes impossible the scenario where a task sleeps forever 50 // because there are no other tasks left to notify it. Since this is safe to do but may 51 // not be strictly necessary, we should revisit whether we can remove this in the future. 52 val memoryManager = SparkEnv.get.memoryManager 53 memoryManager.synchronized { memoryManager.notifyAll() } 54 } 55 } finally { 56 TaskContext.unset() 57 } 58 } 59 }</span> 60
5、抽象方法runTask(),需要Task的子类去实现,ShuffleMapTask、ResaultTask;
1 <span style="font-size:14px;">def runTask(context: TaskContext): T</span>
6、一个ShuffleMapTask会将一个个Rdd元素切分为多个bucket基于在一个ShuffleDependency的中指定的partitioner,
1 <span style="font-size:14px;">private[spark] class ShuffleMapTask( 2 stageId: Int, 3 stageAttemptId: Int, 4 taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]], 5 partition: Partition, 6 @transient private var locs: Seq[TaskLocation], 7 metrics: TaskMetrics, 8 localProperties: Properties, 9 jobId: Option[Int] = None, 10 appId: Option[String] = None, 11 appAttemptId: Option[String] = None) 12 extends Task[MapStatus](stageId, stageAttemptId, partition.index, metrics, localProperties, jobId, 13 appId, appAttemptId) 14 with Logging</span>
7、runTask有MapStatus返回值,对task要处理的数据做一些反序列化操作,然后通过广播变量拿到要处理rdd那部分
数据,获取shuffleManager,调用rdd的iterator(),并且传入了当前要执行的哪个parttion,rdd的iterator(),实现
了针对rdd的某个parttion执行我们定义的算子,之后返回的数据通过ShuffleWriter,经过Hashpartioner后,写入自己对应
bucket中,最后返回mapstatus,里面封装了计算后的数据,存储在Blockmanager中;
1 <span style="font-size:14px;">override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = { 2 // Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable. 3 val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean 4 val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis() 5 val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { 6 threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime 7 } else 0L 8 //对task要处理的数据做一些反序列化操作 9 //通过广播变量拿到要处理的rdd那部分数据 10 val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance() 11 val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])]( 12 ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) 13 _executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime 14 _executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { 15 threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime 16 } else 0L 17 18 var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null 19 try { 20 //获取shuffleManager 21 val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager 22 //从shuffleManager中获取writer 23 writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context) 24 //调用了rdd的iterator(),并且传入了当前要执行的哪个partition 25 //rdd的iterator(),实现了针对rdd的某个parttion执行我们自己定义的算子 26 //执行完我们自己定义的算子,返回的数据通过ShuffleWriter,经过Hashpartioner后,写入自己对应的分区bucket中 27 writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]]) 28 //最后返回MapStatus,里面封装了计算后的数据,存储在Blockmanager中 29 writer.stop(success = true).get 30 } catch { 31 case e: Exception => 32 try { 33 if (writer != null) { 34 writer.stop(success = false) 35 } 36 } catch { 37 case e: Exception => 38 log.debug("Could not stop writer", e) 39 } 40 throw e 41 } 42 } </span>
8、MapPartitionsRDD
针对RDD的某个partition,执行我们给定的算子或者函数;
(注:可以理解成自己定义的算子或者函数,spark对其进行了封装,这里针对rdd的parttion,执行自定义的计算
操作,并返回新的rdd的parttion的数据)
1 <span style="font-size:14px;">private[spark] class MapPartitionsRDD[U: ClassTag, T: ClassTag]( 2 var prev: RDD[T], 3 f: (TaskContext, Int, Iterator[T]) => Iterator[U], // (TaskContext, partition index, iterator) 4 preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false) 5 extends RDD[U](prev) { 6 7 override val partitioner = if (preservesPartitioning) firstParent[T].partitioner else None 8 9 override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = firstParent[T].partitions 10 //针对rdd的某个partiton,执行我们给定的算子或者函数 11 //f:可以理解成自己定义的算子或者函数,spark内部进行了封装 12 //这里针对rdd的partition,执行自定义的计算操作,并返回 新的rdd的partition的数据 13 override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[U] = 14 f(context, split.index, firstParent[T].iterator(split, context)) 15 16 override def clearDependencies() { 17 super.clearDependencies() 18 prev = null 19 } 20 }</span>
9、statusUpdate()是个抽象方法
1 <span style="font-size:14px;">execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FINISHED, serializedResult) 2 // statusUpdate 3 override def statusUpdate(taskId: Long, state: TaskState, data: ByteBuffer) { 4 val msg = StatusUpdate(executorId, taskId, state, data) 5 driver match { 6 case Some(driverRef) => driverRef.send(msg) 7 case None => logWarning(s"Drop $msg because has not yet connected to driver") 8 } 9 } </span>
10、调用TaskSchedulerImpl的statusUpdate(),获取对应的taskset,task结束了,从内存移除;
1 <span style="font-size:14px;">def statusUpdate(tid: Long, state: TaskState, serializedData: ByteBuffer) { 2 var failedExecutor: Option[String] = None 3 var reason: Option[ExecutorLossReason] = None 4 synchronized { 5 try { 6 taskIdToTaskSetManager.get(tid) match { 7 获取对应的taskSet 8 case Some(taskSet) => 9 if (state == TaskState.LOST) { 10 // TaskState.LOST is only used by the deprecated Mesos fine-grained scheduling mode, 11 // where each executor corresponds to a single task, so mark the executor as failed. 12 val execId = taskIdToExecutorId.getOrElse(tid, throw new IllegalStateException( 13 "taskIdToTaskSetManager.contains(tid) <=> taskIdToExecutorId.contains(tid)")) 14 if (executorIdToRunningTaskIds.contains(execId)) { 15 reason = Some( 16 SlaveLost(s"Task $tid was lost, so marking the executor as lost as well.")) 17 removeExecutor(execId, reason.get) 18 failedExecutor = Some(execId) 19 } 20 } 21 if (TaskState.isFinished(state)) { 22 //task结束了从内存中移除 23 cleanupTaskState(tid) 24 taskSet.removeRunningTask(tid) 25 if (state == TaskState.FINISHED) { 26 taskResultGetter.enqueueSuccessfulTask(taskSet, tid, serializedData) 27 } else if (Set(TaskState.FAILED, TaskState.KILLED, TaskState.LOST).contains(state)) { 28 taskResultGetter.enqueueFailedTask(taskSet, tid, state, serializedData) 29 } 30 } 31 case None => 32 logError( 33 ("Ignoring update with state %s for TID %s because its task set is gone (this is " + 34 "likely the result of receiving duplicate task finished status updates) or its " + 35 "executor has been marked as failed.") 36 .format(state, tid)) 37 } 38 } catch { 39 case e: Exception => logError("Exception in statusUpdate", e) 40 } 41 } 42 // Update the DAGScheduler without holding a lock on this, since that can deadlock 43 if (failedExecutor.isDefined) { 44 assert(reason.isDefined) 45 dagScheduler.executorLost(failedExecutor.get, reason.get) 46 backend.reviveOffers() 47 } 48 } </span>
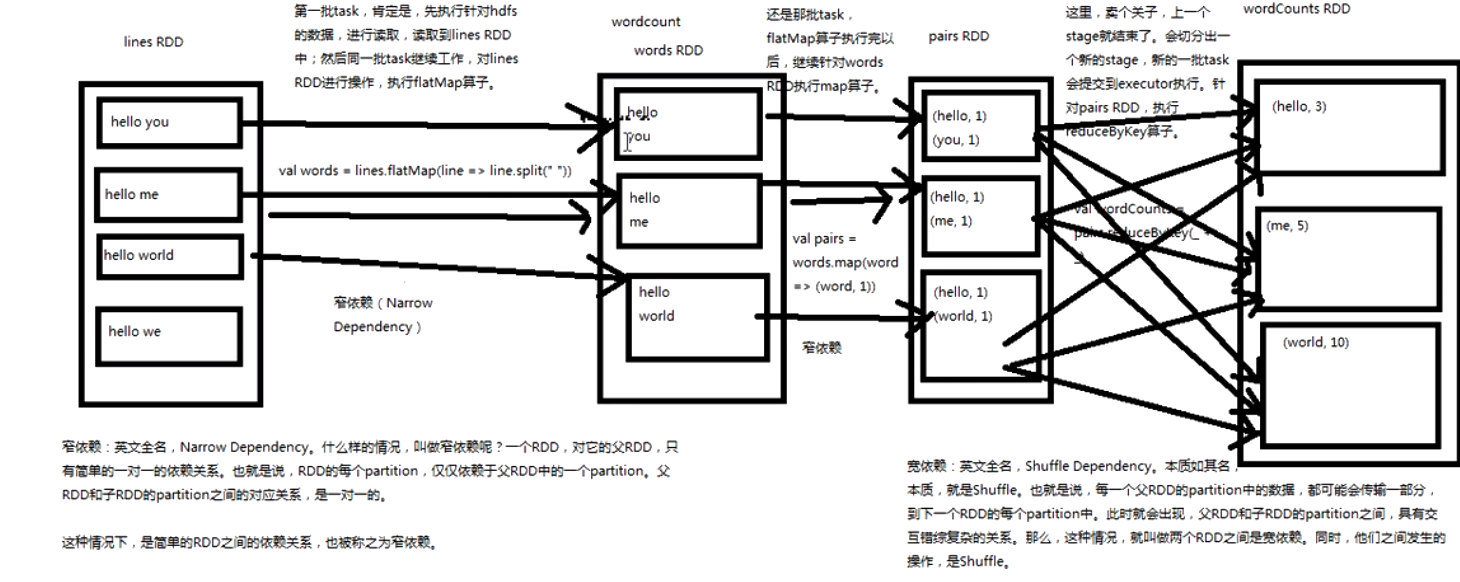
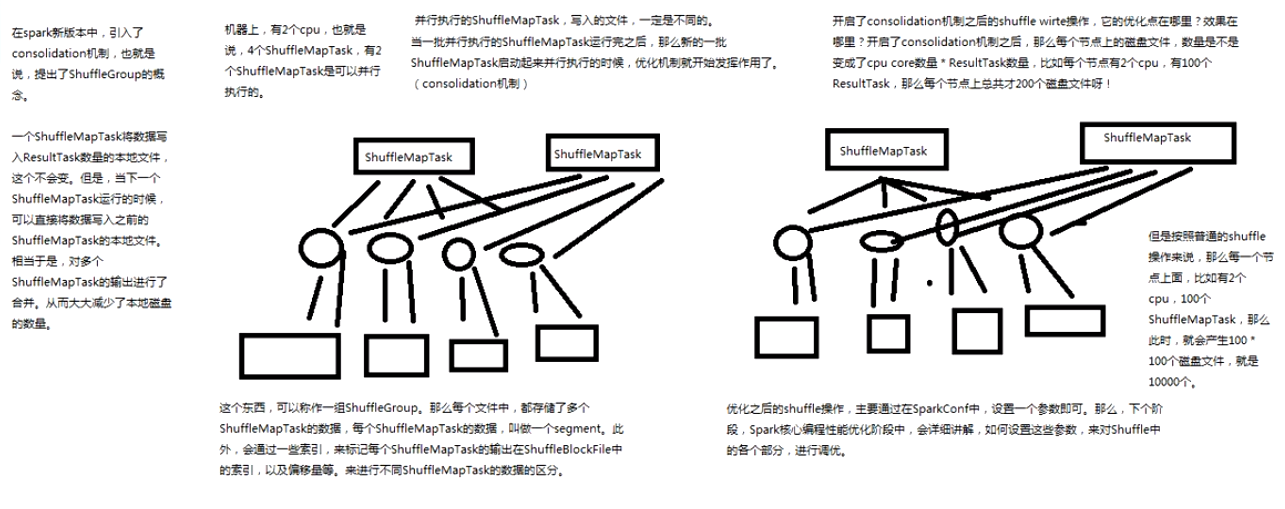
普通Shuffle操作的原理剖析

(注:什么是shuffle过程,它分为map中的和reduce中的
首先看map中的:

再看reduce端的shuffle
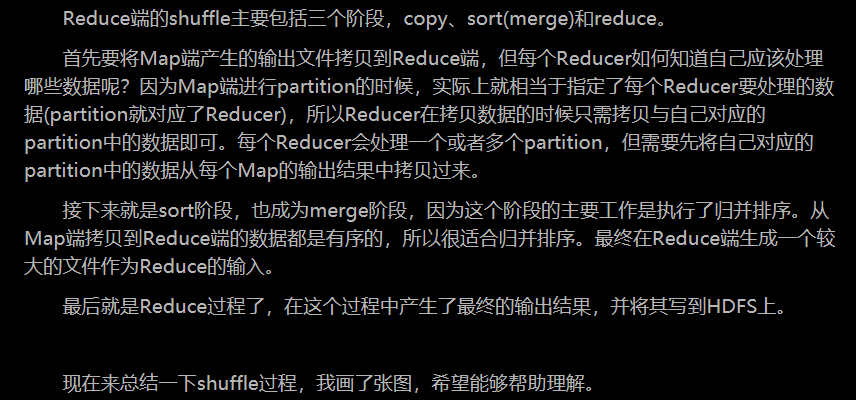
shuffle的过程:
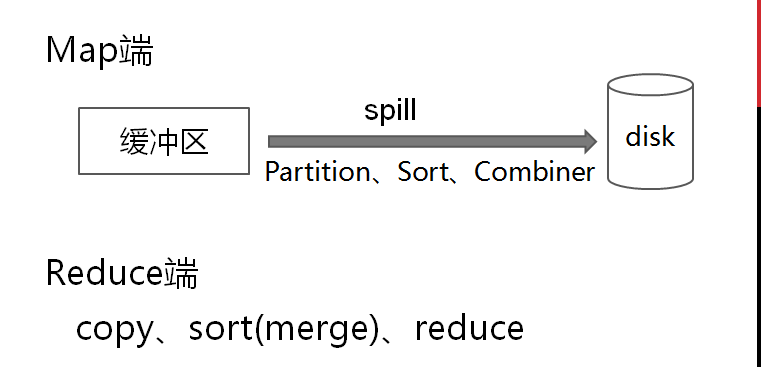
优化过后的shuffle操作的原理剖析
BlockManager原理剖析:
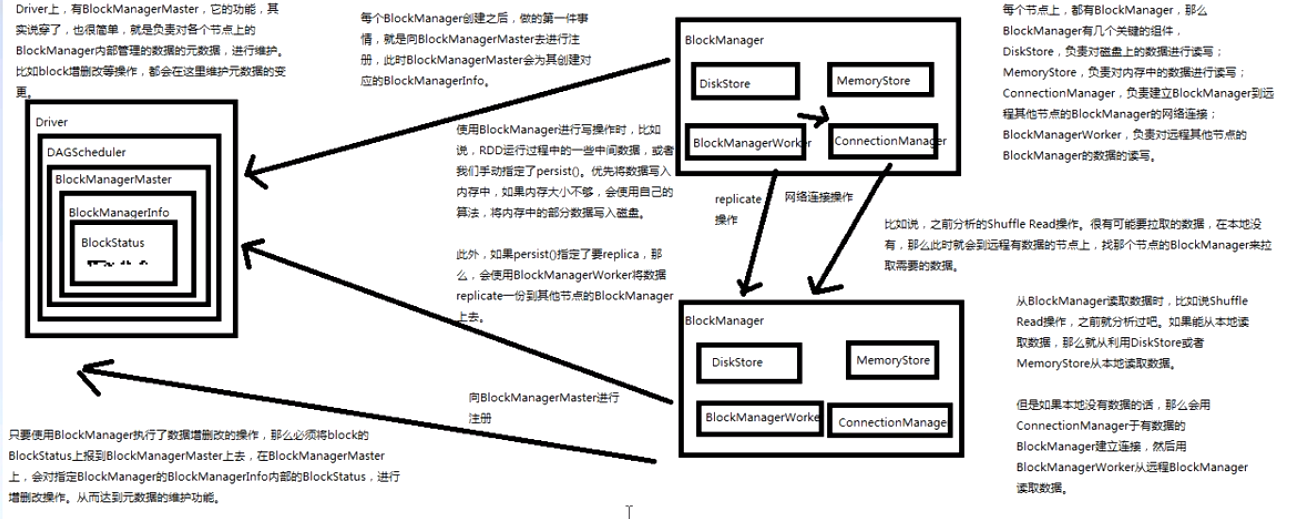
1、Diver上有BlockManagerMaster,负责对各个节点上的BlockManager内部管理的元数据进行维护;
2、每个节点的BlockManager有几个关键组件,DiskStore负责对磁盘上的数据进行读写,MemoryStore负责对内存中的数据进行读写,ConnectionManager负责建立BlockManager到远程其他节点的
BlockManager的网络连接,BlockTransferService负责对远程其他节点的BlockManager数据读写;
3、每个BlockManager创建之后,会向BlockManangerMaster进行注册,BlockManagerMaster会为其创建对应的BlockManagerInfo;
4、BlockManager进行读写时,比如RDD运行过程中的一些中间数据,或者指定的persist(),会优先将数据写入内存,如果内存大小不够,再将内存部分数据写入磁盘;
5、如果persist() 指定了要replica,那么会使用BlockTransferService将数据replica一份到其他节点的BlockManager上去;
6、BlockManager进行读操作时,就会用ConnectionManager与有数据的BlockManager建立连接,然后用BlockTransferService从远程BlockManager读写数据;
7、只要使用了BlockManager执行了数据增删改的操作,那么就必须将block的BlockStatus上报到BlockManagerInfo内部的BlockStatus进行增删改操作,从而对元数据进行维护;
cacheManager原理剖析:
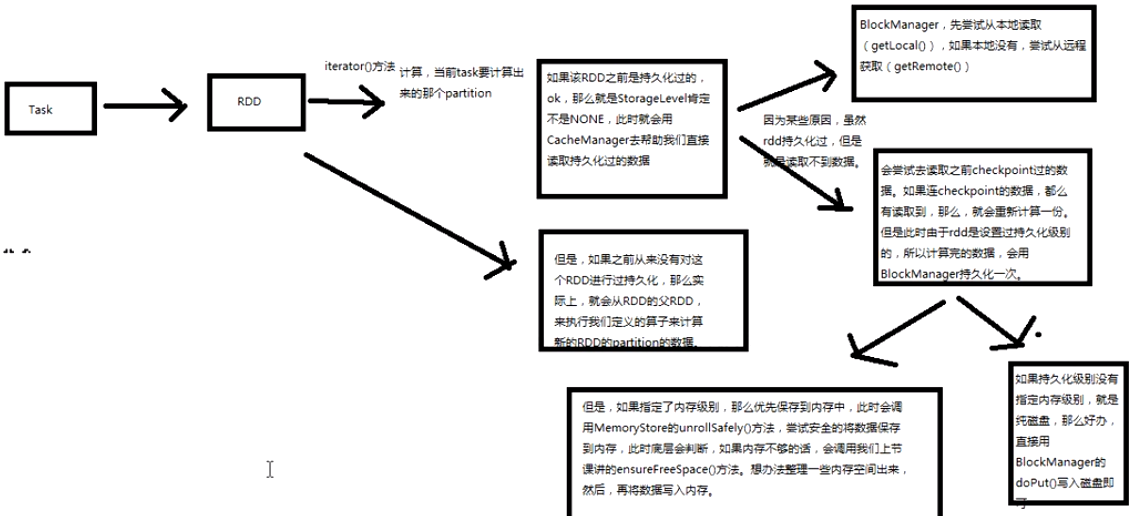
CacheManager 源码解析 :
1、cacheManager管理的是缓存中的数据,缓存可以是基于内存的缓存,也可以是基于磁盘的缓存;
2、cacheManager需要通过BlockManager 来操作数据;
3、每当Task运行的时候回调用RDD的compute方法进行计算,而compute方法会调用iterator方法;
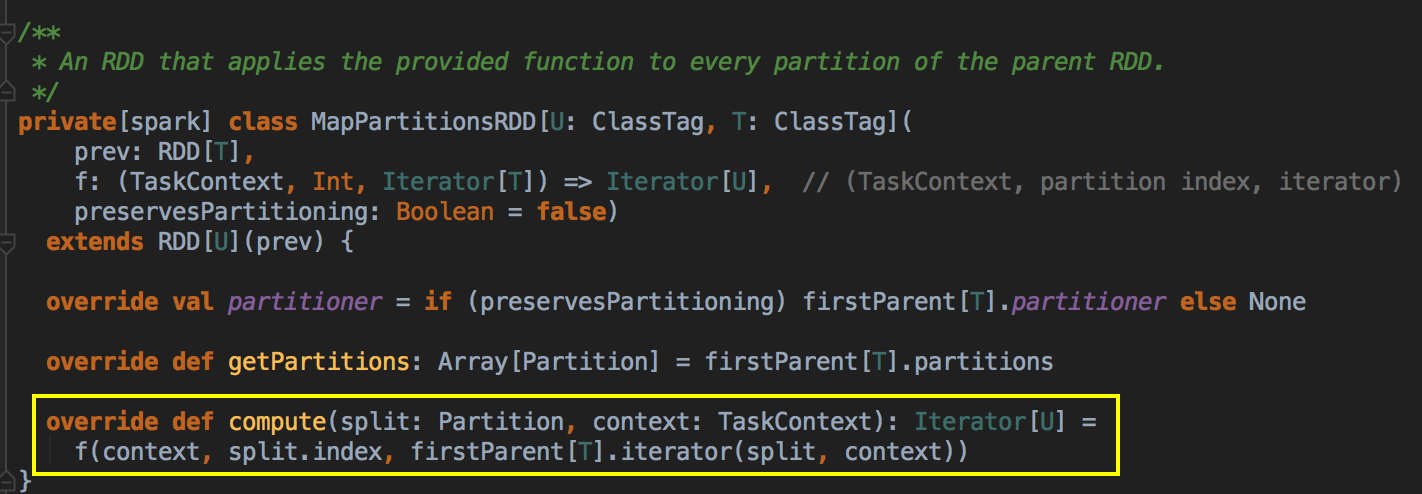
compute方法是final级别不能覆写但可以被子类去使用,可以看见RDD是优先使用内存的,如果存储级别
不等于NONE的情况下,程序会先找CacheManager 获得数据,否则的话会看有没有进行checkpoint;

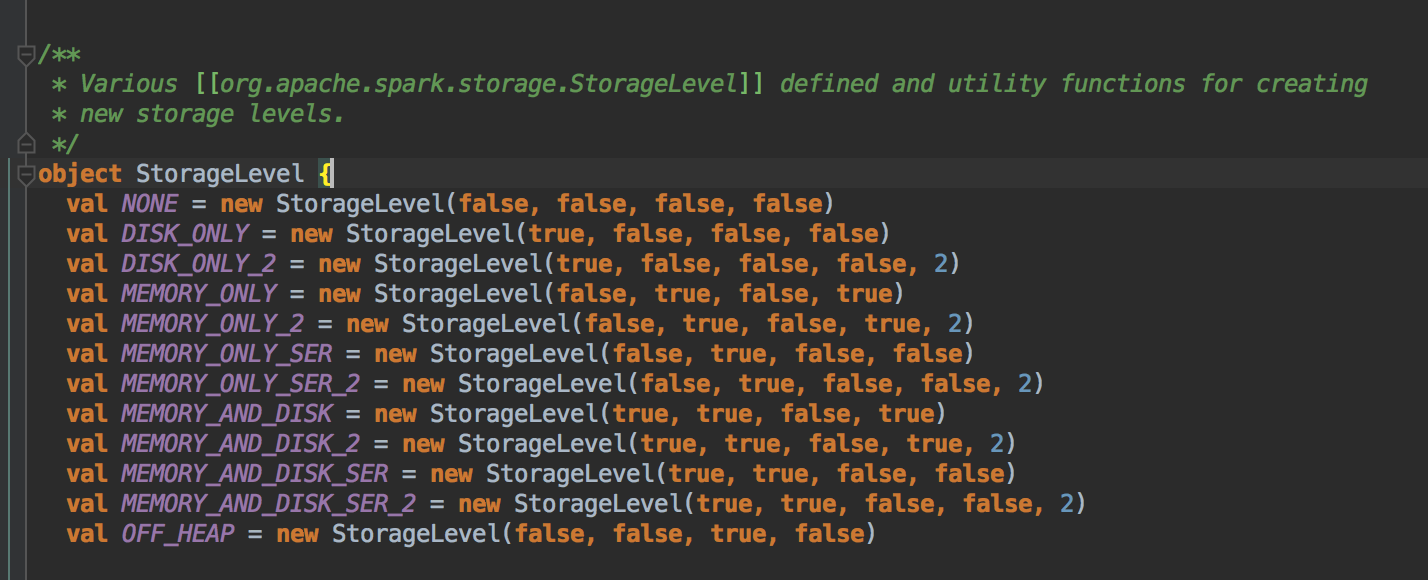
4、cache在工作的时候会最大化的保留数据,但是数据不一定绝对完整,因为当前的计算机如果需要内存空间的话,那么内存中的数据必须让出空间,这是因为执行比缓存重要,此时如何在RDD持久化的时候同时指定了可以把数据放左Disk上,那么部分cache的数据可以从内存转入磁盘,否则的话,数据就会丢失;
在进行Cache时,BlockManager会帮你进行管理,我们可以通过key到BlockManager中找出曾经缓存的数据;
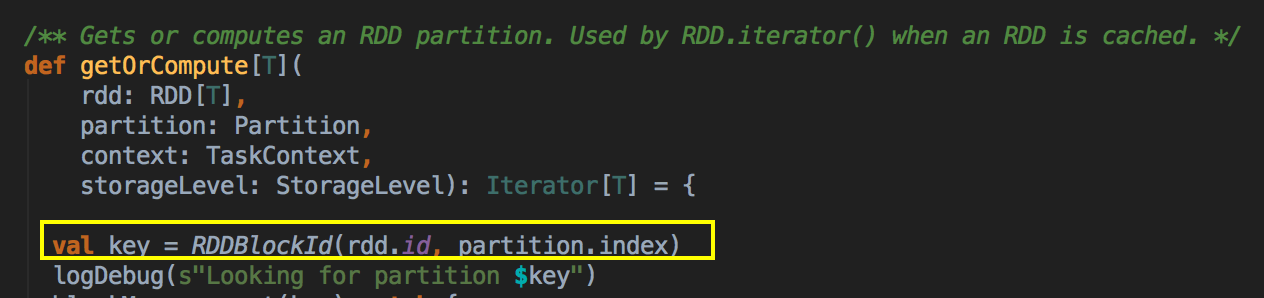
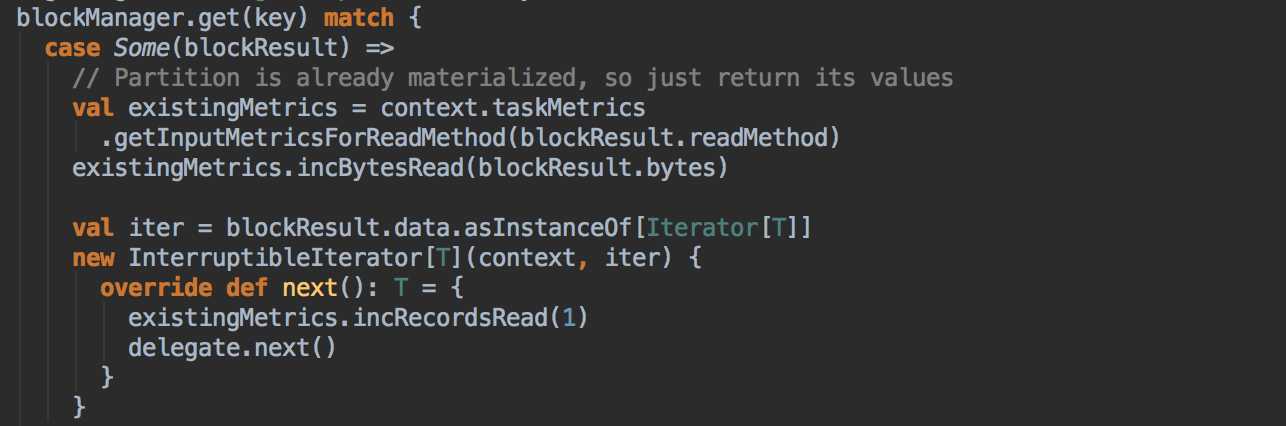
如果有BlockManager.get()方法没有返回任何数据,就调用acquireLockForPartition 方法,因为会有可能多条线程在操作数据,spark有一个东西叫慢任务StraggleTask 推迟,StraggleTask 推迟的时候一般都会运行两个任务在两台机器上;

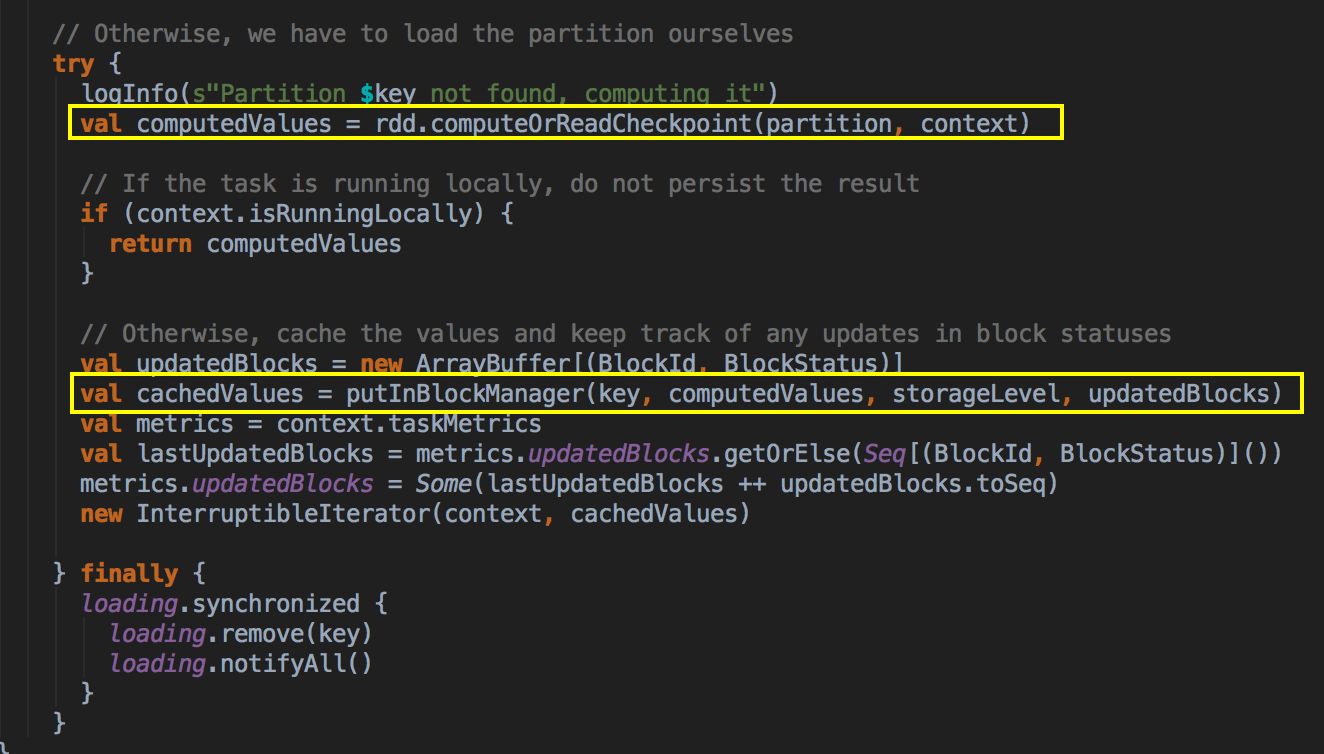
最后还是通过 BlockManager.get 来获得数据

5、具体cacheManager在获得缓存数据的时候会通过BlockManager 来抓到数据,优先在本地找数据或者远程抓数据;
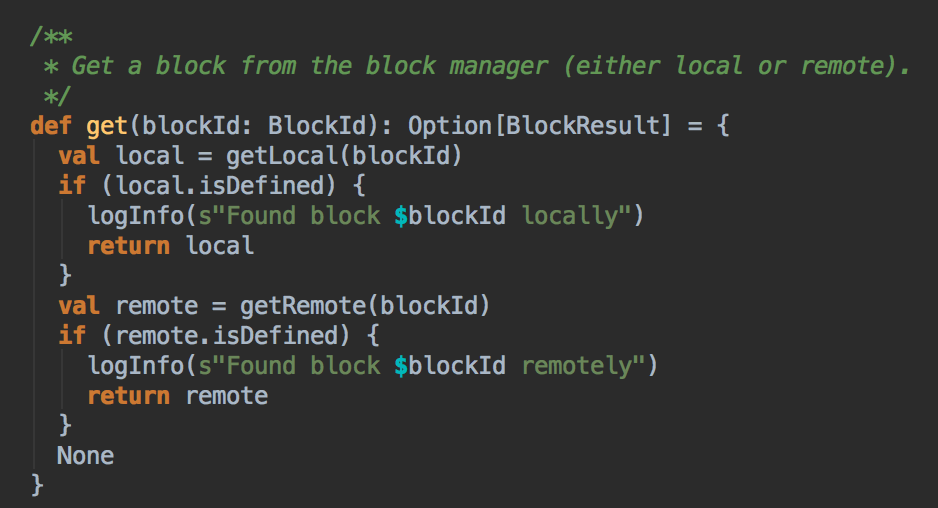
BlockManger.getLocal然后转过来调用doGetLocal方法,在doGetLocal的实现中看到缓存其实不一定在内存中,
缓存可以在存在、磁盘、也可以在offHeap(Tachyon)中;
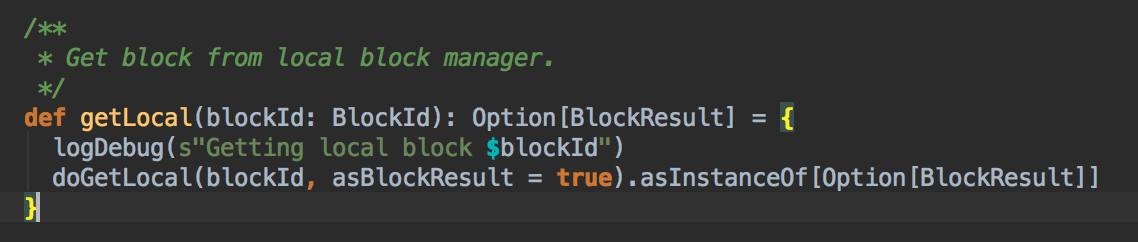
6、在上一步调用了getLocal方法后转过调用了doGetLocal
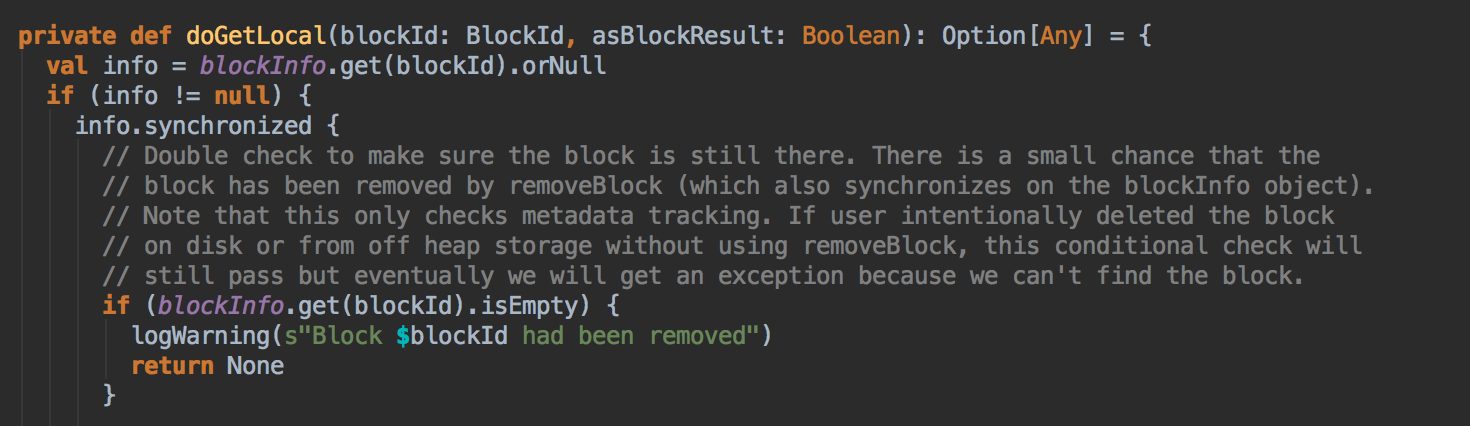


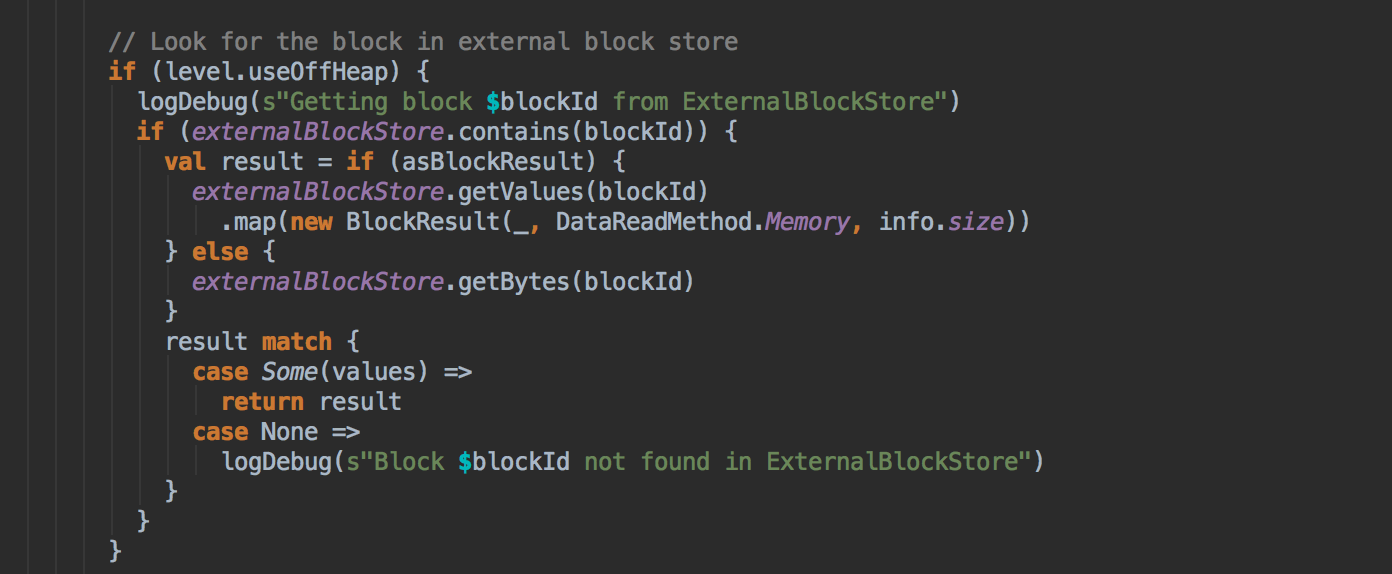


7、在第5步中如果本地没有缓存的话,就调用getRemote方法从远程抓取数据;
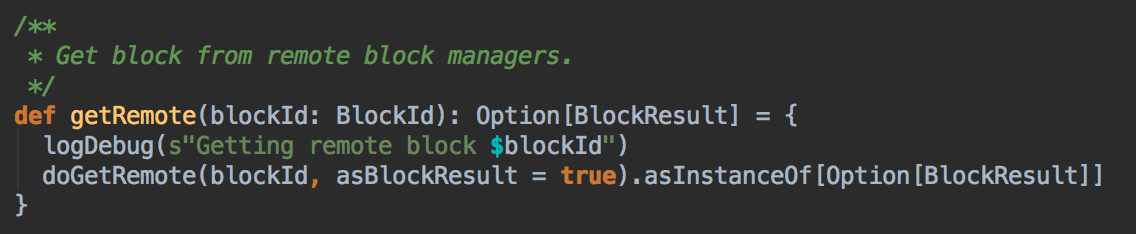

8、如果cacheManager没有通过BlockManager 获得缓存内容的话,其实会通过RDD的computeOrReadCheckpoint ()方法来获得数据;

首先需要检查看当前的RDD是否进行了CheckPoint,如果进行了话就直接读取checkpoint的数据,否则的话就必需进行计算;
checkpoint本身很重要,计算之后通过putInBlockManager 会把数据按照StorageLevel 重新缓存起来;

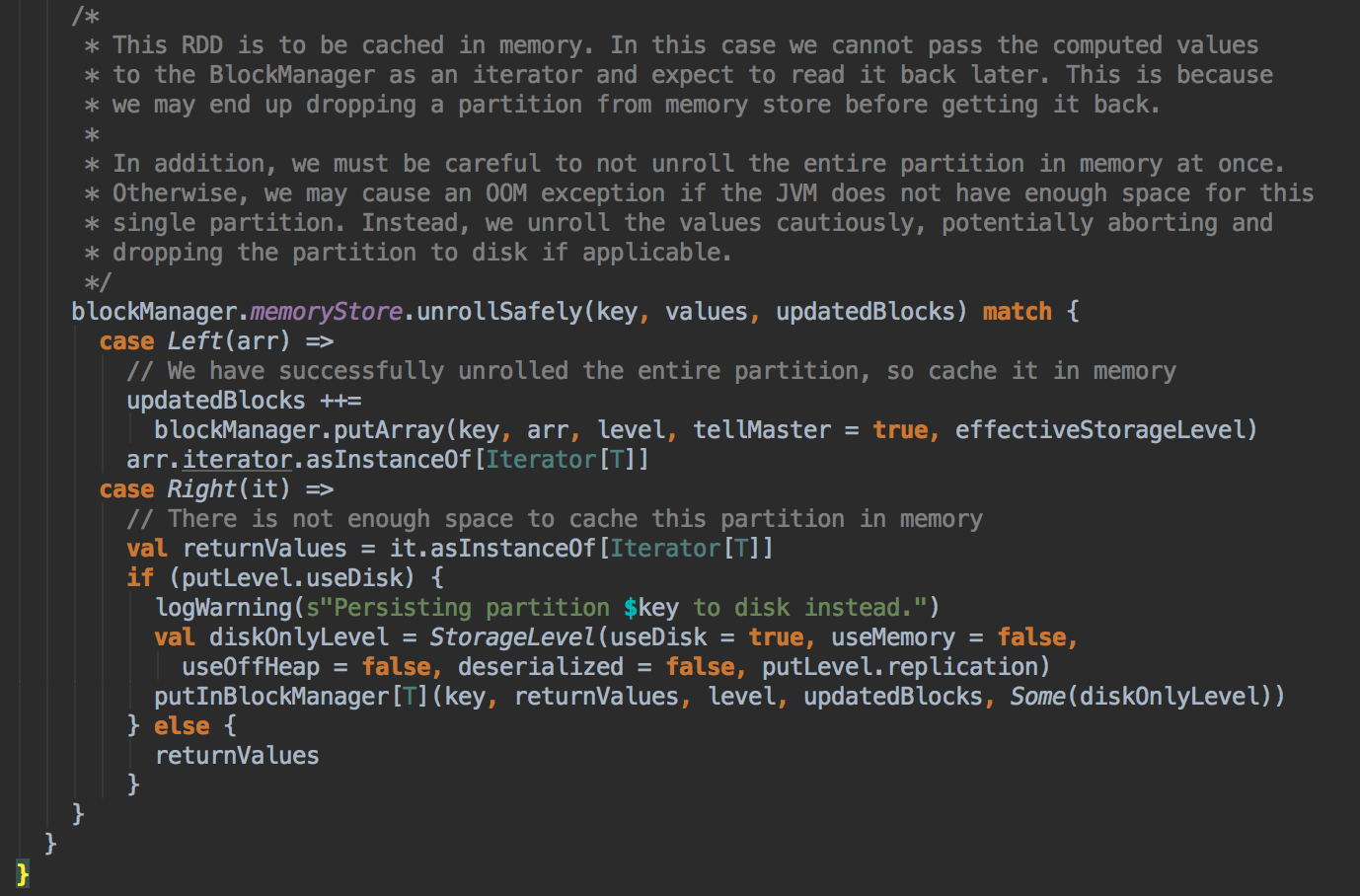
9、如果数据缓存的空间不够,此时会调用memoryStore中的unrollSafety方法,里面有一个循环在内存中放数据;

CheckPoint原理:

原理分析:
1、SparkContext的setCheckpointDir 设置了一个checkpoint 目录
1 def setCheckpointDir(directory: String) { 2 3 // If we are running on a cluster, log a warning if the directory is local. 4 // Otherwise, the driver may attempt to reconstruct the checkpointed RDD from 5 // its own local file system, which is incorrect because the checkpoint files 6 // are actually on the executor machines. 7 if (!isLocal && Utils.nonLocalPaths(directory).isEmpty) { 8 logWarning("Spark is not running in local mode, therefore the checkpoint directory " + 9 s"must not be on the local filesystem. Directory '$directory' " + 10 "appears to be on the local filesystem.") 11 } 12 //利用hadoop的api创建了一个hdfs目录 13 checkpointDir = Option(directory).map { dir => 14 val path = new Path(dir, UUID.randomUUID().toString) 15 val fs = path.getFileSystem(hadoopConfiguration) 16 fs.mkdirs(path) 17 fs.getFileStatus(path).getPath.toString 18 } 19 }
2、RDD核心的CheckPoint方法
def checkpoint(): Unit = RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { // NOTE: we use a global lock here due to complexities downstream with ensuring // children RDD partitions point to the correct parent partitions. In the future // we should revisit this consideration. if (context.checkpointDir.isEmpty) { throw new SparkException("Checkpoint directory has not been set in the SparkContext") } else if (checkpointData.isEmpty) { //创建ReliableRDDCheckpointData指向的RDDCheckpointData的实例 checkpointData = Some(new ReliableRDDCheckpointData(this)) } }
3、创建了一个ReliableRDDCheckpointData
//ReliableRDDCheckpointData 的父类RDDCheckpointData private[spark] class ReliableRDDCheckpointData[T: ClassTag](@transient private val rdd: RDD[T]) extends RDDCheckpointData[T](rdd) with Logging { ...... }
4、父类RDDCheckpointData
/** * RDD 需要经过 * * [ Initialized --> CheckpointingInProgress--> Checkpointed ] * 这几个阶段才能被 checkpoint * */ private[spark] abstract class RDDCheckpointData[T: ClassTag](@transient private val rdd: RDD[T]) extends Serializable { import CheckpointState._ // The checkpoint state of the associated RDD. //标识CheckPoint的状态,第一次初始化时是Initialized protected var cpState = Initialized ...... }
checkpoint写入数据:
1、Spark job运行最终会调用SparkContext的runJob方法将任务提交给Executor去执行;
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag]( rdd: RDD[T], func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U, partitions: Seq[Int], resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit): Unit = { if (stopped.get()) { throw new IllegalStateException("SparkContext has been shutdown") } val callSite = getCallSite val cleanedFunc = clean(func) logInfo("Starting job: " + callSite.shortForm) if (conf.getBoolean("spark.logLineage", false)) { logInfo("RDD's recursive dependencies: " + rdd.toDebugString) } dagScheduler.runJob(rdd, cleanedFunc, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, localProperties.get) progressBar.foreach(_.finishAll()) //在生产环境下会调用ReliableRDDCheckpointData的doCheckpoint方法 rdd.doCheckpoint() }
2、rdd.doCheckpoint()方法
private[spark] def doCheckpoint(): Unit = { RDDOperationScope.withScope(sc, "checkpoint", allowNesting = false, ignoreParent = true) { if (!doCheckpointCalled) { doCheckpointCalled = true if (checkpointData.isDefined) { if (checkpointAllMarkedAncestors) { // TODO We can collect all the RDDs that needs to be checkpointed, and then checkpoint // them in parallel. // Checkpoint parents first because our lineage will be truncated after we // checkpoint ourselves dependencies.foreach(_.rdd.doCheckpoint()) } checkpointData.get.checkpoint() } else { //遍历依赖的rdd,调用每个rdd的doCheckpoint方法 dependencies.foreach(_.rdd.doCheckpoint()) } } } }
3、checkpointData类型是RDDCheckpointData中的doCheckpoint()方法;
final def checkpoint(): Unit = { // Guard against multiple threads checkpointing the same RDD by // atomically flipping the state of this RDDCheckpointData RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { if (cpState == Initialized) { //1、标记当前状态为正在checkpoint中 cpState = CheckpointingInProgress } else { return } } //2 这里调用的是子类的doCheckpoint() val newRDD = doCheckpoint() // Update our state and truncate the RDD lineage // 3 标记checkpoint已完成,清空RDD依赖 RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { cpRDD = Some(newRDD) cpState = Checkpointed rdd.markCheckpointed() } }
4、子类ReliableRDDCheckpointData的doCheckpoint()方法;
1 protected override def doCheckpoint(): CheckpointRDD[T] = { 2 /** 3 * 为该 rdd 生成一个新的依赖,设置该 rdd 的 parent rdd 为 CheckpointRDD 4 * 该 CheckpointRDD 负责以后读取在文件系统上的 checkpoint 文件,生成该 rdd 的 partition 5 */ 6 val newRDD = ReliableCheckpointRDD.writeRDDToCheckpointDirectory(rdd, cpDir) 7 8 // Optionally clean our checkpoint files if the reference is out of scope 9 // 是否清除checkpoint文件如果超出引用的资源范围 10 if (rdd.conf.getBoolean("spark.cleaner.referenceTracking.cleanCheckpoints", false)) { 11 rdd.context.cleaner.foreach { cleaner => 12 cleaner.registerRDDCheckpointDataForCleanup(newRDD, rdd.id) 13 } 14 } 15 16 logInfo(s"Done checkpointing RDD ${rdd.id} to $cpDir, new parent is RDD ${newRDD.id}") 17 // 将新产生的RDD返回给父类 18 newRDD 19 }
5、ReliableCheckpointRDD.writeRDDToCheckpointDirectory(rdd, cpDir)方法
/** * Write RDD to checkpoint files and return a ReliableCheckpointRDD representing the RDD. * * 触发runJob 来执行当前的RDD 中的数据写到Checkpoint 的目录中,同时会产生ReliableCheckpointRDD 实例 */ def writeRDDToCheckpointDirectory[T: ClassTag]( originalRDD: RDD[T], checkpointDir: String, blockSize: Int = -1): ReliableCheckpointRDD[T] = { val checkpointStartTimeNs = System.nanoTime() val sc = originalRDD.sparkContext // Create the output path for the checkpoint //把checkpointDir设置我们checkpoint的目录 val checkpointDirPath = new Path(checkpointDir) // 获取HDFS文件系统API接口 val fs = checkpointDirPath.getFileSystem(sc.hadoopConfiguration) // 创建目录 if (!fs.mkdirs(checkpointDirPath)) { throw new SparkException(s"Failed to create checkpoint path $checkpointDirPath") } // Save to file, and reload it as an RDD // 将配置文件信息广播到所有节点 val broadcastedConf = sc.broadcast( new SerializableConfiguration(sc.hadoopConfiguration)) // TODO: This is expensive because it computes the RDD again unnecessarily (SPARK-8582) // 核心代码 /** * 此处新提交一个Job,也是对RDD进行计算,那么如果原有的RDD对结果进行了cache的话, * 那么是不是减少了很多的计算呢,这就是为啥checkpoint的时候强烈推荐进行cache的缘故 */ sc.runJob(originalRDD, writePartitionToCheckpointFile[T](checkpointDirPath.toString, broadcastedConf) _) // 如果rdd的partitioner不为空,则将partitioner写入checkpoint目录 if (originalRDD.partitioner.nonEmpty) { writePartitionerToCheckpointDir(sc, originalRDD.partitioner.get, checkpointDirPath) } val checkpointDurationMs = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - checkpointStartTimeNs) logInfo(s"Checkpointing took $checkpointDurationMs ms.") // 创建一个CheckpointRDD,该分区数目应该和原始的rdd的分区数是一样的 val newRDD = new ReliableCheckpointRDD[T]( sc, checkpointDirPath.toString, originalRDD.partitioner) if (newRDD.partitions.length != originalRDD.partitions.length) { throw new SparkException( "Checkpoint RDD has a different number of partitions from original RDD. Original " + s"RDD [ID: ${originalRDD.id}, num of partitions: ${originalRDD.partitions.length}]; " + s"Checkpoint RDD [ID: ${newRDD.id}, num of partitions: " + s"${newRDD.partitions.length}].") } newRDD }
最后,会返回新的CheckpointRDD ,父类将它复值给成员cpRDD,最终标记当前状态为Checkpointed并清空当RDD的依赖链;到此Checkpoint的数据就被序列化到HDFS上了;
checkpoint读出数据
1、RDD的iterator()
1 /** 2 * 先调用presist(),再调用checkpoint() 3 * 先执行到rdd的iterator()的时候,storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE,就会通过CacheManager获取数据 4 * 此时发生BlockManager获取不到数据,就会第一次计算数据,在通过BlockManager进行持久化 5 * 6 * rdd的job执行结束,启动单独的一个job,进行checkpoint, 7 * 下一次又运行到rdd的iterator()方法就会发现持久化级别不为空,默认从BlockManager中读取持久化数据(正常情况下) 8 * 9 * 在非正常情况下,就会调用computeOrReadCheckpoint方法,判断如果isCheckpoint为ture, 10 * 就会调用父rdd的iterator(),从外部文件系统中读取数据 11 */ 12 final def iterator(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = { 13 if (storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE) { 14 getOrCompute(split, context) 15 } else { 16 //进行RDD的partition计算 17 computeOrReadCheckpoint(split, context) 18 } 19 }
2、继续调用computeOrReadCheckpoint
1 private[spark] def computeOrReadCheckpoint(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = 2 { 3 if (isCheckpointedAndMaterialized) { 4 firstParent[T].iterator(split, context) 5 } else { 6 //抽象方法,找具体实现类,比如MapPartitionsRDD 7 compute(split, context) 8 } 9 }
调用rdd.iterator() 去计算rdd的partition的时候,会调用computeOrReadCheckpoint(split: Partition)去查看该rdd是否被checkPoint过了,
如果是,就调用rdd的parent rdd的iterator()也就是CheckpointRDD.iterator(),否则直接调用该RDD的compute
3、CheckpointRDD(ReliableCheckpointRDD)的compute
1 //Path上读取我们的CheckPoint数据 2 override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = { 3 val file = new Path(checkpointPath, ReliableCheckpointRDD.checkpointFileName(split.index)) 4 ReliableCheckpointRDD.readCheckpointFile(file, broadcastedConf, context) 5 }
4、readCheckpointFile方法
1 def readCheckpointFile[T]( 2 path: Path, 3 broadcastedConf: Broadcast[SerializableConfiguration], 4 context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = { 5 val env = SparkEnv.get 6 // 用hadoop API 读取HDFS上的数据 7 val fs = path.getFileSystem(broadcastedConf.value.value) 8 val bufferSize = env.conf.getInt("spark.buffer.size", 65536) 9 val fileInputStream = { 10 val fileStream = fs.open(path, bufferSize) 11 if (env.conf.get(CHECKPOINT_COMPRESS)) { 12 CompressionCodec.createCodec(env.conf).compressedInputStream(fileStream) 13 } else { 14 fileStream 15 } 16 } 17 val serializer = env.serializer.newInstance() 18 val deserializeStream = serializer.deserializeStream(fileInputStream) 19 20 // Register an on-task-completion callback to close the input stream. 21 context.addTaskCompletionListener[Unit](context => deserializeStream.close()) 22 //反序列化数据后转换为一个Iterator 23 deserializeStream.asIterator.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]] 24 }
