1、运算符重载:实质就是函数重载
返回值类型 operator运算符(形参表)
{
......
}
运算符重载为普通函数:

运算符重载为成员函数:

Note:重载成全局函数时操作数个数等于函数参数个数。
2、赋值运算符“=”的重载
赋值运算符两边的类型可以不匹配,此时我们需要重载赋值运算符“=”,且只能重载为成员函数。例如:
(1)把一个int型变量赋值给Complex对象
(2)把一个char*类型的字符串赋值给一个字符串对象
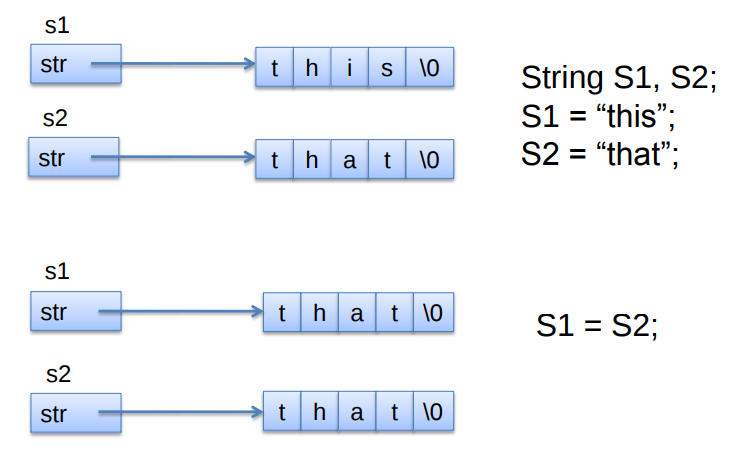
重载赋值运算符的意义:浅复制(浅拷贝),深复制(深拷贝)
浅:执行逐字节的复制工作。
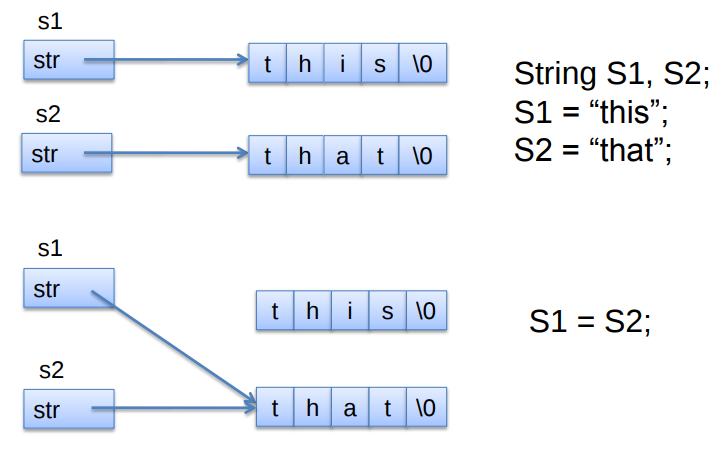

深:将一个对象中指针变量指向的内容复制到另一个对象中指针成员对象指向的地方。

3、运算符重载为友元函数
成员函数不能满足使用要求;普通函数不能访问类的私有成员。这两种情况下需要把运算符重载为友元函数。
4、实例:可变长整型数组

class CArray { int size; //数组元素的个数 int *ptr; //指向动态分配的数组 public: CArray(int s = 0); //s代表数组元素的个数,构造函数 CArray(CArray & a);~CArray(); void push_back(int v); //用于在数组尾部添加一个元素v CArray & operator=( const CArray & a);//用于数组对象间的赋值 int length() { return size; } //返回数组元素个数 int& CArray::operator[](int i) //返回值是什么类型? {//用以支持根据下标访问数组元素, //如n = a[i]和a[i] = 4; 这样的语句 return ptr[i]; } };
Note:非引用的函数返回值不可以作为左值使用。 所以用int&
5、流插入/流提取运算符重载
#include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; class Complex{ double real; double imag; public: Complex(double i = 0, double j = 0):real(i), imag(j){}; Complex(const Complex &c); friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &o, Complex &c); friend istream & operator>>(istream &i, Complex &c); }; Complex::Complex(const Complex &c) { real = c.real; imag = c.imag; } ostream & operator<<(ostream &o, Complex &c){ o<<c.real<<"+"<<c.imag<<"i"<<endl; return o; } istream & operator>>(istream &i, Complex &c){ string s; i>>s; int pos = s.find("+",0); string sTemp = s.substr(0,pos); c.real = atof(sTemp.c_str());//atof库函数能将const char*指针只想的内容转换成float sTemp = s.substr(pos+1, s.length()-pos-2); c.imag = atof(sTemp.c_str()); return i; } int main(int argc, char * argv[]){ Complex k; int n; cin>>k>>n; cout<<k<<","<<n<<endl; return 0; }
6、自加/自减运算符
(1)前置作为一元运算符重载:
重载为成员函数:
T & operator++(); T & operator--();
重载为全局函数:
T & operator++(T &); T & operator--(T &);
++obj, obj.operator++(), operator++(obj) 都调用上述函数。
(2)后置作为二元运算符重载:
需要比前置多写一个参数,无具体意义,只是加以区别。
重载为成员函数:
T operator++(int); T operator--(int);
重载为全局函数:
T operator++(T &, int); T operator--(T &, int);
obj++, obj.operator++(0), operator++(obj,0) 都调用上述函数。
(3)
operator int ( ) { return n; } Demo s; (int) s ; //等效于 s.int()
int 作为一个类型强制转换运算符被重载。
类型强制转换运算符重载时,
• 不能写返回值类型
• 实际上其返回值类型为类型强制转换运算符代表的类型
Note:
C++不允许定义新的运算符,
运算符重载不改变运算符的优先级,
以下运算符不能被重载: “.”, “.*”, “::”, “?:”, sizeof,
重载运算符(), [ ], ->或者赋值运算符=时, 重载函数必须声明为类的成员函数。