背景
- 二叉树是数据结构中的重点,也是难点。二叉树比数组、栈、队列等线性结构相比复杂度更高,想要做到心中有“树”,需要自己动手画图、观察、思考,才能领会其真谛。
- 在上篇文章《自己动手作图深入理解二叉树、满二叉树及完全二叉树》中,我们对完全二叉树有了一定认识,该文将对一种特殊的完全二叉树”最大堆”进行底层研究。
概念
堆(heap)通常是一个可以被看做一棵二叉树的数组对象。堆总是满足下列性质:
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值;
最大堆
- 根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆
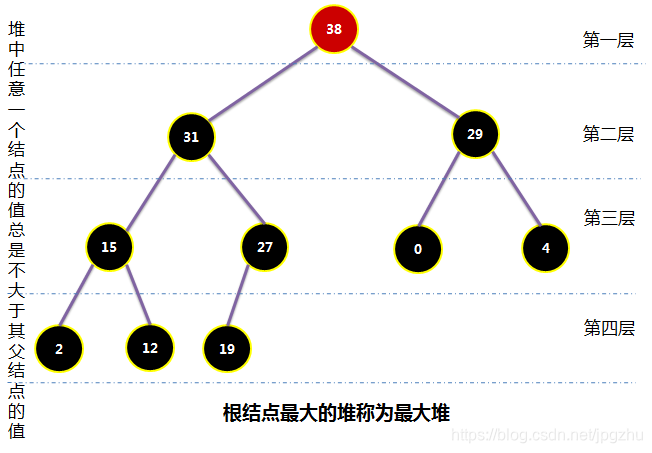
最大堆的线性存储
- 由于堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树,可以利用数组集合形成线性存储的数据结构。
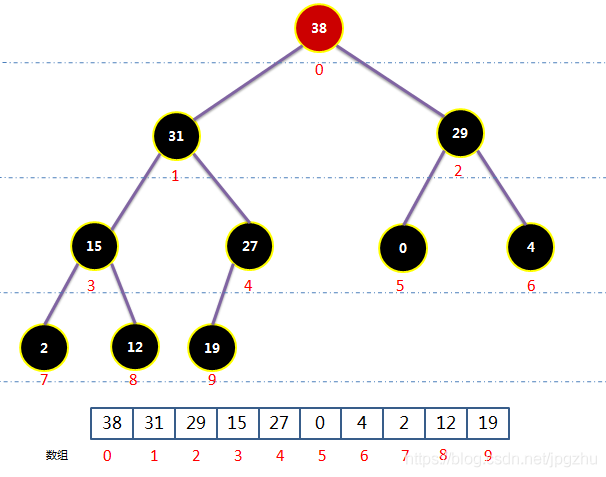
/**
* 最大堆的底层实现--数组集合形成线性存储的数据结构
* * @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-28
*/
public class MaxHeap<E extends Comparable<E>> {
// 存放元素的数组集合
private ArrayList<E> list;
MaxHeap() {
this.list = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 得到左孩子索引
private int getLeftChildIndex(int i) {
return (2 * i + 1);
}
// 得到右孩子索引
private int getRightChildIndex(int i) {
return (2 * i + 2);
}
// 得到父结点索引
private int getParentIndex(int i) {
if (i == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法索引值");
} else {
return ((i - 1) / 2);
}
}
}
动画实现最大堆加入新元素
- 加入到数组集合尾部的元素与父结点进行比较,通过上浮操作,保证所有子结点不能大于父结点。

代码实现最大堆加入新元素
/**
* 最大堆的底层实现
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-28
*/
public class MaxHeap<E extends Comparable<E>> {
// 存放元素的数组集合
private ArrayList<E> list;
MaxHeap() {
this.list = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 得到左孩子索引
private int getLeftChildIndex(int i) {
return (2 * i + 1);
}
// 得到右孩子索引
private int getRightChildIndex(int i) {
return (2 * i + 2);
}
// 得到父结点索引
private int getParentIndex(int i) {
if (i == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法索引值");
} else {
return ((i - 1) / 2);
}
}
// 添加元素
public void add(E e) {
this.list.add(e);
/**
* 将加入的结点与父结点进行比较:
* 如果加入的结点大于父结点,则进行上浮
* 直至新结点小于或等于父结点为止
*/
// 获取当前添加元素在数组中的索引
int i = this.list.size() - 1;
while (i > 0) {
E current = this.list.get(i);
E parent = this.list.get(getParentIndex(i));
// 如果父结点元素大于当前加入的元素,则进行交换
if (parent.compareTo(current) < 0) {
// 交换新加入的结点与父结点的位置
Collections.swap(this.list, i, getParentIndex(i));
} else {
break;
}
i = getParentIndex(i);
}
}
}
动画实现最大堆取出最大元素
- 获取最大堆中的根结点,即为最大元素;并把尾部结点放置到根结点,并通过下沉操作,把子结点中的最大元素移动根结点。
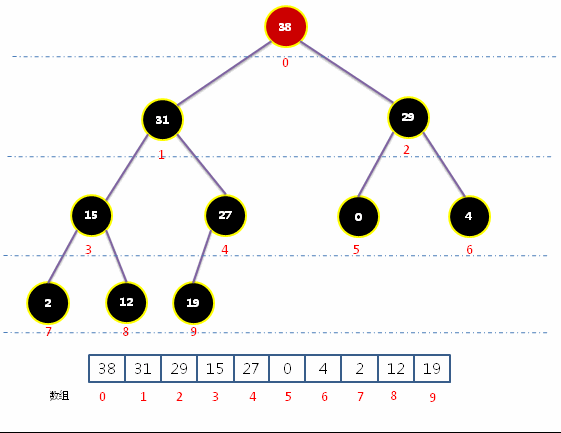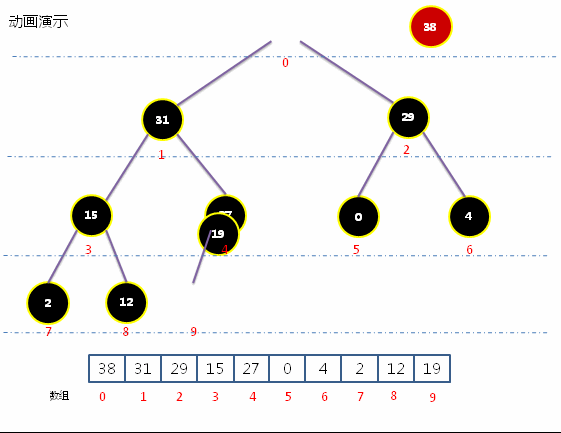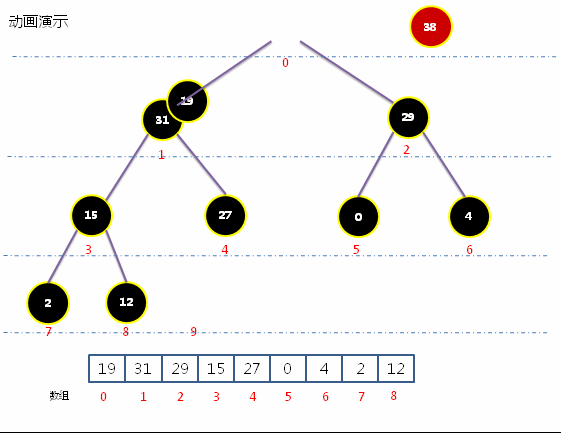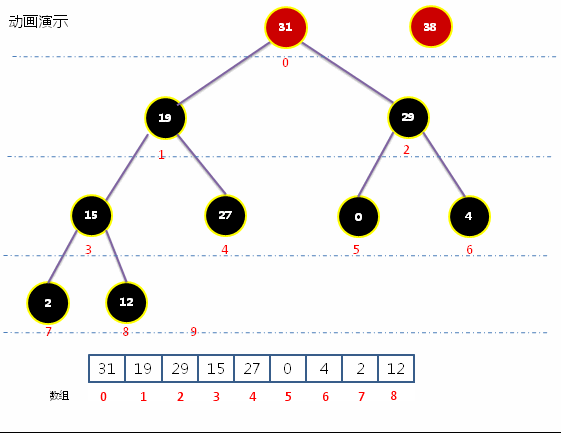
代码实现最大堆取出最大元素
/**
* 最大堆的底层实现
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-28
*/
public class MaxHeap<E extends Comparable<E>> {
// 存放元素的数组集合
private ArrayList<E> list;
MaxHeap() {
this.list = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 得到左孩子索引
private int getLeftChildIndex(int i) {
return (2 * i + 1);
}
// 得到右孩子索引
private int getRightChildIndex(int i) {
return (2 * i + 2);
}
// 得到父结点索引
private int getParentIndex(int i) {
if (i == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法索引值");
} else {
return ((i - 1) / 2);
}
}
// 查找最大元素
public E findMax() {
if (this.list.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
// 最大堆中的元素永远在根结点
return this.list.get(0);
}
// 取出最大元素
public E getMax() {
if (findMax() != null) {
E e = findMax();
/**
* 取出最大元素后,需要把堆中第二大的元素放置在根结点:
* 将根结点元素与最后面的元素进行交换,
* 让最后面的元素出现在根结点,并移除最大元素
* 将根结点的元素与左右孩子结点比较,直至根结点的元素变成最大值
*/
int i = 0;
Collections.swap(this.list, i, this.list.size() - 1);
this.list.remove(this.list.size() - 1);
// 通过循环进行当前结点与左右孩子结点的大小比较
while (getLeftChildIndex(i) < this.list.size() && getRightChildIndex(i) < this.list.size()) {
int leftIndex = getLeftChildIndex(i);
int rightIndex = getRightChildIndex(i);
// 通过比较左右孩子的元素哪个较大,确定当前结点与哪个孩子进行交换
int index = this.list.get(leftIndex).compareTo(this.list.get(rightIndex)) > 0 ? leftIndex : rightIndex;
if (this.list.get(i).compareTo(this.list.get(index)) < 0) {
Collections.swap(this.list, i, index);
} else {
// 如果当前结点都大于左右孩子,则结束比较
break;
}
i = index;
}
return e;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
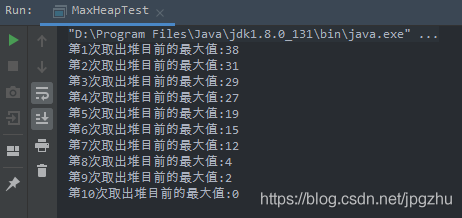
程序测试
/**
* 最大堆的底层实现--测试程序
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-28
*/
public class MaxHeapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MaxHeap<Integer> maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>();
// 将10个数字加入形成最大堆
int[] arrays = {19,29,4,2,27,0,38,15,12,31};
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
maxHeap.add(arrays[i]);
}
// 依次从堆中取出最大值
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"次取出堆目前的最大值:"+maxHeap.getMax());
}
}
}
最大堆的应用--优先队列
优先队列:出队的和顺序与入队的顺序无关,只与优先级相关;
优先队列通常可以采用最大堆的数据结构来实现。
/**
* 用最大堆的数据结构实现优先队列
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-28
*/
public class PriorityQueue<E extends Comparable<E>> {
private MaxHeap<E> mhp;
PriorityQueue() {
mhp=new MaxHeap<>();
}
// 入队
public void enqueue(E e) {
mhp.add(e);
}
// 优选级最高的元素出队
public E dequeue() {
return mhp.getMax();
}
// 查看优先级最高的元素
public E getFront() {
return mhp.findMax();
}
}
写在最后
- 以上通过画图、动画演示、代码编写对堆与最大堆的概念和底层实现方式,都作了深入分析;作为最大堆的反向结构,最小堆的实现也是一样,读者可参考以上动画和代码,动手练习。
- 画图、编码不易,请点赞、收藏、关注三连!!!