本文主要讲实现过程的一些坑。
先说下要实现的目标,主要功能在UE4/Unity中都要用,能同时捕获多个摄像头,并且捕获的图片要达到1080p25桢上,并且需要经过复杂的图片处理(如深度图与颜色图的对齐,结合深度摄像头的自然背景扣色,用于直播传输带Alpha通道的编码等)后丢给UE4/Unity3D,并且要CPU要占用小,以便在UE4/Unity有大的余地做更多的事件。
市面上一般1080p后的摄像头,在20桢以上都不会提供原生的rgba32数据,一般常见的有压缩格式mjpg,末压缩的一般是nv12,牛点的会提供yuv2,正常的实现会把内存流里的数据提供给对应的UE4/Unity3D,然后做复杂的图片处理。这种做法对于我们来说,有三个问题,一是内存流里的数据提供给UE4/Unity3D对应的gpu时,unity里操作texture只能在主线程,试过Texture2D.LoadRawTextureData(IntPtr data,int size),不知为啥慢的接受不能,在UE4中一样,只能在渲染线程和游戏线程中更新纹理,这二个线程互相之间有同步等待的关系,但是还算好,UE4中一个摄像头的情况还能接受。第二是上面说的图片处理,不说后面复杂的,首先要把上面的nv12/yuv2转化成UE4/Unity3D能用的rgba32纹理,在UE4/Unity3D就要分别实现一次,对程序员一点都不友好,后续改动全是二套,可能有的同学要说了,为啥不在交给UE4/Unity3D之前,把数据处理成rgba32格式,简单点,你网上找段nv12转rgba代码试试,1080p直接占用你10%左右cpu,并且后面还有很多的复杂处理,在这之前用CPU处理是不可行的。第三,如果前面可以受点了,那么如果同时开二个或是多个摄像头的1080p,你还要处理各个设备的数据同步问题,这个解决后,你也就只能看幻灯片了。
根据如上问题,我们要解决的是,如何把UE4/Unity3D的图片处理逻辑写在一块,如何让我们程序快速的从插件中得到处理后的图片数据,如何让多个摄像头能同时工作。我们深化一下,里面所说的都是图片处理,对于cpu来说,是拿诸葛亮去做臭皮匠的活。那我们相当于能不能给每个摄像头一个线程,每个线程有一个GPU的上下文,线程最开始把流的数据读到gpu中,然后处理图片,最后给UE4/Unity3D,给UE4/Unity3D这一步我们要考虑的是如何给,是用通用的方式,先给到cpu上内存,然后由UE4/Unity3D分别读内存流里的数据到各自引擎里的渲染dx上下文,或是能不能直接由我们摄像头里的gpu上下文的显存数据移到对应UE4/Unity的gpu上下文的显存数据中。第一种相当于GPU-CPU-GPU,第二种就是GPU-GPU,第二种肯定要快的多,因为GPU与CPU的数据交互很费时,所以在下面,我们来打造一个UE4/Unity3D通用的插件,由各自的设备读取数据的线程把数据放入各自的gpu上下文中,经过复杂的图像处理后,分别找到对应UE4/Unity3D上的gpu中的对应位置,把数据直接复制过去,是一条起点经过cpu后,就直接一步到位全经GPU处理后直接到引擎里显示的方案。
确定技术实现后,就是技术方案选型,语言方面,二者通用的插件,没的选,只有C++,平台只考虑window平台,没有那么多的需求,时间与精力去考虑多平台,那么摄像头捕获程序我们选择ms最新的多媒体技术Media Foundation,包含常用的视频编解码,GPU方面我们只要图像处理,以及和UE4/Unity能原始对接的接口,那么也没选择,Dx11是UE4/Unity3D在window平台默认的底层渲染技术,DX11里的ComputeShader来处理图像逻辑不多不少,逻辑更清晰,与dx11的纹理无逢对接。嗯,至于为啥以前我是做opengl,为啥不选opengl/opencl这路,首先在window平台,方便性,效率,与UE4/Unity3D引擎对接都是dx11方便,其次,我自认为对opengl熟悉,那么对dx也不会陌生,顺便能熟悉下dx也很兴奋。因为都是window平台方案,后面生成的库想不到的小,只有400K左右实现了很多功能,包含webcamera,decklink视频捕获,realsense深度摄像头,以及与UE4/Unity3D的CPU/GPU对接,记录系统声音,PCM转ACC,记录H264视频,ACC/MP3与H264视频合成,以及视频播放。
在这只讲上面摄像头捕获相关,如下是相关的类图关系,为了显示清晰,只列出主要相关的类。
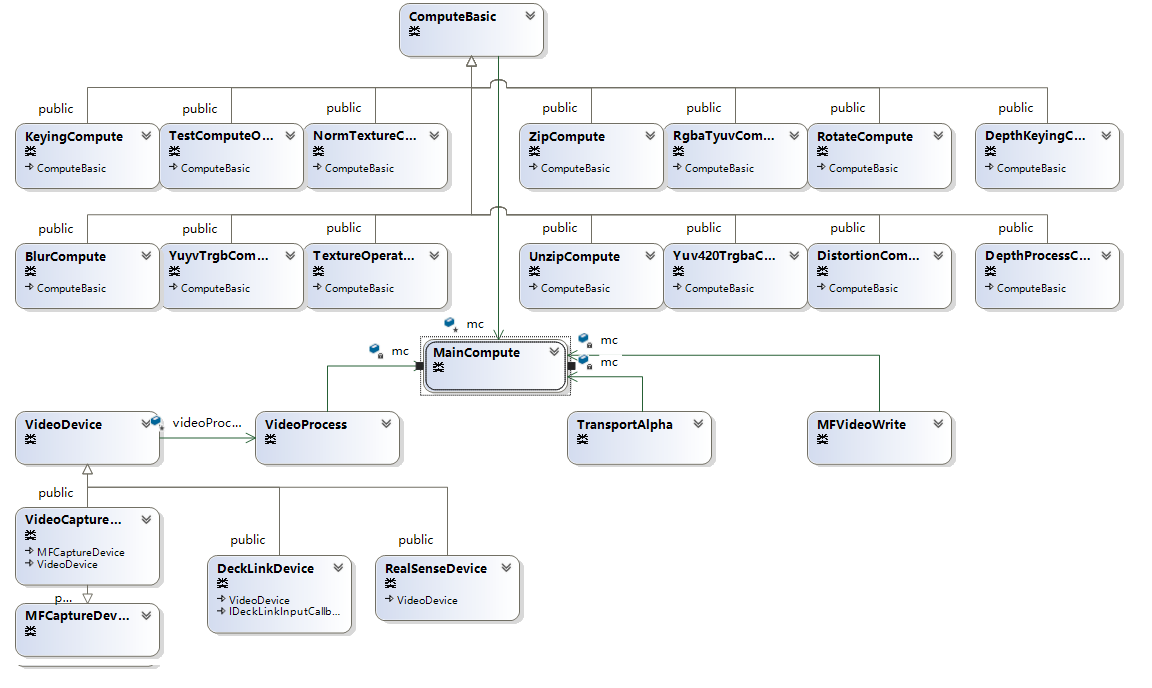
主要说下,分别是数据处理与数据提供。数据处理的设计参照游戏引擎的后处理特效的设计,每个处理一个特定的功能,可以组合链接,不同于游戏的后处理特效,Computeshader对于数据的长宽很敏感,所以设计的时候要考虑好这个。
ComputeBasic做为数据处理的基类,一是处理如上长宽的变化,二是处理ComputeBasic与ComputeBasic的连接,针对数据长宽的变化,主要是把初始化/注销buffer与初始化/注销shader分开,当数据维度变化后,针对buffer的那一块全部重新生成,二是定义维度如何影响下一块,毕竟很多功能在本身上就会改变维度,如yuv转换,压缩与解压等。第二块ComputeBasic与ComputeBasic的连接在如上的基础上,链接后下一块自动知道相应的大小,并提供针对整个功能链表功能。下面就是数据处理的各个具体实现,选择实现基类定义的一些接口,就有了基类处理链接下一块与大小变化自动处理,每个具体的数据处理类只需要实现具体功能就可。
如下贴一个常见的yuv2rgb的Computeshader与代码实现。

//YUV2,YuYv, 指定交叉格式。 enum YUV422Format { BC_YUYV = 0, BC_YVYU = 1, BC_UYVY = 2, BC_VYUY = 3, }; //提供yuyv,yvyu,uyuv转rgba32的能力 class YuyvTrgbCompute : public ComputeBasic { public: YuyvTrgbCompute(MainCompute* mainCompute, bool resultText = false, YUV422Format bcFormat = BC_YUYV) :ComputeBasic(mainCompute) { bResultTex = resultText; format = bcFormat; } ~YuyvTrgbCompute(); public: virtual void UpdateData(void* data, int index = 0) override; virtual void UpdateBuffer(ID3D11Texture2D* buffer, int index = 0) override; virtual void ShowDebugBuffer(int index = 0) override; virtual void OnChangeSize(TexSize& newSize) override; public: // 通过 ComputeBasic 继承 virtual bool InitShader() override; virtual bool InitBuffer() override; virtual bool runCompute() override; public: //0 yuyv,1 yvyu, YUV422Format format; }; #include "YuyvTrgbCompute.h" YuyvTrgbCompute::~YuyvTrgbCompute() { } void YuyvTrgbCompute::UpdateData(void * data, int index) { } void YuyvTrgbCompute::UpdateBuffer(ID3D11Texture2D * buffer, int index) { g_tBuf = buffer; mc->CreateBufferSRV(g_tBuf, &g_pBufSRV); bInitInput = true; } void YuyvTrgbCompute::ShowDebugBuffer(int index) { } void YuyvTrgbCompute::OnChangeSize(TexSize & newSize) { nextSize.width = newSize.width * 2; nextSize.height = newSize.height; } bool YuyvTrgbCompute::InitShader() { char* strResultTex = bResultTex ? "1" : "0"; char* yfront = (format == BC_YUYV || format == BC_YVYU) ? "1" : "0"; char* ufront = (format == BC_YUYV || format == BC_UYVY) ? "1" : "0"; const D3D_SHADER_MACRO defines[] = { "RESULT_TEX",strResultTex,"YFRONT",yfront,"UFRONT",ufront, "SIZE_X", "4", "SIZE_Y","4" ,nullptr,nullptr }; //bInitShader = mc->CreateComputeShader(L"rgba2yuv420p.hlsl", "main", &g_pCS, defines); bInitShader = mc->CreateCustomComputeShader(MAKEINTRESOURCE(112), "main", &g_pCS, defines); return bInitShader; } bool YuyvTrgbCompute::InitBuffer() { bInitBuffer = mc->CreateConstBuffer(&nextSize, sizeof(nextSize), &g_cBuf); if (bResultTex) { bInitBuffer &= mc->CreateTextureBuffer(nullptr, nextSize.width, nextSize.height, DXGI_FORMAT_R8G8B8A8_UNORM, &g_tBufResult); bInitBuffer &= mc->CreateBufferUAV(g_tBufResult, &g_pBufResultUAV); } else { bInitBuffer &= mc->CreateStructuredBuffer(sizeof(UINT), nextSize.width*nextSize.height, nullptr, &g_pBufResult); bInitBuffer &= mc->CreateBufferUAV(g_pBufResult, &g_pBufResultUAV); } return bInitBuffer; } bool YuyvTrgbCompute::runCompute() { vector<ID3D11ShaderResourceView*> srvs = { g_pBufSRV }; vector<ID3D11UnorderedAccessView*> uavs = { g_pBufResultUAV }; vector<ID3D11Buffer*> cons = { g_cBuf }; mc->RunComputeShader(g_pCS, nextSize.width / SIZE_X, nextSize.height / SIZE_Y, 1, srvs, uavs, cons); return true; }

#include "Common.hlsl" #ifndef YFRONT #define YFRONT 1 #endif #ifndef UFRONT #define UFRONT 1 #endif cbuffer texSize : register(b0) { uint width; uint height; } Texture2D<float4> colorData : register(t0); #if RESULT_TEX RWTexture2D<float4> outData : register(u0); #else RWStructuredBuffer<uint> outData : register(u0); #endif uint u22u1(uint2 uv) { return uv.y * width + uv.x; } [numthreads(SIZE_X, SIZE_Y, 1)] void main(uint3 DTid : SV_DispatchThreadID) { uint2 uv = DTid.xy; uint3 tuv = uint3(DTid.x / 2, DTid.y, DTid.z); float4 fyuyv = colorData.Load(tuv); int4 yuyv = fyuyv * 255; //二点一个计算 uint offset = DTid.x % 2; #if UFRONT uint uIndex = 0; uint vIndex = 2; #else uint uIndex = 2; uint vIndex = 0; #endif #if YFRONT int y = yuyv[2 * offset]; uint uvOffset = 1; #else int y = yuyv[2 * offset + 1]; uint uvOffset = 0; #endif int u = yuyv[uIndex + uvOffset]; int v = yuyv[vIndex + uvOffset]; uint4 rgba = yuv2Rgb(y, u - 128, v - 128, 255); //rgba = yuyv; #if RESULT_TEX outData[uv] = float4(rgba / 255.0); #else uint index = u22u1(uv); outData[index] = rgba.r | rgba.g << 8 | rgba.b << 16 | rgba.a << 24; #endif }
简单说下别的类主要功能,代码和上面yuv2rgb就逻辑上有区别。
NormTextureCompute:规范输入流成正常的4通道数据,如r/rg/rgb变成rgba数据,以及去掉纹理需要32倍宽限制(内存块数据直接放入更新到纹理中可能不对,宽度会自动修正,MSDN说是4的倍数,但是在我机器上测试要满足32倍整数,先放入buffer,再通过compute shader写入纹理就可避免。).
keyingCompute:整合我们公司另一牛人根据何恺明大神的导向滤波算法,扣图达到发丝极,当然算法也是非常复杂,七段compute shader组合而成。
Yuv420TrgbaCompute/RgbaTyuvCompute是一套可以带Alpha通道的平面420的传输,具体细节就不说了。其中Compute shader如果逻辑要针对texture多次采样,可能考虑使用groupshared/GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync来改变逻辑提高效率。
TextureOperateCompute:提供通道映射的能力,如bgra转rgba,rgba转rggr,还有上下,左右翻转功能。
RotateCompute:翻转的能力,注意如果是贴图如1920*1080翻转90后是1080*1920,直接GPU复制不会引起问题,但是从CPU读出来,内存数据宽度是1088面不是1080,所以相应你用这个数据后需要生成的是1088*1920的图,注意上面所说的32倍宽。
ZipCompute/UnzipCompute:提供压缩4 byte成1个int,或是反过来,主要是有些数据如yuv420,nv12这种宽度对应,但是在compute shader里都是4字节的存放,内存读出来的数据先经过unzip,反倒后续使用。
DistortionCompute:提供针对原图的UV重新映射,主要用于摄像头校正。
DepthKeyingCompute:深度摄像头专用,结合深度图与上面的keyingCompute的导向滤波算法,对应如上的RealSense Camera,可以做到自然环境下的扣图。
DepthProcessCompute:深度摄像头专用,原始深度图需要做很多处理,比如对齐,去燥,这里主要把RealSense SDK的CPU算法全改成Compute Shader,不然做不到二个RealSense对齐等算法后还能同时30桢,RealSense的SDK设计有些奇怪,需要在同一线程把所有设备的数据全拿出来,但是可以在不同的线程去处理这些数据,所以这里先是在同一线程读取数据,然后是各取设备里的线程去读取对应数据,然后用GPU处理,这样才能做到选择最高分辨率颜色1080,深度720后加上后处理还能多个RealSense同时30桢。
在这总结下Compute shader遇上的坑。
1. ID3D11Texture2D的宽度最好为32的倍数,不然map数据需要根据RowPitch来调整。(在这上一共遇到二次,第一次组织内存数据上传到纹理中,发现结果不对,第二次,1920*1080的图处理后加上倒转成1080*1920,通过在UE4/Unity3D的GPU更新没问题,倒是在测试项目里读出内存数据放入opencv的mat里,发现图不对了,后面想到这里,试了试用1088*1920,结果显示正确).
2. Compute shader运行的结果全是0,没有报错,可能是一个buffer给了几个uav。
3. Const buffer中结构与传入的C++结构对应,如int与float不对应,就会导致传入的数据不对,并且数据要是4字节整倍,不要想把bool放入,bool应转化成int放入。
4. Compute shader如果逻辑要针对texture多次采样,可能考虑使用groupshared/GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync来改变逻辑提高效率。
5. Compute shader里面加入了头文件,如果Compute shader变成了资源文件,那么头文件引用就会失效,用ID3DInclude包含头文件来编译Compute shader.
6. Compute shader使用条件编译符,可以在头部用ifndef包含下默认定义,这样还可以用hlsl编译不会出错,后面编译shader传的编译指令会覆盖默认。
7. 在uav里每段GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync里反复读写uav,结果可能不是你想要的,试试分开shader,每次写调用一次Dispatch。
8. uv与线程调度的每块对应关系,如果你感觉你算的uv放入你纹理算的不对,如多次blur感觉有移位,可以试下如下uv算法float2 uv = float2((DTid.x+0.5) / sizeX, (DTid.y +0.5)/ sizeY),这条是上面写keyingCompute的牛人根据遇到问题总结出来的。(20181115,在查看CUDA提供的例子里simpleLayeredTexture里有提到,在纹理中,访问原始数据点需要0.5f偏移和除法,这样就不会激活双线性插值,这个应该是科学的解释)。
Compute shader的部分到此结束,我们开始说下MainCompute,这个类包装一个DX的设备与上下文,如果想每个设备或是线程想不互相干扰,在各自线程声明自己的MainCompute,每个数据处理ComputeBasic初始化时会要求一个MainCompute,这样设备与处理就绑定在自己的上下文中互不影响。
对于数据提供者,我在上面拉出三个,一个是我们本文在讲的视频捕获设备,二是如何网络直播传输带alpha的rgba数据,三是通过Mediafoundation生成H264视频,这三个部分我们都可以通过上面dx让GPU来完成其中所需要的大量图片处理。
本文主要记录视频捕获设备的基本实现思路,如上图,主要有二种视频捕获设备,一种是免驱的webcamera,一种是decklink,二者继承VideoDevice,后续的设想,视频以及上面不支持的采集视频都可以继承这个类,通过这个类提供同种接口。
Mediafoundation与decklink都提供异步读取数据,需要注意的是,这里异步只是隐藏了线程的实现,用同步只是多了个线程的调用,你还是要把你逻辑传入给他隐藏的线程调用,并且因为线程的隐藏,你更要注意操作相关资源时需要处理相应同步数据,不然关闭时,很容易因为二个线程互相还握有同一资源,造成关闭时崩溃。
在这也总结下我常用的三种同步方法,一是锁定资源,同步访问,直接用std::lock_guard区域锁就好,如果是关闭对象,还有线程在引用对象上变量,加个flag配合使用。二是在一个线程里等待另一个线程执行完,锁的资源一般不在同一函数内,一般用std::unique_lock/std::condition_variable配合使用,使用信号量wait_for合理时间。三是在一个线程等待多个线程完成,用std::future/std::async配合完成比较轻松。
我取一段VideoProcess里的代码,可以看下如何根据不同的源始数据与目标数据,来组装ComputeBasic列表的流水线。
如上,数据经过流水线处理完成后,就是包装,考虑到导出给UE4/Unity3D二者能使用同一份,我们使用C的导出方式,如下列出几个API.
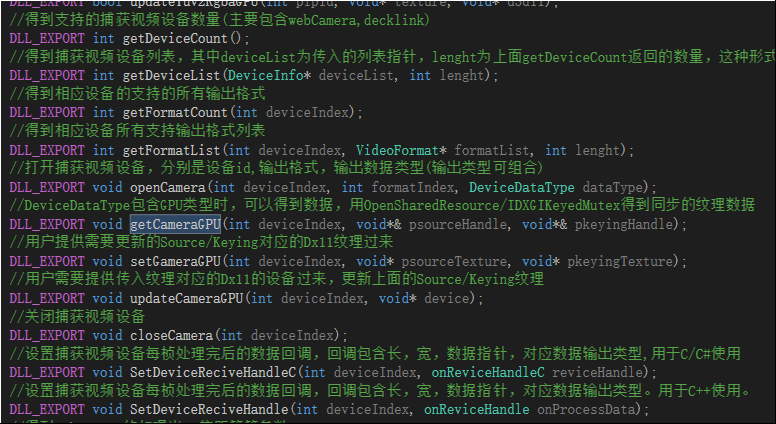
考虑到C++用静态函数当函数指针会导致代码写法与可读性变脏,故带有函数指针的方法会提供二个,如上。
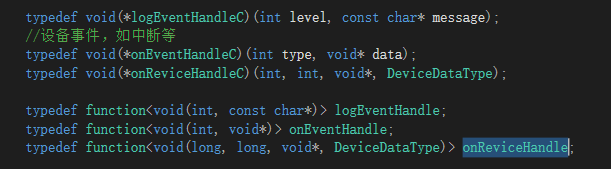
DLL内部指针传递全用的C++11标准里的function,再给C/C#的接口时,会加一个C里的函数针转接一下。
包装好后,我们再建立一个C++的测试项目,针对图形上的显示,我们引用opencv来做测试,注意一点,opencv默认使用bgra,我们要先用如上的通道映射成rgba,然后使用opencv查看查看各个功能是否正常,根据测试,再反馈前面调整相应逻辑,使接口更方便使用,我们可以给UE4/Unity3D使用了。
下面贴出共享纹理buffer如何复制到另一个dx上下文的代码,这段代码是解决如何在二个不同的上下文之间共享。通过这样,我们就能直接在UE4/Unity3D中线程与当前线程中不同的上下文之间直接复制GPU数据。

一 得到共享buffer的共享句柄。 mc->CreateTextureBuffer(nullptr, showWidth, showHeight, DXGI_FORMAT_R8G8B8A8_UNORM, &keyingTexture, false, true); textureDesc.MiscFlags = D3D11_RESOURCE_MISC_SHARED_KEYEDMUTEX; keyingSharedHandle = MainCompute::GetSharedHandle(keyingTexture); HANDLE MainCompute::GetSharedHandle(ID3D11Resource * source) { HANDLE Hnd = nullptr; // QI IDXGIResource interface to synchronized shared surface. IDXGIResource* DXGIResource = nullptr; HRESULT hr = source->QueryInterface(__uuidof(IDXGIResource), reinterpret_cast<void**>(&DXGIResource)); if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { // Obtain handle to IDXGIResource object. DXGIResource->GetSharedHandle(&Hnd); DXGIResource->Release(); DXGIResource = nullptr; } return Hnd; } 二 我们在当前上下文中给共享纹理赋值,注意同步。 CComPtr<IDXGIKeyedMutex> pDX11Mutex = nullptr; auto hResult = keyingTexture->QueryInterface(__uuidof(IDXGIKeyedMutex), (LPVOID*)&pDX11Mutex); DWORD result = pDX11Mutex->AcquireSync(0, syncTime); if (result == WAIT_OBJECT_0) { mc->CopyBuffer(keyingTexture, tc->GetResultBuffer()); result = pDX11Mutex->ReleaseSync(1); if (result == WAIT_OBJECT_0 && onProcessData) onProcessData(videoFormat.width, videoFormat.height, keyingSharedHandle, KeyingGPU); } 三 从UE4/Unity3D的上下文得到这个共享buffer的数据 void copySharedToTexture(ID3D11Device * d3ddevice, HANDLE & sharedHandle, ID3D11Texture2D * texture) { if (!d3ddevice) return; ID3D11DeviceContext* d3dcontext = nullptr; d3ddevice->GetImmediateContext(&d3dcontext); if (!d3dcontext) return; if (sharedHandle && texture) { CComPtr<ID3D11Texture2D> pBuffer = nullptr; HRESULT hr = d3ddevice->OpenSharedResource(sharedHandle, __uuidof(ID3D11Texture2D), (void**)(&pBuffer)); if (FAILED(hr)) { LogMessage(error, "open shared texture error."); } CComPtr<IDXGIKeyedMutex> pDX11Mutex = nullptr; auto hResult = pBuffer->QueryInterface(__uuidof(IDXGIKeyedMutex), (LPVOID*)&pDX11Mutex); if (FAILED(hResult) || (pDX11Mutex == nullptr)) { LogMessage(error, "get IDXGIKeyedMutex failed."); return; } DWORD result = pDX11Mutex->AcquireSync(1, syncTime); if (result == WAIT_OBJECT_0) { d3dcontext->CopyResource(texture, pBuffer); result = pDX11Mutex->ReleaseSync(0); } } }
我们先说UE4里的,先看下在UE4里简单封装调用。

struct CameraSetting { KeyingSetting ks = {}; TextureOperate sourceTo = {}; TextureOperate keyingTo = {}; TextureOperate transportTo = {}; DepthSetting ds = {}; }; class MRCORETEST_API CameraCommon { private: UTexture2D* sourceTex = nullptr; UTexture2D* keyingTex = nullptr; DeviceInfo* device = nullptr; CameraSetting* cameraSetting = nullptr; TArray<VideoFormat> formatList; VideoFormat format = {}; bool bSetCamera = false; bool bSetFormat = false; public: int GetIndex() { return device->id; } bool IsInit() { return bSetCamera && bSetFormat; } bool IsOpen() { if (IsInit()) return bOpen(device->id); else return false; } bool IsDepth() { if (bSetCamera) return bDepth(device->id); return false; } UTexture2D* GetSourceTex() { return sourceTex; } UTexture2D* GetKeyingTex() { return keyingTex; } DeviceInfo* GetDevice() { return device; } DeviceDataType GetDataType() { if (IsOpen()) return getDataType(device->id); return DeviceDataType::None; } TArray<VideoFormat>& GetFormatList() { return formatList; } VideoFormat& GetCurrentFormat() { return format; } CameraSetting& GetCameraSetting() { return *cameraSetting; } public: void SetCameraIndex(int index, CameraSetting* cameraSet = nullptr); void SetFormatIndex(int index); void Update(); bool Open(bool bTrans, bool bKeying = true); void Close(); void UserPostProcess(bool bUser); void UserBG(bool bUser); bool SaveBGFile(FString path); bool LoadBG(FString path); private: void InitTexture(); void updateTexture(UTexture2D** texture, int width, int height); void findFormatIndex(int cameraIndex, int& first, int& second, int& three); public: CameraCommon(); ~CameraCommon(); }; #include "CameraCommon.h" CameraCommon::CameraCommon() { device = new DeviceInfo(); cameraSetting = new CameraSetting(); } CameraCommon::~CameraCommon() { delete device; delete cameraSetting; if (sourceTex->IsValidLowLevel()) { sourceTex->RemoveFromRoot(); sourceTex->ConditionalBeginDestroy(); sourceTex = nullptr; } if (keyingTex->IsValidLowLevel()) { keyingTex->RemoveFromRoot(); keyingTex->ConditionalBeginDestroy(); keyingTex = nullptr; } } void CameraCommon::SetCameraIndex(int index, CameraSetting * cameraSet) { bSetFormat = false; bSetCamera = false; int count = getDeviceCount(); if (index >= 0 && index < count) { getDeviceIndex(index, device); bSetCamera = true; } if (bSetCamera) { int count = getFormatCount(index); formatList.SetNumUninitialized(count); getFormatList(index, formatList.GetData(), count); //获取当前参数的默认设置 if (cameraSet != nullptr) { memcpy(&cameraSetting, cameraSet, sizeof(CameraSetting)); } else { getKeySetting(index, &cameraSetting->ks); getTextureOperate(index, &cameraSetting->sourceTo, SourceRGBA32); getTextureOperate(index, &cameraSetting->keyingTo, Keying); getTextureOperate(index, &cameraSetting->transportTo, TransportYUVA); getDepthSetting(index, &cameraSetting->ds); } } } void CameraCommon::SetFormatIndex(int index) { if (!bSetCamera) return; bSetFormat = false; if (index < 0 || index >= formatList.Num()) { int first = -1; int second = -1; int three = 0; findFormatIndex(0, first, second, three); index = first >= 0 ? first : (second >= 0) ? second : three; } if (index >= 0 && index < formatList.Num()) { format = formatList[index]; bSetFormat = true; InitTexture(); } } void CameraCommon::Update() { if (!IsOpen()) return; auto dataType = GetDataType(); if ((dataType & SourceRGBA32GPU) == SourceRGBA32GPU || (dataType & SourceRGBA32) == SourceRGBA32) { updateTextureOperate(device->id, &cameraSetting->sourceTo, SourceRGBA32); } if ((dataType & KeyingGPU) == KeyingGPU || (dataType & Keying) == Keying) { updateKeySetting(device->id, &cameraSetting->ks); updateTextureOperate(device->id, &cameraSetting->keyingTo, Keying); } if ((dataType & TransportYUVA) == TransportYUVA) { updateTextureOperate(device->id, &cameraSetting->transportTo, TransportYUVA); } if (IsDepth()) updateDepthSetting(device->id, &cameraSetting->ds); ENQUEUE_UNIQUE_RENDER_COMMAND_ONEPARAMETER( UpdateCameraTexture, int, cameraIndex, device->id, { void* device = RHICmdList.GetNativeDevice(); if (device != nullptr) { updateCameraGPU(cameraIndex, device); } }); } bool CameraCommon::Open(bool bTrans, bool bKeying) { if (!IsInit() || IsOpen()) return false; auto dataType = SourceRGBA32GPU; if (bKeying) dataType = (DeviceDataType)(dataType | KeyingGPU); if (bTrans) dataType = (DeviceDataType)(dataType | TransportYUVA); return openCamera(device->id, format.index, dataType); } void CameraCommon::Close() { if (!IsInit() || !IsOpen()) return; closeCamera(device->id); bSetFormat = false; bSetCamera = false; } void CameraCommon::UserPostProcess(bool bUser) { if (!IsInit() || !IsDepth()) return; setUserPostProcess(device->id, bUser); } void CameraCommon::UserBG(bool bUser) { if (!IsOpen() || !IsDepth()) return; saveBG(device->id, bUser); } bool CameraCommon::SaveBGFile(FString path) { if (!IsOpen() || !IsDepth()) return false; return saveBGToFile(device->id, *path); } bool CameraCommon::LoadBG(FString path) { if (!IsOpen() || !IsDepth()) return false; return loadBG(device->id, *path); } void CameraCommon::InitTexture() { if (!bSetFormat) return; updateTexture(&sourceTex, format.width, format.height); updateTexture(&keyingTex, format.width, format.height); ENQUEUE_UNIQUE_RENDER_COMMAND_THREEPARAMETER( SetCameraTexture, int, cameraIndex, device->id, UTexture2D*, cameraSourceTex, sourceTex, UTexture2D*, cameraKeyingTex, keyingTex, { auto sourceResource = cameraSourceTex->Resource->TextureRHI->GetNativeResource(); auto keyingResource = cameraKeyingTex->Resource->TextureRHI->GetNativeResource(); setGameraGPU(cameraIndex, sourceResource, keyingResource); }); } void CameraCommon::updateTexture(UTexture2D ** ptexture, int width, int height) { UTexture2D * texture = *ptexture; bool bValid = texture->IsValidLowLevel(); bool bChange = false; if (bValid) { int twidth = texture->GetSizeX(); int theight = texture->GetSizeY(); bChange = (twidth != width) || (theight != height); if (bChange) { texture->RemoveFromRoot(); texture->ConditionalBeginDestroy(); texture = nullptr; } } if (!bValid || bChange) { *ptexture = UTexture2D::CreateTransient(width, height, PF_R8G8B8A8); (*ptexture)->UpdateResource(); (*ptexture)->AddToRoot(); } } void CameraCommon::findFormatIndex(int cameraIndex, int & first, int & second, int & three) { first = -1; second = -1; three = 0; if (!bSetFormat) return; int index = 0; VideoFormat preFormat = formatList[0]; for (VideoFormat format : formatList) { if (format.width == 1920 && format.height == 1080) { if (format.fps == 30) { //MJPG需要解码,损失CPU,默认不找MJPG格式的 if (format.videoType != VideoType::MJPG) { first = index; } else if (first == -1) { first = index; } } else if (format.fps >= 20 && format.fps <= 60) { if (format.videoType != VideoType::MJPG) { second = index; } else if (second == -1) { second = index; } } } //如果没有1920*1080 20fps的,选一个最合适的 if (format.height >= preFormat.height && format.width >= preFormat.height && format.fps >= 20 && format.fps <= 60) { //桢优先然后是格式 if (format.fps > preFormat.fps || (format.fps == preFormat.fps && format.videoType != VideoType::MJPG)) { three = index; preFormat = format; } } index++; } }
这个脚本用的是GPU更新方式,CPU更新方式把注册对应事件能拿到对应CPU数据然后自己填充到UE4纹理,这里就不提供了,代码不多,GPU更新去掉中间的CPU转接过程效率会高不少,开多少个设备都不影响游戏的显示。ENQUEUE_UNIQUE_RENDER_COMMAND_TWOPARAMETER我原来介绍UE4的渲染线程里提过,这里就简单提下,因为我们要拿到原生的Dx11的设备与dx11的纹理指针,我们必需在RHI线程中才能访问到,这个宏能帮我们生成一个类,提交宏里的逻辑到渲染线程的队列中去执行。
如下是UE4中显示效果。

Unity3D里的要麻烦一点,直接在C#里是拿不到Unity3D在用的dx11上下文与对应的纹理指针,好在Unity3D也提供原生的插件让我们来做到这一点(https://docs.unity3d.com/530/Documentation/Manual/NativePluginInterface.html),我们需要的是写一个Unity3D的原生插件,再包装一下我们上面提供的接口。可以看到,我们并没做太多的事,主要就是拿到d3d11设备,调用我们之前的接口。
如下在Unity3D里的包装。

#pragma once #include "IUnityGraphics.h" typedef void (UNITY_INTERFACE_API * UnityRenderingEvent)(int eventId); #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif // If exported by a plugin, this function will be called when the plugin is loaded. void UNITY_INTERFACE_EXPORT UNITY_INTERFACE_API UnityPluginLoad(IUnityInterfaces* unityInterfaces); // If exported by a plugin, this function will be called when the plugin is about to be unloaded. void UNITY_INTERFACE_EXPORT UNITY_INTERFACE_API UnityPluginUnload(); void UNITY_INTERFACE_EXPORT UNITY_INTERFACE_API OnGraphicsDeviceEvent(UnityGfxDeviceEventType eventType); void UNITY_INTERFACE_EXPORT UNITY_INTERFACE_API SetCameraTexture(int cameraID, void* sourceTexture, void* keyingTexture); void UNITY_INTERFACE_EXPORT UNITY_INTERFACE_API UpdateTexture(int cameraID); UNITY_INTERFACE_EXPORT UnityRenderingEvent UNITY_INTERFACE_API GetRenderEventFunc(); #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif #include "UnityExport.h" #include <d3d11.h> #include <MRCommon.h> #include "IUnityGraphicsD3D11.h" #include <atlbase.h> #include <map> #include <memory> static IUnityInterfaces* s_UnityInterfaces = nullptr; static IUnityGraphics* s_Graphics = nullptr; static UnityGfxRenderer s_DeviceType = kUnityGfxRendererNull; static ID3D11Device* g_D3D11Device = nullptr; static ID3D11DeviceContext* g_pContext = nullptr; void UNITY_INTERFACE_API UnityPluginLoad(IUnityInterfaces * unityInterfaces) { s_UnityInterfaces = unityInterfaces; s_Graphics = s_UnityInterfaces->Get<IUnityGraphics>(); s_Graphics->RegisterDeviceEventCallback(OnGraphicsDeviceEvent); // Run OnGraphicsDeviceEvent(initialize) manually on plugin load OnGraphicsDeviceEvent(kUnityGfxDeviceEventInitialize); } void UNITY_INTERFACE_API UnityPluginUnload() { s_Graphics->UnregisterDeviceEventCallback(OnGraphicsDeviceEvent); } void UNITY_INTERFACE_API OnGraphicsDeviceEvent(UnityGfxDeviceEventType eventType) { switch (eventType) { case kUnityGfxDeviceEventInitialize: { s_DeviceType = s_Graphics->GetRenderer(); if (s_DeviceType != kUnityGfxRendererD3D11) { writeMessage(error, "暂时只支持dx11."); } IUnityGraphicsD3D11* d3d11 = s_UnityInterfaces->Get<IUnityGraphicsD3D11>(); g_D3D11Device = d3d11->GetDevice(); g_D3D11Device->GetImmediateContext(&g_pContext); break; } case kUnityGfxDeviceEventShutdown: writeMessage(error, "unity mr关闭."); break; }; } void UNITY_INTERFACE_API SetCameraTexture(int cameraID, void * sourceTexture, void * keyingTexture) { ID3D11Texture2D* sourceResource = nullptr; ID3D11Texture2D* keyingResource = nullptr; if (sourceTexture) sourceResource = reinterpret_cast<ID3D11Texture2D*>(sourceTexture); if (keyingTexture) keyingResource = reinterpret_cast<ID3D11Texture2D*>(keyingTexture); setGameraGPU(cameraID, sourceResource, keyingResource); } void UNITY_INTERFACE_API UpdateTexture(int cameraID) { if (g_D3D11Device == nullptr) return; updateCameraGPU(cameraID, g_D3D11Device); } UNITY_INTERFACE_EXPORT UnityRenderingEvent UNITY_INTERFACE_API GetRenderEventFunc() { return UpdateTexture; }
说一下这里的一个坑,当时并没想为什么要用GL.IssuePluginEvent,直接调用的更新纹理,发现运行时很容易崩,后面想了下,和UE4里一样,应该是有个渲染线程专门来更新渲染,Unity3d脚本里虽然暴露给我们的只有一个主线程,但如果直接在这个主线程里调用原生d3d11更新设备,二边线程可能操纵了同一块资源,后面改为使用GL.IssuePluginEvent来发送给底层渲染线程来更新纹理,GL.IssuePluginEvent需要传入的是个函数也是这个原因,问题解决。这里Unity3D里没提供CPU更新,因为慢的我受不了。
如下是Unity针对上面接口的再包装,主要是C++与C#的交互封装。

[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, CharSet = CharSet.Unicode)] public struct DeviceInfo { public int id; [MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.ByValArray, SizeConst = 128)] public char[] deviceName; [MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.ByValArray, SizeConst = 128)] public char[] deviceID; } [Serializable] public struct TextureOperate { public bool bFlipX;// = false; public bool bFlipY;// = false; public int mapR;// = 0; public int mapG;// = 1; public int mapB;// = 2; public int mapA;// = 3; }; [UnmanagedFunctionPointer(CallingConvention.Cdecl)] public delegate void LogHandlerDelegate(int level, string message); [UnmanagedFunctionPointer(CallingConvention.Cdecl)] public delegate void OnDataReviceDelegate(int width, int height, IntPtr data, DeviceDataType dataType); public static class MRCommonHelper { const string mrDll = "MRCommon"; const string mrUnityDll = "MRUnityPlugins"; public const CallingConvention importCall = CallingConvention.Cdecl; [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void SetLogHandleC(LogHandlerDelegate handler); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void initMedia(); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void shutdownMedia(); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern int getDeviceCount(); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern int getDeviceList(IntPtr deviceList, int lenght); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern int getFormatList(int deviceIndex, IntPtr formatList, int lenght); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern int getFormatCount(int deviceIndex); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void getDeviceParametrs(int deviceIndex, out CamParametrs parametrs); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void setDeviceParametrs(int deviceIndex, ref CamParametrs parametrs); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void updateSetting(int deviceIndex, ref KeyingSetting ksetting, ref TextureOperate tsetting); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void getSetting(int deviceIndex, ref KeyingSetting ksetting, ref TextureOperate tsetting); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void openCamera(int deviceIndex, int formatIndex, DeviceDataType dataType); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void closeCamera(int deviceIndex); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void setRotate(int deviceIndex,bool bRotate); [DllImport(mrDll, CallingConvention = importCall)] public static extern void SetDeviceReciveHandleC(int deviceIndex, OnDataReviceDelegate handle); [DllImport(mrUnityDll)] public static extern void SetCameraTexture(int cameraID, IntPtr sourceTexture, IntPtr keyingTexture); [DllImport(mrUnityDll)] public static extern IntPtr GetRenderEventFunc(); } [Serializable] public class CameraDevice { public int id = -1; public string deviceName = string.Empty; public string deviceID = string.Empty; public bool bOpen = false; } public class MediaManager : MSingleton<MediaManager> { private List<CameraDevice> cameraList = null; protected override void Init() { MRCommonHelper.initMedia(); MRCommonHelper.SetLogHandleC(logMessage); cameraList = GetCameraDeviceList(); } public void logMessage(int level, string message) { Debug.Log(message); } public bool GetCamera(int index, ref CameraDevice cameraDevice) { if (index >= 0 && index < cameraList.Count) { cameraDevice = cameraList[index]; return true; } cameraDevice = null; return false; } public List<CameraDevice> GetCameraDeviceList() { List<CameraDevice> cameraList = new List<CameraDevice>(); int count = MRCommonHelper.getDeviceCount(); Console.WriteLine(count); DeviceInfo[] deviceList = new DeviceInfo[count]; int deviceLenght = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(DeviceInfo)); byte[] data = new byte[deviceLenght * count]; GCHandle handle = GCHandle.Alloc(data, GCHandleType.Pinned); IntPtr pin = handle.AddrOfPinnedObject(); MRCommonHelper.getDeviceList(pin, count); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { deviceList[i] = ByteArrayToStructure<DeviceInfo>(data, pin, i * deviceLenght); } handle.Free(); foreach (var device in deviceList) { CameraDevice camera = new CameraDevice(); camera.id = device.id; camera.deviceID = new string(device.deviceID); camera.deviceName = new string(device.deviceName); cameraList.Add(camera); } return cameraList; } public List<VideoFormat> GetCameraFormatList(int index) { List<VideoFormat> cameraList = new List<VideoFormat>(); int count = MRCommonHelper.getFormatCount(index); Console.WriteLine(count); VideoFormat[] deviceList = new VideoFormat[count]; int deviceLenght = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(VideoFormat)); byte[] data = new byte[deviceLenght * count]; GCHandle handle = GCHandle.Alloc(data, GCHandleType.Pinned); IntPtr pin = handle.AddrOfPinnedObject(); MRCommonHelper.getFormatList(index, pin, count); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { deviceList[i] = ByteArrayToStructure<VideoFormat>(data, pin, i * deviceLenght); } handle.Free(); cameraList.AddRange(deviceList); return cameraList; } T ByteArrayToStructure<T>(byte[] bytes, IntPtr pin, int offset) where T : struct { try { return (T)Marshal.PtrToStructure(new IntPtr(pin.ToInt64() + offset), typeof(T)); } catch (Exception e) { return default(T); } } public override void Close() { MRCommonHelper.shutdownMedia(); } }
本来认为就一点代码,发现还是有点多,其实就是一个包装的皮,调出的这些代码主要记录下C++与C#的主要交互,关于多媒体音频与视频的部分就先不放出来了。
如下和UE4的逻辑差不多。

public class CameraCommon { private Texture2D sourceTex = null; private Texture2D keyingTex = null; private CameraDevice device = null; private List<VideoFormat> formatList = null; private VideoFormat format = new VideoFormat(); private bool bSetCamera = false; private bool bSetFormat = false; public CameraSetting cameraSetting = new CameraSetting(); public int Index { get { if (device == null) return -1; return device.id; } } public bool IsOpen { get { if (IsInit) return MRCommonHelper.bOpen(device.id); return false; } } public bool IsInit { get { return bSetCamera && bSetFormat; } } public bool IsDepth { get { if (bSetCamera) return MRCommonHelper.bDepth(device.id); ; return false; } } public Texture2D SourceTex { get { return sourceTex; } } public Texture2D KeyingTex { get { return keyingTex; } } public CameraDevice Device { get { return device; } } public List<VideoFormat> FormatList { get { return formatList; } } public VideoFormat Format { get { return format; } } /// <summary> /// 摄像机可能不是由当前DLL打开,我们直接获得 /// </summary> public DeviceDataType DataType { get { if (IsOpen) return MRCommonHelper.getDataType(device.id); return DeviceDataType.None; } } public void SetCameraIndex(int index, CameraSetting cameraSet = null) { bSetFormat = false; bSetCamera = false; if (index >= 0 && index < MRCommonManager.Instance.CameraList.Count) { device = MRCommonManager.Instance.CameraList[index]; bSetCamera = true; } if (bSetCamera) { formatList = MRCommonManager.Instance.GetCameraFormatList(index); //获取当前参数的默认设置 if (cameraSet != null) cameraSetting = cameraSet; if (cameraSetting.IsDefault()) { MRCommonHelper.getKeySetting(index, ref cameraSetting.ks); MRCommonHelper.getTextureOperate(index, ref cameraSetting.sourceTo, DeviceDataType.SourceRGBA32); MRCommonHelper.getTextureOperate(index, ref cameraSetting.keyingTo, DeviceDataType.Keying); MRCommonHelper.getTextureOperate(index, ref cameraSetting.transportTo, DeviceDataType.TransportYUVA); MRCommonHelper.getDepthSetting(index, ref cameraSetting.ds); } } } public void SetFormatIndex(int index) { if (!bSetCamera) return; bSetFormat = false; if (index < 0 || index >= formatList.Count) { int first = -1; int second = -1; int three = 0; MRCommonManager.Instance.FindFormatIndex(0, ref first, ref second, ref three); index = first >= 0 ? first : (second >= 0) ? second : three; Debug.Log("formindex:" + index + " first:" + first + " second:" + second + " three:" + three); } if (index >= 0 && index < formatList.Count) { format = formatList[index]; bSetFormat = true; InitTexture(); } } /// <summary> /// 这个函数要在Unity里主线程执行 /// </summary> public void InitTexture() { if (IsInit) { if (sourceTex == null || sourceTex.width != format.width || sourceTex.height != format.height) { sourceTex = new Texture2D(format.width, format.height, TextureFormat.RGBA32, false); sourceTex.Apply(); } if (keyingTex == null || keyingTex.width != format.width || keyingTex.height != format.height) { keyingTex = new Texture2D(format.width, format.height, TextureFormat.RGBA32, false); keyingTex.Apply(); } MRUnityHelper.SetCameraTexture(device.id, sourceTex.GetNativeTexturePtr(), keyingTex.GetNativeTexturePtr()); } } /// <summary> /// 这个函数要在Unity里主线程执行 /// </summary> public bool Update() { if (IsOpen) { var dataType = MRCommonHelper.getDataType(device.id); if ((dataType & DeviceDataType.SourceRGBA32GPU) == DeviceDataType.SourceRGBA32GPU || (dataType & DeviceDataType.SourceRGBA32) == DeviceDataType.SourceRGBA32) { MRCommonHelper.updateTextureOperate(device.id, ref cameraSetting.sourceTo, DeviceDataType.SourceRGBA32); } if ((dataType & DeviceDataType.KeyingGPU) == DeviceDataType.KeyingGPU || (dataType & DeviceDataType.Keying) == DeviceDataType.Keying) { MRCommonHelper.updateKeySetting(device.id, ref cameraSetting.ks); MRCommonHelper.updateTextureOperate(device.id, ref cameraSetting.keyingTo, DeviceDataType.Keying); } if ((dataType & DeviceDataType.TransportYUVA) == DeviceDataType.TransportYUVA) { MRCommonHelper.updateTextureOperate(device.id, ref cameraSetting.transportTo, DeviceDataType.TransportYUVA); } if (IsDepth) MRCommonHelper.updateDepthSetting(device.id, ref cameraSetting.ds); GL.IssuePluginEvent(MRUnityHelper.GetRenderCameraFunc(), device.id); return true; } return false; } public void Open(bool bTrans, bool bKeying = true) { if (!IsInit || IsOpen) return; var dataType = DeviceDataType.SourceRGBA32GPU; if (bKeying) dataType = dataType | DeviceDataType.KeyingGPU; if (bTrans) dataType = dataType | DeviceDataType.TransportYUVA; MRCommonHelper.openCamera(device.id, format.index, dataType); } public void Close() { if (!IsInit || !IsOpen) return; MRCommonHelper.closeCamera(device.id); bSetFormat = false; bSetCamera = false; } public void UserPostProcess(bool bUser) { if (!IsInit || !IsDepth) return; MRCommonHelper.setUserPostProcess(device.id, bUser); } public void UserBG(bool bUser) { if (!IsOpen || !IsDepth) return; MRCommonHelper.saveBG(device.id, bUser); } public bool SaveBGFile(string path) { if (!IsOpen || !IsDepth) return false; return MRCommonHelper.saveBGToFile(device.id, path); } public bool LoadBG(string path) { if (!IsOpen || !IsDepth) return false; return MRCommonHelper.loadBG(device.id, path); } }
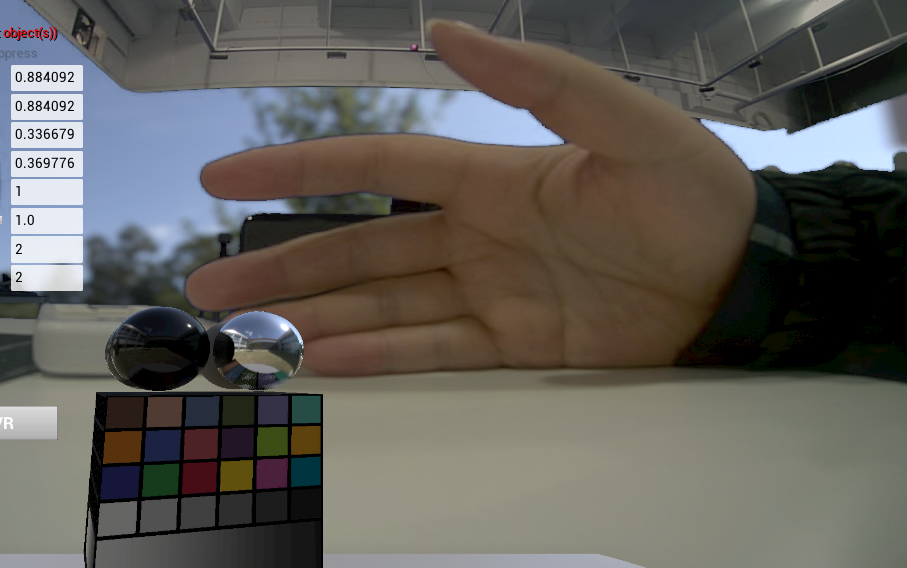
如下是在Unity里的显示效果。

二个设备,每个设备都开的都是1920*1080*30FPS,其中有张原图,有张扣色图,四张图一起更新,不影响Unity一点。
到这差不多就完了,最说简单说用Mediafoundation完成别的一些功能上遇到的坑 :
生成视频时:你提供的桢率要和你写入的速度对应上,不然视频的快慢会改变。
录系统声音时,用的是wasapi,录到一定大小,然后写到文件,释放内存,然后又录。顺便说下,C++标准中,想后期改文件,需要用std::ios::in | std::ios::ate,用app只能在最后追加,不能修改前面的值,单独的ate会删除文件。
用MF合成音频与视频文件,视频文件是H264压缩格式,音频也必需是mp3或是acc,pcm转acc就和把图片流压缩成h264在MF中的写法差不多,没什么问题,在合成时发现,单独把音频或是视频写到一个文件很快,但是一块就非常慢,其中搜到说是同时写视频与音频的会有一个同步时间戳的问题,后面需要把写音频与写视频分开用线程写,结果秒合,如下是改进后代码。

//合成视频 hr = pSinkWriter->BeginWriting(); //https://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/windowsdesktop/en-US/20727947-98fe-4245-ad3a-8056d168a1b5/imfsinkwriter-very-slow-and-use-of-mfsinkwriterdisablethrottling?forum=mediafoundationdevelopment //这里是个大坑,在一个线程同时写音频与视频会导致pSinkWriter->WriteSample非常慢,因为同时写的时候,会自动去同步音频与视频的时间戳. //在同一线程就会造成要同步时就卡一段时间,故用二个线程同时写,让pSinkWriter->WriteSample能自动同步不需要等待 std::future<bool> writeVideo = std::async([&videoReader, &videoIndex, &pSinkWriter, &audioTime]() { bool result = true; LONGLONG videoTimeStamp = 0;// 100-nanosecond units.100纳秒 1秒= 1000000000纳秒 while (true) { DWORD streamIndex, flags; CComPtr<IMFSample> videoSample = nullptr; HRESULT hr = videoReader->ReadSample(MF_SOURCE_READER_FIRST_VIDEO_STREAM, 0, &streamIndex, &flags, &videoTimeStamp, &videoSample); if (SUCCEEDED(hr) && videoSample) { videoSample->SetSampleTime(videoTimeStamp); hr = pSinkWriter->WriteSample(videoIndex, videoSample); } else { if (FAILED(hr)) result = false; break; } if (videoTimeStamp > audioTime) break; } return result; }); std::future<bool> writeAudio = std::async([&audioReader, &audioIndex, &pSinkWriter, &videoTime]() { bool result = true; LONGLONG audioTimeStamp = 0; while (true) { DWORD streamIndex, flags; CComPtr<IMFSample> audioSample = nullptr; HRESULT hr = audioReader->ReadSample(MF_SOURCE_READER_FIRST_AUDIO_STREAM, 0, &streamIndex, &flags, &audioTimeStamp, &audioSample); if (SUCCEEDED(hr) && audioSample) { audioSample->SetSampleTime(audioTimeStamp); hr = pSinkWriter->WriteSample(audioIndex, audioSample); } else { if (FAILED(hr)) result = false; break; } if (audioTimeStamp > videoTime) break; } return result; }); bool result = writeVideo.get() && writeAudio.get(); pSinkWriter->Finalize();
以后有时间讲下,如何用VS2015编写C++的安卓插件,还有用vs2015与安卓模拟器调试在C++项目中调试,并把生成的so文件给unity3d使用。
