不难看出,这是一道图论的题,只要要求在(r),的个数最小时,(r)的个数与文章长度。
预备知识
- STL之map (内置应该是hash之类的)
- tarjan缩点
- 树形dp
- 简单字符串
- 邻接表存边
问题分析
由于同义是单向的,我们建起了单向边,容易的是,如果一个单词可以最后回到他自己,那就把这个环上的点缩成一个scc,记下每个scc的最优(r)和最优(leg)(即(length)但我由于个人原因更喜欢用(lgh))
在对我们所得的每一个强连通,进行重构图。最后跑一个(dp)即可(可以用深搜实现)
统计答案时,对每一个word独立操作即可
如果你还是不太清楚,我们再来看图(样例一)
我们先建一个对应关系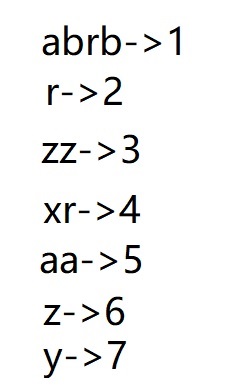
然后,我们间的图即为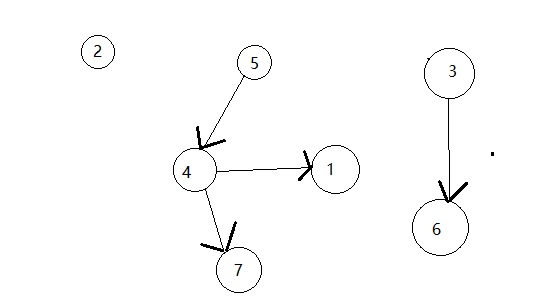
然后,我们先进行缩点,然后统计出每个强连通的最优值,最后跑一遍树形dp就可以了
其实只要看清楚这个题的意思,就很好AC了
时间复杂度分析
- tarjan O(n+m)
- 统计最优值 O(n)
- 树形dp O(n)
好的没有毒瘤(n^2) ,此题可过
附上代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int Maxn=1e5+1;
map<string,int> wd2;
int num,n,m,cnt,leg[Maxn],r[Maxn],h[Maxn],vcnt,col[Maxn],dfn[Maxn],low[Maxn],dep,sta[Maxn],top;
bool fsta[Maxn],flag[Maxn];
long long ans1,ans2;
string word[Maxn],str1,str2;
struct Edge{
int fr,to,lac;
}edge[Maxn];
struct Node{
int rmin,legmin;
}scc[Maxn];
int read(){
int x=0;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') ch=getchar();
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0'){
x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch-'0');
ch=getchar();
}
return x;
}
char me(char ch){
if(ch>='A'&&ch<='Z') ch+=32;
return ch;
}
void insert(int x,int y){
edge[vcnt].fr=x;
edge[vcnt].to=y;
edge[vcnt].lac=h[x];
h[x]=vcnt++;
}
string Getstr(){
string str;
char ch=getchar();
while(!((ch>='A'&&ch<='Z')||(ch>='a'&&ch<='z'))){
ch=getchar();
}
while((ch>='A'&&ch<='Z')||(ch>='a'&&ch<='z')){
str+=me(ch);
ch=getchar();
}
return str;
}
void make(string str){
leg[cnt]=str.size();
for(int i=0;i<=str.size();i++){
if(str[i]=='r') r[cnt]++;
}
return ;
}
void sol(string str){
if(wd2[str]==0){
wd2[str]=++cnt;
make(str);
}
}
void tarjan(int u){
dfn[u]=low[u]=++dep;
sta[++top]=u;fsta[u]=1;
for(int i=h[u];i!=-1;i=edge[i].lac){
int to=edge[i].to;
if(dfn[to]){
if(fsta[to]) low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[to]);
continue;
}
tarjan(to);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[to]);
}
if(low[u]==dfn[u]){
num++;
while(fsta[u]){
fsta[sta[top]]=0;
col[sta[top--]]=num;
}
}
return ;
}
void dfs(int u){
flag[u]=1;
for(int i=h[u];i!=-1;i=edge[i].lac){
int to=edge[i].to;
if(!flag[to]) dfs(to);
if(scc[to].rmin<=scc[u].rmin){
if(scc[to].rmin<scc[u].rmin) scc[u].legmin=scc[to].legmin;
else scc[u].legmin=min(scc[u].legmin,scc[to].legmin);
scc[u].rmin=scc[to].rmin;
}
}
return ;
}
int main() {
// wd1 int-> str 每个str的号->对应str
// wd2 str-> int 每个strstr对应 号
// freopen("puditan.in","r",stdin);
m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) {
word[i]=Getstr();
sol(word[i]);
}
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
n=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
str1=Getstr(),str2=Getstr();
sol(str1);sol(str2);
insert(wd2[str1],wd2[str2]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)
if(!dfn[i])
tarjan(i);//cnt指节点个数
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++) scc[i].legmin=0x3f3f3f3f,scc[i].rmin=0x3f3f3f3f;//num是强连通
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)
if(scc[col[i]].rmin>=r[i]){
if(scc[col[i]].rmin>r[i]) scc[col[i]].legmin=leg[i];
else scc[col[i]].legmin=min(scc[col[i]].legmin,leg[i]);
scc[col[i]].rmin=r[i];
}
int q=vcnt;
vcnt=0;
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
for(int i=0;i<q;i++){
int to=edge[i].to,fr=edge[i].fr;
if(col[to]==col[fr]) continue;
insert(col[fr],col[to]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++) if(!flag[i]) dfs(i);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
ans1+=scc[col[wd2[word[i]]]].rmin;
ans2+=scc[col[wd2[word[i]]]].legmin;
}
printf("%lld %lld",ans1,ans2);
return 0;
}
感想 ,这道题拖了很久没做,还是内心的惧怕呀