Bubble Sort
Bubble Sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in wrong order.
Example:
First Pass:
( 5 1 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 5 4 2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
( 1 5 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 5 2 8 ), Swap since 5 > 4
( 1 4 5 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
Second Pass:
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 )
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
Now, the array is already sorted, but our algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.
Third Pass:
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
// Java program for implementation of Bubble Sort class BubbleSort { void bubbleSort(int arr[]) { int n = arr.length; for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) { // swap arr[j+1] and arr[i] int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j+1]; arr[j+1] = temp; } } /* Prints the array */ void printArray(int arr[]) { int n = arr.length; for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); System.out.println(); } // Driver method to test above public static void main(String args[]) { BubbleSort ob = new BubbleSort(); int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90}; ob.bubbleSort(arr); System.out.println("Sorted array"); ob.printArray(arr); } } /* This code is contributed by Ethan */Sorted array: 11 12 22 25 34 64 90
Optimized Implementation:
The above function always runs O(n^2) time even if the array is sorted. It can be optimized by stopping the algorithm if inner loop didn’t cause any swap.
// Optimized java implementation // of Bubble sort import java.io.*; class GFG { // An optimized version of Bubble Sort static void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) { int i, j, temp; boolean swapped; for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { swapped = false; for (j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { // swap arr[j] and arr[j+1] temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = temp; swapped = true; } } // IF no two elements were // swapped by inner loop, then break if (swapped == false) break; } } // Function to print an array static void printArray(int arr[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); System.out.println(); } // Driver program public static void main(String args[]) { int arr[] = { 64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90 }; int n = arr.length; bubbleSort(arr, n); System.out.println("Sorted array: "); printArray(arr, n); } } // This code is contributed // by Nikita Tiwari. |
Output:
Sorted array: 11 12 22 25 34 64 90
Worst and Average Case Time Complexity: O(n*n). Worst case occurs when array is reverse sorted.
Best Case Time Complexity: O(n). Best case occurs when array is already sorted.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Boundary Cases: Bubble sort takes minimum time (Order of n) when elements are already sorted.
Sorting In Place: Yes
Stable: Yes
Due to its simplicity, bubble sort is often used to introduce the concept of a sorting algorithm.
In computer graphics it is popular for its capability to detect a very small error (like swap of just two elements) in almost-sorted arrays and fix it with just linear complexity (2n). For example, it is used in a polygon filling algorithm, where bounding lines are sorted by their x coordinate at a specific scan line (a line parallel to x axis) and with incrementing y their order changes (two elements are swapped) only at intersections of two lines (Source: Wikipedia)
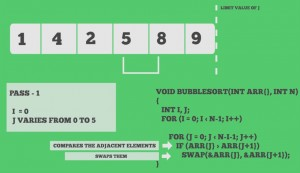
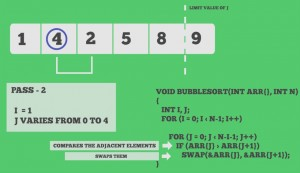
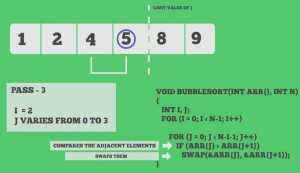
Snapshots:


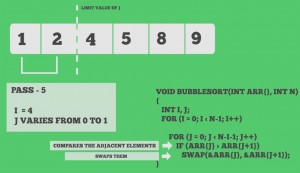
Quiz on Bubble Sort
Other Sorting Algorithms on GeeksforGeeks/GeeksQuiz: