1.函数和类也是对象,属于python的一等公民
-
赋值给一个变量
-
可以添加到集合对象之中
-
可以作为参数传递给函数
-
可以当作函数的返回值
1 def ask(name="ask_wzh"):
2 print(name)
3
4
5 class Person:
6 def __init__(self):
7 print("Person_wzh")
8
9
10 # 函数赋值给变量
11 my_fun = ask
12 my_fun("王智豪") # 王智豪
13
14 # 类赋值给变量
15 my_class = Person
16 my_class() # Person_wzh
17
18 # 添加到集合对象之中
19 obj_list = []
20 obj_list.append(ask)
21 obj_list.append(Person)
22
23 for item in obj_list:
24 print(item()) # ask_wzh,None,Person_wzh,<__main__.Person object at 0x033DC4C0>
25
26
27 # 作为参数和返回值
28 def decorator_func(fun):
29 print("dec start")
30 return fun
31
32
33 dec_func = decorator_func(ask) # dec start
34 dec_func() # ask_wzh
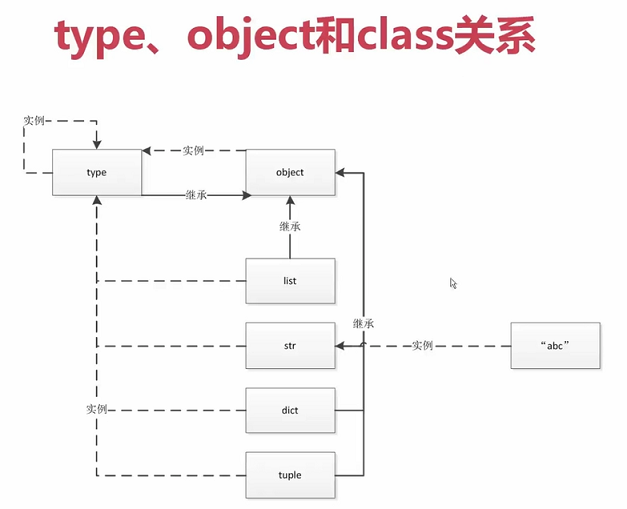
2.type、object和class的关系
- 所有类的类型都是type
- 所有类的最上层基类是object类
- type也是一个类,同时type也是一个对象
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 __author__ = 'bobby'
3 a = 1
4 b = "abc"
5 print(type(1)) # <class 'int'>
6 print(type(int)) # <class 'type'>
7 print(type(b)) # <class 'str'>
8 print(type(str)) # <class 'type'>
9
10
11 class Student:
12 pass
13
14
15 stu = Student()
16 print(type(stu)) # <class '__main__.Student'>
17 print(type(Student)) # <class 'type'>
18 print(int.__bases__) # (<class 'object'>,)
19 print(str.__bases__) # (<class 'object'>,)
20 print(Student.__bases__) # (<class 'object'>,)
21 print(type.__bases__) # (<class 'object'>,)
22 print(object.__bases__) # ()
23 print(type(object)) # <class 'type'>
24 print(type(type)) # <class 'type'>
25
26 # 所有类的类型(包括type类)都是type
27 # 所有类的最上层基类是object类
28 # type也是一个类,同时type也是一个对象
3.python中常见内置类型
- 对象的三个特征
- None类型:全局只有一个
- 数值类型:int,float,complex(复数),bool
- 迭代器类型:之后讲解
- 序列类型:之后讲解
- list
- bytes,tyearray,memoryview(二进制类型)
- range
- tuple
- str
- array
- 映射(dict)
- 集合
- 上下文管理器类型:之后讲解
- 其他类型:之后讲解
- 模块类型
- class和实例
- 函数类型
- 方法类型
- 代码类型
- object对象
- type类型
- ellipsis类型
- notimplemented类型
- 生成器对象类型
1 # id:内存地址
2 a = 1
3 id(a)
4
5 # None全局只有一个
6 a = None
7 b = None
8 print(id(a) == id(b)) # true
