1.意图
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,Decorator模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
2.别名
包装器 Wrapper.
3.动机
给某个对象而不是整个类添加一些功能。一个较为灵活的方式时将组件嵌入另一个对象中。
4.适用性
- 在不影响其它对象的情况下,以动态、透明的方式给单个对象添加职责。
- 处理那些可以撤销的职责。
- 当不能采用子类的方法进行扩充时。一种情况是,可能有大量独立的扩展,为支持每一种组合将产生大量的子类,使得子类数目呈爆炸性增长。另一种情况可能是因为类定义被隐藏或类定义不能用于生成子类。
5.结构

6.代码实例
#include <memory>
class Component
{
public:
virtual void Operation()=0;
};
class ConcreteComponent : public Component
{
public:
void Operation();
};
class Decorator : public Component
{
public:
virtual void Operation();
void SetComponent(std::shared_ptr<Component> pComponent);
protected:
std::shared_ptr<Component> m_pComponent;
};
class ConcreteDecoratorA : public Decorator
{
public:
void Operation();
void OtherBehavior();
};
class ConcreteDecoratorB : public Decorator
{
public:
void Operation();
void OtherBehavior();
};
#include "Component.h"
#include <iostream>
void ConcreteComponent::Operation()
{
std::cout << "ConcreteComponent Operation executed" <<std::endl;
}
void Decorator::Operation()
{
m_pComponent->Operation();
}
void Decorator::SetComponent(std::shared_ptr<Component> pComponent)
{
m_pComponent = pComponent;
}
void ConcreteDecoratorA::Operation()
{
Decorator::Operation();
OtherBehavior();
}
void ConcreteDecoratorA::OtherBehavior()
{
std::cout<<"ConceteDecoratorA OtherBehavior executed" << std::endl;
}
void ConcreteDecoratorB::Operation()
{
Decorator::Operation();
OtherBehavior();
}
void ConcreteDecoratorB::OtherBehavior()
{
std::cout<<"ConcreteDecoratorB OtherBehavior executed" << std::endl;
}
#include "Component.h"
int main()
{
std::shared_ptr<Component> pComponent(new ConcreteComponent);
std::shared_ptr<Decorator> pDecoratorA(new ConcreteDecoratorA);
pDecoratorA->SetComponent(pComponent);
pDecoratorA->Operation();
std::shared_ptr<Decorator> pDecoratorB(new ConcreteDecoratorB);
pDecoratorB->SetComponent(pComponent);
pDecoratorB->Operation();
while(1);
}
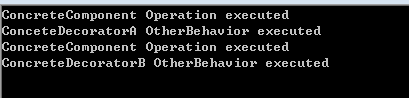
7.测试结果
8.效果
- 比静态继承更灵活 可以添加和分离方法,用装饰在运行时刻增加和删除职责。
- 避免在层次结构高层的类有太多的特征
- Decorator与它的Component不一样 Decorator是一个透明的包装。如果我们从对象表示的观点出发,一个被装饰了的组件与这个组件是有差别的,因此,使用装饰时不应该依赖对象标识。
- 有许多小对象 有很多看上去很类似的小对象,这些对象仅仅在他们相互连接的方式上有所不同,而不是它们的类或它们的属性值有所不同。对于了解这些系统的人来说,很容易对它们进行定制,但是很难学习这些系统。
