Book Imformation :
<Pratical Programming : An Introduction to Computer Science Using Python 3> 2nd Edtion

Author : Paul Gries,Jennifer Campbell,Jason Montojo
Page : Chapter 1 and Chapter 2.1-2.2
1.every computer runs operating system,which it's the only program on the computer that's allowed direct access to the hardware(硬件).
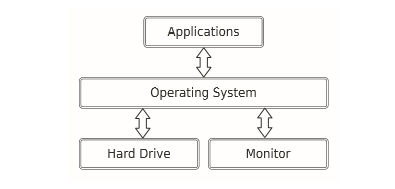
or more complicate(add another layer between the programmer and the hardware) :
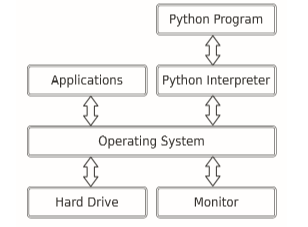
2.two ways to use the Python interpreter(解释器) :
(1).execute a saved Python program with .py extension(扩展,后缀)
(2).using a Python shell(壳,命令解析器)
3.the >>> symbol is called a prompt(提示),prompting you to type something
4.the result of interger division has a decimal point even is a whole number :
1 >>> 5 / 2 2 2.5 3 >>> 4 / 2 4 2.0
5.when the operands (操作数) are int and float,Python automatically convert the int into a float :
1 >>> 17.0 - 10 2 7.0 3 >>> 17 - 10.0 4 7.0
and you can omit zero like ‘17.’ (but most people think it is a bad idea)
6.integer division,modulo(取模)
1 >>> 53 // 24 2 2 3 >>> 53 % 24 4 5
//:整除
when the operands are negative or float,it takes the floor(向下取整) of the result.
1 >>> -17 // 10 2 -2 3 >>> 17 // 10 4 1
1 >>> 3.5 // 1.0 2 3.0 3 >>> 3 // 1.1 4 2.0 5 >>> 3.3 // 1 6 3.0
when using modulo,the sign of the result matches the divisor(除数)
定义:a % b = a - n*b,n为不超过a/b的整数
1 >>> -17 % 10 2 3 3 >>> 17 % -10 4 -3
7.exponentiation(取幂):**
1 >>> 2 ** 3 2 8 3 >>> 3 ** 3 4 27
8.binary operators(双目运算符),unary operators(单目运算符)
+、-、*、/:binary operators
-(nagetive):unary operators
1 >>> -5 2 -5 3 >>> --5 4 5 5 >>> ---5 6 -5