1、State
提供唯一公共数据源,所有共享数据都要放在Store的State里面进行存储
组件中访问State数据的第一种方式:
this.$store.state.全局数据名称
组件中访问State数据的第二种方式:
在组件中按需导入mapState辅助函数
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
将当前组件所需的全局数据,映射为当前组件的computed计算属性
computed:{
...mapState(['count'])
}
然后,直接使用
<h5>当前最新的count值为:{{count}}</h5>
2、Mutation
在vuex中更改store中的数据的唯一方法是提交 mutation,不能直接操作store中的数据。
定义方法:
mutations: {
//减 cut(state){ state.count-- }, //加 add(state){ state.count++ }, },
触发mutation的第一种方法:
methods:{ btnHandler1(){ this.$store.commit('add') }
}
触发mutation的第二种方法:
在组件中按需导入mapMutations辅助方法:
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'
将当前组件所需的mutation方法,映射为当前组件的methods方法,然后直接调用:
methods:{ ...mapMutations(['cut']), btnHandler1(){ this.cut()//直接调用即可 } }
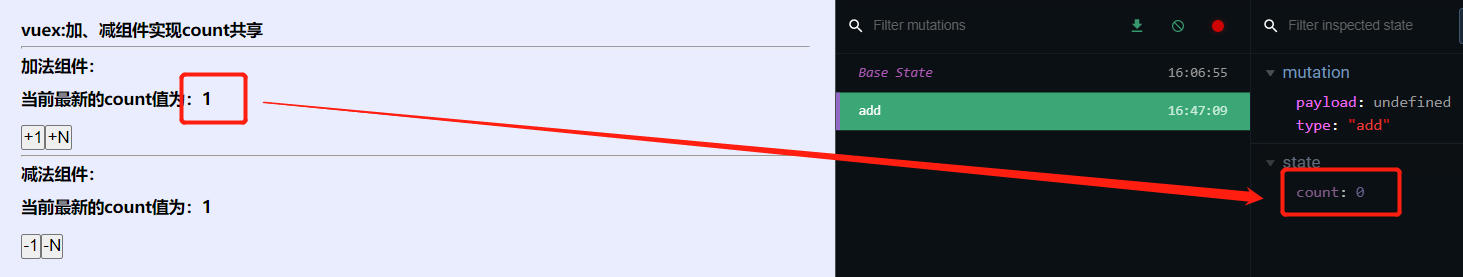
注意:mutations中不能执行异步操作。
例如:
mutations: { //加 add(state){ setTimeout(()=>{ state.count++ },500) }, },
导致页面更新和state数据不一致:
3、Action
如果需要使用异步操作改变数据,则要通过Action,不能使用Mutation。
不过,在action中还是要通过触发mutation中的方法来间接改变数据。
定义方法:
actions: { // context相当于Store对象 addAsync(context){ setTimeout(()=>{ // actions中不能直接修改state中的数据 // 必须通过context.commit 去触发某个mutation方法才行 context.commit('add') },1000) } },
触发action的第一种方法:
btnHandler3(){ // dispatch用来触发action this.$store.dispatch('addAsync') }
触发action的第二种方法:
在组件中按需导入mapActions辅助方法:
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'
将当前组件所需的mutation方法,映射为当前组件的methods方法,然后直接调用:
methods:{ ...mapActions(['cutAsync']), btnHandler3(){ this.cutAsync(5) } }
4、Getter
对store中的数据进行加工处理,类似于计算属性。
store中的数据发生变化,getter中的数据也会跟着变化,是联动的。
定义getter:
getters:{ showNum:state=>{ return '当前最新的数量是【'+state.count+'】' } },
使用getter的第一种方式:
this.$store.getters.数据名称
使用getter的第二种方式:
在组件中按需导入mapGetters辅助函数:
import {mapGetters} from 'vuex'
将当前组件所需的getter数据,映射为当前组件的computed计算属性:
computed:{ ...mapGetters(['showNum']) },
然后直接使用:
<h5>{{showNum}}</h5>