一、卷积神经网络应用于MNIST数据集分类
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True) #从MNIST_data目录读入数据,如果没有就自动下载
#每个批次的大小
batch_size = 100
#计算一共有多少个批次
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
#初始化权值
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1)#生成一个截断的正态分布(shape表示生成张量的维度,stddev是标准差)
return tf.Variable(initial) #initial是初始化参数
#初始化偏置
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape) #0.1表示常量,shape来指定其形状
return tf.Variable(initial) #initial是初始化参数
#卷积层
def conv2d(x,W):
#x input tensor(张量) of shape `[batch, in_height(高度), in_width(宽度), in_channels(通道)]`
#W filter / kernel tensor of shape [filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]
#`strides[0] = strides[3] = 1`. strides[1]代表x方向的步长,strides[2]代表y方向的步长
#padding: A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"` Valid: 用过滤器在输入的矩阵中按步长移动时候,会把最后的不足部分的列和行抛弃;Same: 先在输入矩阵上下各加个值为0的行,在左右各加个个值为0的列,也就是用0把原先的矩阵包裹一层,然后在移动的时候如果输入矩阵的列或者行长度不够,就用0来补齐
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
#池化层
def max_pool_2x2(x):
#ksize [1,x,y,1]池化窗口的大小,取一个四维向量
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
#定义两个placeholder(占位符)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])#28*28的张量
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
#改变x的格式转为4D的向量[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]`
x_image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) #如果shape的一个分量是特殊值-1,则计算该维度的大小,以使总大小保持不变.如果shape是1-D或更高,则操作返回形状为shape的张量,其填充为tensor的值。在这种情况下,隐含的shape元素数量必须与tensor元素数量相同。
#初始化第一个卷积层的权值和偏置
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32])#5*5的采样窗口,32个卷积核从1个平面抽取特征
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])#每一个卷积核一个偏置值
#把x_image和权值向量进行卷积,再加上偏置值,然后应用于relu激活函数
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)#进行max-pooling(进行最大化卷积)
#初始化第二个卷积层的权值和偏置
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64])#5*5的采样窗口,64个卷积核从32个平面抽取特征
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])#每一个卷积核一个偏置值
#把h_pool1和权值向量进行卷积,再加上偏置值,然后应用于relu激活函数
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)#进行max-pooling(进行最大化卷积)
#28*28的图片第一次卷积后还是28*28,第一次池化后变为14*14
#第二次卷积后为14*14,第二次池化后变为了7*7
#进过上面操作后得到64张7*7的平面
#初始化第一个全连接层的权值
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])#上一层有7*7*64个神经元,全连接层有1024个神经元
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])#1024个节点
#把池化层2的输出扁平化为1维
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2,[-1,7*7*64])
#求第一个全连接层的输出
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat,W_fc1) + b_fc1)
#keep_prob用来表示神经元的输出概率
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1,keep_prob)
#初始化第二个全连接层
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
#计算输出
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,W_fc2) + b_fc2)
#交叉熵代价函数
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction))
#tf.reduce_mean(计算张量的各个维度上的元素的平均值)
#使用AdamOptimizer进行优化
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) #1e-4是10的4次方
#结果存放在一个布尔列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction,1),tf.argmax(y,1))#argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
# tf.equal对比这两个矩阵或者向量的相等的元素,如果是相等的那就返回True,反正返回False
#求准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32)) #tf.cast是类型转换函数
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
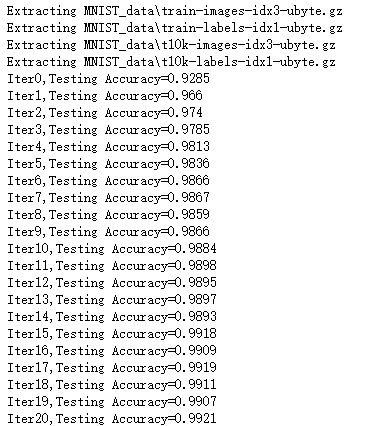
for epoch in range(21):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.7})
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0})
#mnist.test.images 是验证图像,mnist.test.labels是测试标签
print ("Iter " + str(epoch) + ", Testing Accuracy= " + str(acc))