前言:在并发中,最熟悉的JUC编程,问的最多的也是下面四个包,随手写篇博客记录日常中的学习一下!

一、读写锁
java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
ReadWriteLock管理一组锁,一个是只读的锁,一个是写锁。读锁可以在没有写锁的时候被多个线程同时持有,写锁是独占的。
所有读写锁的实现必须确保写操作对读操作的内存影响。换句话说,一个获得了读锁的线程必须能看到前一个释放的写锁所更新的内容。
读写锁比互斥锁允许对于共享数据更大程度的并发。每次只能有一个写线程,但是同时可以有多个线程并发地读数据。ReadWriteLock适用于读多写少的并发情况。
举个例子,有六个线程进行读写操作,但是呢,我们在写入数据的时候是并不希望有别的线程来加塞,我们在读取的时候可以多个线程进行读取:
1 import java.util.HashMap; 2 import java.util.Map; 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock; 5 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; 6 7 /** 8 * @author zhangzhixi 9 * @date 2021-4-18 22:25 10 */ 11 public class Demo_01_读写锁 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 MyCache myCache = new MyCache(); 14 // 六个写的线程 15 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 16 final int temp = i; 17 new Thread(() -> { 18 myCache.put(temp + "", temp + ""); 19 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 20 } 21 // 六个读的线程 22 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 23 final int temp = i; 24 new Thread(() -> { 25 myCache.get(temp + ""); 26 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * 定义缓存类 33 */ 34 class MyCache { 35 volatile Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); 36 37 public void put(String key, String value) { 38 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在写入" + key); 39 // 模拟网络延迟 40 try { 41 TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(300); 42 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 map.put(key, value); 46 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 写入完成"); 47 } 48 49 public void get(String key) { 50 // 模拟网络延迟 51 try { 52 TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(200); 53 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 54 e.printStackTrace(); 55 } 56 Object value = map.get(key); 57 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 读取完成->" + value); 58 } 59 }
通过上面的测试可以看到,线程在写入数据的时候,有其他线程过来加塞。

改进后的读写锁代码:
1 import java.util.HashMap; 2 import java.util.Map; 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock; 5 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; 6 7 /** 8 * @author zhangzhixi 9 * @date 2021-4-18 22:25 10 */ 11 public class Demo_01_读写锁 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 MyCache myCache = new MyCache(); 14 // 六个写的线程 15 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 16 final int temp = i; 17 new Thread(() -> { 18 myCache.put(temp + "", temp + ""); 19 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 20 } 21 // 六个读的线程 22 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 23 final int temp = i; 24 new Thread(() -> { 25 myCache.get(temp + ""); 26 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * 定义缓存类 33 */ 34 class MyCache { 35 volatile Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); 36 ReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); 37 public void put(String key, String value) { 38 // 写入数据 39 lock.writeLock().lock(); 40 try { 41 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在写入" + key); 42 // 模拟网络延迟 43 try { 44 TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(300); 45 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 map.put(key, value); 49 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 写入完成"); 50 } catch (Exception e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } finally { 53 lock.writeLock().unlock(); 54 } 55 } 56 57 public void get(String key) { 58 lock.readLock().lock(); 59 try { 60 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 正在读取" + key); 61 // 模拟网络延迟 62 try { 63 TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(200); 64 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 65 e.printStackTrace(); 66 } 67 Object value = map.get(key); 68 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 读取完成->" + value); 69 } catch (Exception e) { 70 e.printStackTrace(); 71 } finally { 72 lock.readLock().unlock(); 73 } 74 } 75 }

二、倒计时锁存器:秦一统六国实例
java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
CountDownLatch主要有两个方法,当一个或多个线程调用await方法时,调用线程会被阻塞。
其它线程调用countDown方法会将计数器减1(调用countDown方法的线程不会阻塞),
当计数器的值变为零时,因调用await方法被阻塞的线程会被唤醒,继续执行。
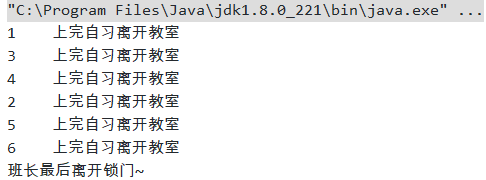
例子:班级放学后班长最后一个走人,班长锁门
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; /** * @author zhangzhixi * @date 2021-4-18 23:15 */ public class Demo_02_倒计时锁存器 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6); for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { new Thread(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 上完自习离开教室"); countDownLatch.countDown(); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } countDownLatch.await(); System.out.println("班长最后离开锁门~"); } }
CountDownLatch实例之枚举的应用
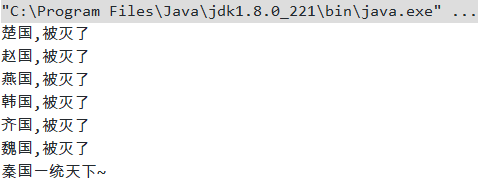
秦国一统天下,歼灭各国怎么用代码表示呢?
下面使用的是枚举的方式定义线程的名称:
1 import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; 2 3 /** 4 * @author zhangzhixi 5 * @date 2021-4-19 9:19 6 */ 7 public class Demo_03_倒计时锁存器之枚举的应用 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 9 // 倒计时计数器 10 CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6); 11 12 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 13 new Thread(() -> { 14 // 减少寄存器的数量 15 countDownLatch.countDown(); 16 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "国,被灭了"); 17 }, CountEnum.forEachEnum(i).getName()).start(); 18 } 19 20 // 导致当前线程等待,直到锁存器递减计数到零为止,除非该线程被中断 21 countDownLatch.await(); 22 System.out.println("秦国一统天下~"); 23 } 24 } 25 26 enum CountEnum { 27 ONE(1, "齐"), TWO(2, "楚"), THREE(3, "燕"), FORE(4, "韩"), FIVE(5, "赵"), SIX(6, "魏"); 28 29 private Integer id; 30 private String name; 31 32 CountEnum(Integer id, String name) { 33 this.id = id; 34 this.name = name; 35 } 36 37 public Integer getId() { 38 return id; 39 } 40 41 public String getName() { 42 return name; 43 } 44 45 public static CountEnum forEachEnum(int index) { 46 // 以声明顺序返回包含此枚举类型的常量的数组 47 CountEnum[] values = CountEnum.values(); 48 for (CountEnum element : values) { 49 if (index == element.getId()) { 50 return element; 51 } 52 } 53 return null; 54 } 55 }
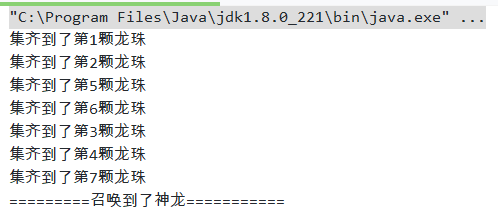
三、循环屏障:七龙珠实例
1 import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException; 2 import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier; 3 4 /** 5 * @author zhangzhixi 6 * @date 2021-4-19 22:28 7 */ 8 public class Demo_04_循环屏障之七龙珠 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 集齐七颗龙珠召唤神龙 11 CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(7, () -> { 12 System.out.println("=========收集到了神龙==========="); 13 }); 14 for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) { 15 final int emp = i; 16 new Thread(() -> { 17 System.out.println("集齐到了第" + emp + "颗龙珠"); 18 try { 19 // 等到所有各方都在此障碍上调用await 20 barrier.await(); 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 27 } 28 29 } 30 }
四、信号灯Semaphore:抢车位实例
1 import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; 2 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 3 4 /** 5 * @author zhangzhixi 6 * @date 2021-4-19 22:38 7 */ 8 public class Demo05_信号量_抢车位 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // 给了三个车位 11 Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3); 12 13 // 模拟6个车子 14 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 15 new Thread(() -> { 16 // 抢到车位(抢占) 17 try { 18 semaphore.acquire(); 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 号车子抢到抢到了"); 20 // 模拟停车时间 21 try { 22 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 号车子停车2S后离开车位"); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } finally { 30 // 车子离开车位, 31 semaphore.release(); 32 } 33 }, String.valueOf(i)).start(); 34 } 35 } 36 }
