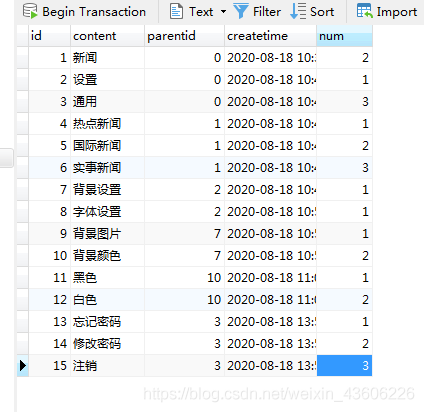
parentid为0的都是根节点,也就是一级菜单,后面的子菜单的parentid为父菜单的ID。 二、MenuDTO类(菜单类)的结构: @Data public class MenuDTO { private Integer id; private String content; private Integer parentid; private Date createtime; private Integer num; private List<MenuDTO> childs; 三、业务层:采用递归方法,遍历成树级结构菜单 //获得树级结构菜单 public List<MenuDTO> getMenuList() throws IOException { //拿到菜单的所有数据 List<MenudTO> list=menuMapper.getMenuList(); //存储根节点的菜单,即一级菜单 List<MenuDTO> rootlist=new ArrayList<>(); //遍历所有数据,找到根节点菜单 for (MenuDTO menuDTO: list) { if(menuDTO.getParentid().equals(0)){ //找到根节点菜单的时候,寻找这个根节点菜单下的子节点菜单。 findChilds(menuDTO,list); //添加到根节点的列表中 rootlist.add(menuDTO); } } return rootlist; } private void findChilds(MenuDTO root,List<MenuDTO> list){ List<MenuDTO> childlist=new ArrayList<>(); //遍历所有数据,找到是入参父节点的子节点的数据,然后加到childlist集合中。 for (MenuDTO menu : list) { if (root.getId().equals(menu.getParentid())) childlist.add(menu); } //若子节点不存在,那么就不必再遍历子节点中的子节点了 直接返回。 if(childlist.size()==0) return; //设置父节点的子节点列表 root.setChilds(childlist); //若子节点存在,接着递归调用该方法,寻找子节点的子节点。 for (MenuDTO childs : childlist) { findChilds(childs, list); } } 需求二:这种需要传任何参数,可以传多个 一、分类实体类 public class ChildNodeCategoryDto { /** * 分类ID */ private Integer catId; /** * 分类父ID */ private Integer parentId; /** * 分类名称 */ private String catName; /** * 分类级别 */ private String catLevel; /** * 分类缩略图 */ private String catThumb; /** * 子分类列表 */ List<ChildNodeCategoryDto> childCategory = new ArrayList<ChildNodeCategoryDto>(); 二、业务层:采用递归方法,遍历成树级结构分类 public List<ChildNodeCategoryDto> getGoodsCategory(String ids) { List<ChildNodeCategoryDto> list = new ArrayList<ChildNodeCategoryDto>(); GoodsCategoryDto dto = new GoodsCategoryDto(); //查询所有的分类 dto.setPlatformCode("0001"); dto.setIsShow(1); List<EcsCategory> ecsCategoryList = ecsCategoryMapper.findAllByShowAndPlatformCodeOrderBySortOrder(dto); for (EcsCategory ecsCategory : ecsCategoryList) { ChildNodeCategoryDto childNodeCategory = new ChildNodeCategoryDto(); childNodeCategory.setCatId(ecsCategory.getCatId()); childNodeCategory.setParentId(ecsCategory.getParentId()); childNodeCategory.setCatName(ecsCategory.getCatName()); childNodeCategory.setCatLevel(ecsCategory.getCatCode()); childNodeCategory.setCatThumb(ecsCategory.getCatThumb()); list.add(childNodeCategory); } //查询根节点数据 List<ChildNodeCategoryDto> rootLists = new ArrayList<ChildNodeCategoryDto>(); String[] strArray = ids.split(","); for(int i = 0; i<strArray.length ;i++) { Integer catId = Integer.parseInt(strArray[i]); //先找到所有的一级菜单 for (ChildNodeCategoryDto childNodeCategoryResponse : list) { if (childNodeCategoryResponse.getCatId().equals(catId)) { rootLists.add(childNodeCategoryResponse); getChild(childNodeCategoryResponse, list); } } } } return rootLists;
private void getChild(ChildNodeCategoryDto category, List<ChildNodeCategoryDto> list) { // 存放子菜单的集合 List<ChildNodeCategoryDto> childList = new ArrayList<ChildNodeCategoryDto>(); category.setChildCategory(childList); for (ChildNodeCategoryDto childNodeCategoryResponse : list) { if (childNodeCategoryResponse.getParentId().equals(category.getCatId())) { childList.add(childNodeCategoryResponse); getChild(childNodeCategoryResponse, list); } } } 三、总结: 先拿到所有的菜单数据,然后遍历菜单数据,找到根节点,找到根节点。然后调用找到子节点的方法,在子节点方法中递归调用自己, 也就是说如果这个节点有子节点,那么递归调用方法找到子节点的子节点,直到某个节点下面没有子节点。