他里面包含了各层协议的头部,比如ethernet, ip ,tcp ,udp等等。熟悉他是进一步了解Linux网络协议栈的基础
此结构定义头文件
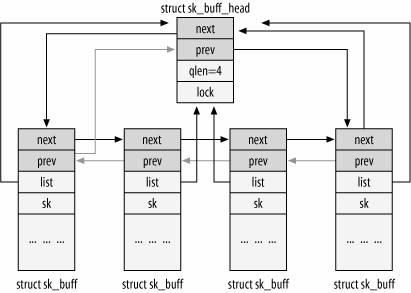
<include/linux/skbuff.h>struct sk_buff_head {
/* These two members must be first. */
struct sk_buff *next;
struct sk_buff *prev;
__u32 qlen; //代表元素节点数目
spinlock_t lock; //加锁,防止对表的并发访问
};管理函数
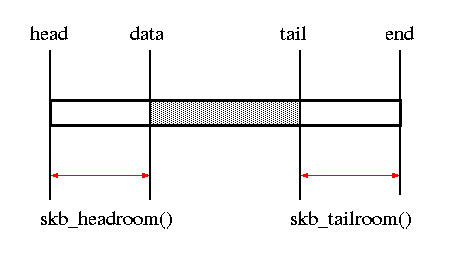
int skb_headroom(const struct sk_buff *skb)
int skb_tailroom(const struct sk_buff *skb)skb_headroom通常比较小(只有48),用的时候小心越界
skb_tailroom大小1500,足够自由调整
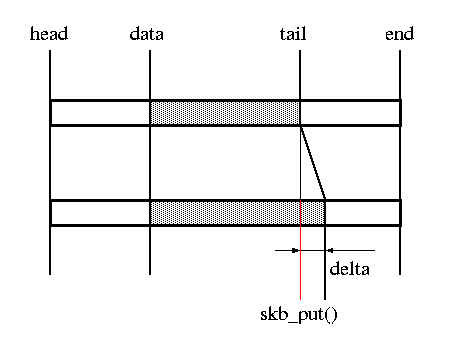
//同时增加len和tail。用于向数据报尾部追加数据。返回原来tail所在位置
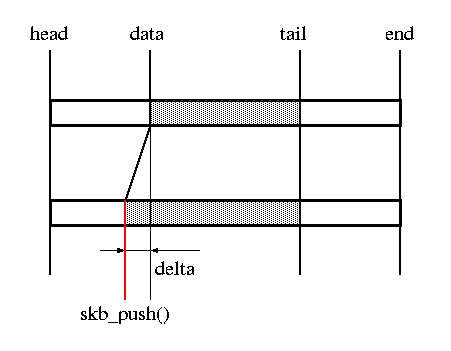
unsigned char *skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) //将data指针上移并增加len长度。这个函数用来向头部添加一些数据。当然前提是有足够的headroom
unsigned char *skb_push(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) //将data指针下移,并减小len的值。这个函数一般用来除去某个头部
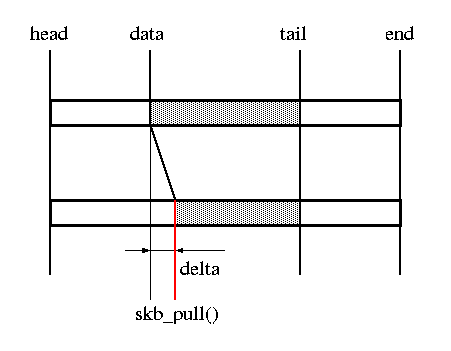
unsigned char *skb_pull(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) //将data指针和tail指针同时下移。这个操作在存储空间的头部预留len长度的空隙
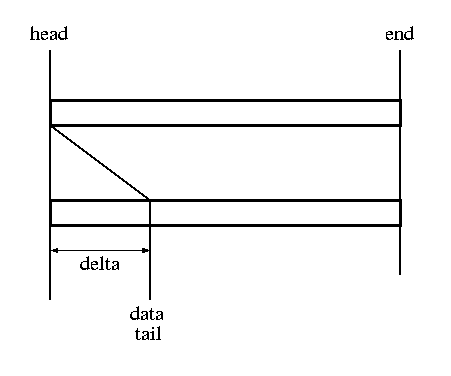
void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) //将网络报文的长度缩减到len。这个操作丢弃了网络报文尾部的填充值
void skb_trim(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) 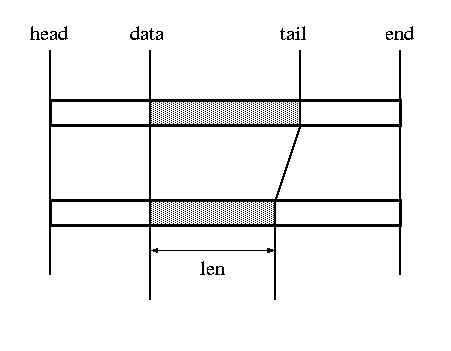
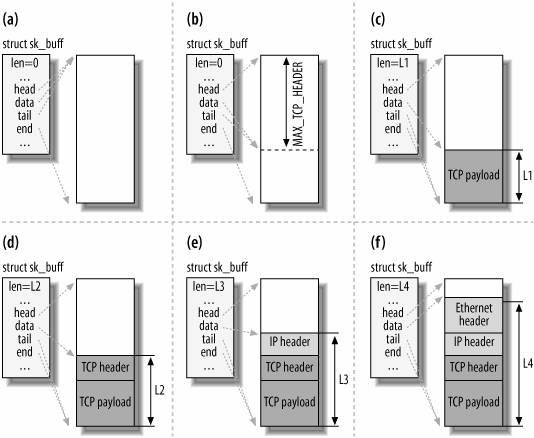
下图是穿过协议栈从tcp层向下到链路层的过程
分配内存
alloc_skb 分配缓冲区和一个sk_buff结构
dev_alloc_skb 设备驱动程序使用的缓冲区分配函数
释放内存
kfree_skb 只有skb->users计数器为1时才释放
dev_kfree_skb
缓冲区克隆
skb_clone
sk_buff
/**
* struct sk_buff - socket buffer
* @next: Next buffer in list
* @prev: Previous buffer in list
* @tstamp: Time we arrived
* @sk: Socket we are owned by
* @dev: Device we arrived on/are leaving by
* @cb: Control buffer. Free for use by every layer. Put private vars here
* @_skb_refdst: destination entry (with norefcount bit)
* @sp: the security path, used for xfrm
* @len: Length of actual data
* @data_len: Data length
* @mac_len: Length of link layer header
* @hdr_len: writable header length of cloned skb
* @csum: Checksum (must include start/offset pair)
* @csum_start: Offset from skb->head where checksumming should start
* @csum_offset: Offset from csum_start where checksum should be stored
* @priority: Packet queueing priority
* @local_df: allow local fragmentation
* @cloned: Head may be cloned (check refcnt to be sure)
* @ip_summed: Driver fed us an IP checksum
* @nohdr: Payload reference only, must not modify header
* @nfctinfo: Relationship of this skb to the connection
* @pkt_type: Packet class
* @fclone: skbuff clone status
* @ipvs_property: skbuff is owned by ipvs
* @peeked: this packet has been seen already, so stats have been
* done for it, don't do them again
* @nf_trace: netfilter packet trace flag
* @protocol: Packet protocol from driver
* @nfct: Associated connection, if any
* @nfct_reasm: netfilter conntrack re-assembly pointer
* @nf_bridge: Saved data about a bridged frame - see br_netfilter.c
* @skb_iif: ifindex of device we arrived on
* @tc_index: Traffic control index
* @tc_verd: traffic control verdict
* @rxhash: the packet hash computed on receive
* @queue_mapping: Queue mapping for multiqueue devices
* @ndisc_nodetype: router type (from link layer)
* @ooo_okay: allow the mapping of a socket to a queue to be changed
* @l4_rxhash: indicate rxhash is a canonical 4-tuple hash over transport
* ports.
* @wifi_acked_valid: wifi_acked was set
* @wifi_acked: whether frame was acked on wifi or not
* @no_fcs: Request NIC to treat last 4 bytes as Ethernet FCS
* @dma_cookie: a cookie to one of several possible DMA operations
* done by skb DMA functions
* @secmark: security marking
* @mark: Generic packet mark
* @dropcount: total number of sk_receive_queue overflows
* @vlan_tci: vlan tag control information
* @inner_transport_header: Inner transport layer header (encapsulation)
* @inner_network_header: Network layer header (encapsulation)
* @transport_header: Transport layer header
* @network_header: Network layer header
* @mac_header: Link layer header
* @tail: Tail pointer
* @end: End pointer
* @head: Head of buffer
* @data: Data head pointer
* @truesize: Buffer size
* @users: User count - see {datagram,tcp}.c
* @destructor: Destruct function
*/
struct sk_buff {
/* These two members must be first. */
struct sk_buff *next;
struct sk_buff *prev;
ktime_t tstamp; //skb接收包的时间
struct sock *sk; //从属于哪个socket,被4层用到
struct net_device *dev; //一个网络设备,当发出包时它表示输出设备,当接收包时它表示输入设备
/*
* This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
*/
char cb[48] __aligned(8); //保存每层的控制信息
unsigned long _skb_refdst; //用于路由子系统。保存了一些路由相关信息
#ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
struct sec_path *sp;
#endif
unsigned int len, //当前skb中的数据长度,这个值会随着从一层到另一层而改变
data_len; //分片数据长度
__u16 mac_len, //mac头长度
hdr_len; //clone的skb头长度
union {
__wsum csum;
struct {
__u16 csum_start;
__u16 csum_offset;
};
};
__u32 priority; //优先级。用于QOS
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1);
__u8 local_df:1, //是否可以本地切片
cloned:1, //头是否被clone
ip_summed:2, //硬件驱动是否已经进行了校验
nohdr:1, //skb的头指针是否分配完毕(比如head和data)
nfctinfo:3;
__u8 pkt_type:3, //数据包的类型
fclone:2, //clone标记。在fast clone中被设置
ipvs_property:1, //ipvs拥有的域
peeked:1,
nf_trace:1;
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1);
__be16 protocol; //L3层的协议
#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)
struct nf_conntrack *nfct;
#endif
#ifdef NET_SKBUFF_NF_DEFRAG_NEEDED
struct sk_buff *nfct_reasm;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER
struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;
#endif
int skb_iif; //接收设备的index
__u32 rxhash;
__u16 vlan_tci;
//流量控制的相关域
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
__u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */
#endif
#endif
__u16 queue_mapping; //多队列设备的映射,映射到那个队列
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags2);
#ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE
__u8 ndisc_nodetype:2;
#endif
__u8 pfmemalloc:1;
__u8 ooo_okay:1;
__u8 l4_rxhash:1;
__u8 wifi_acked_valid:1;
__u8 wifi_acked:1;
__u8 no_fcs:1;
__u8 head_frag:1;
/* Encapsulation protocol and NIC drivers should use
* this flag to indicate to each other if the skb contains
* encapsulated packet or not and maybe use the inner packet
* headers if needed
*/
__u8 encapsulation:1;
/* 7/9 bit hole (depending on ndisc_nodetype presence) */
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags2);
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_DMA
dma_cookie_t dma_cookie;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK
__u32 secmark;
#endif
union {
__u32 mark; //skb的标记
__u32 dropcount;
__u32 reserved_tailroom;
};
sk_buff_data_t inner_transport_header;
sk_buff_data_t inner_network_header;
sk_buff_data_t transport_header; //传输层的头
sk_buff_data_t network_header; //网络层的头
sk_buff_data_t mac_header; //链路层的头
/* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
sk_buff_data_t tail; //skb数据操作指针
sk_buff_data_t end;
unsigned char *head,
*data;
unsigned int truesize; //整个skb的大小
atomic_t users; //skb的引用计数
void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb); //skb的析构函数(sock_rfree和sock_wfree)
};skb_put
static inline unsigned char *__skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)
{
unsigned char *tmp = skb_tail_pointer(skb);
SKB_LINEAR_ASSERT(skb);
skb->tail += len;
skb->len += len;
return tmp;
}skb_push
static inline unsigned char *__skb_push(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)
{
skb->data -= len;
skb->len += len;
return skb->data;
}skb_pull
static inline unsigned char *__skb_pull(struct sk_buff *skb , unsigned int len)
{
skb->len -= len ;
BUG_ON(skb->len < skb->data_len ) ;
return skb->data += len ;
} alloc_skb
struct sk_buff *__alloc_skb(unsigned int size, gfp_t gfp_mask,
int fclone, int node)
{
struct kmem_cache *cache;
struct skb_shared_info *shinfo;
struct sk_buff *skb;
u8 *data;
//这里通过fclone的值来判断是要从fclone cache还是说从head cache中取
cache = fclone ? skbuff_fclone_cache : skbuff_head_cache;
//首先是分配skb,也就是包头
skb = kmem_cache_alloc_node(cache, gfp_mask & ~__GFP_DMA, node);
if (!skb)
goto out;
//首先将size对齐,这里是按一级缓存的大小来对齐
size = SKB_DATA_ALIGN(size);
//然后是数据区的大小,大小为size+ sizeof(struct skb_shared_info的大小
data = kmalloc_node_track_caller(size + sizeof(struct skb_shared_info),
gfp_mask, node);
if (!data)
goto nodata;
//初始化相关域
memset(skb, 0, offsetof(struct sk_buff, tail));
//这里truesize可以看到就是我们分配的整个skb+data的大小
skb->truesize = size + sizeof(struct sk_buff);
//users加一
atomic_set(&skb->users, 1);
//一开始head和data是一样大的
skb->head = data;
skb->data = data;
//设置tail指针
skb_reset_tail_pointer(skb);
//一开始tail也就是和data是相同的
skb->end = skb->tail + size;
kmemcheck_annotate_bitfield(skb, flags1);
kmemcheck_annotate_bitfield(skb, flags2);
#ifdef NET_SKBUFF_DATA_USES_OFFSET
skb->mac_header = ~0U;
#endif
//初始化shinfo,这个我就不介绍了,前面的blog分析切片时,这个结构很详细的分析过了
shinfo = skb_shinfo(skb);
atomic_set(&shinfo->dataref, 1);
shinfo->nr_frags = 0;
shinfo->gso_size = 0;
shinfo->gso_segs = 0;
shinfo->gso_type = 0;
shinfo->ip6_frag_id = 0;
shinfo->tx_flags.flags = 0;
skb_frag_list_init(skb);
memset(&shinfo->hwtstamps, 0, sizeof(shinfo->hwtstamps));
//fclone为1,说明多分配了一块内存,因此需要设置对应的fclone域
if (fclone) {
//可以看到多分配的内存刚好在当前的skb的下方
struct sk_buff *child = skb + 1;
atomic_t *fclone_ref = (atomic_t *) (child + 1);
kmemcheck_annotate_bitfield(child, flags1);
kmemcheck_annotate_bitfield(child, flags2);
//设置标记。这里要注意,当前的skb和多分配的skb设置的fclone是不同的
skb->fclone = SKB_FCLONE_ORIG;
atomic_set(fclone_ref, 1);
child->fclone = SKB_FCLONE_UNAVAILABLE;
}
out:
return skb;
nodata:
kmem_cache_free(cache, skb);
skb = NULL;
goto out;
}skb_linearize
int skb_linearize(struct sk_buff *skb, gfp_t gfp) 将frag_list链表里面的数据包整合成一个报文
skb_clone
struct sk_buff *skb_clone(struct sk_buff *skb, gfp_t gfp_mask)
{
struct sk_buff *n;
//n为skb紧跟着那块内存,这里如果skb是通过skb_fclone分配的,那么n就是一个skb
n = skb + 1;
//skb和n的fclone都要符合要求,可以看到这里的值就是我们在__alloc_skb中设置的值
if (skb->fclone == SKB_FCLONE_ORIG &&
n->fclone == SKB_FCLONE_UNAVAILABLE) {
//到这里,就说明我们不需要alloc一个skb,直接取n就可以了,并且设置fclone的标记。并修改引用计数
atomic_t *fclone_ref = (atomic_t *) (n + 1);
n->fclone = SKB_FCLONE_CLONE;
atomic_inc(fclone_ref);
} else {
//这里就需要从cache中取得一块内存
n = kmem_cache_alloc(skbuff_head_cache, gfp_mask);
if (!n)
return NULL;
kmemcheck_annotate_bitfield(n, flags1);
kmemcheck_annotate_bitfield(n, flags2);
//设置新的skb的fclone域。这里我们新建的skb,没有被fclone的都是这个标记
n->fclone = SKB_FCLONE_UNAVAILABLE;
}
return __skb_clone(n, skb);
}只是复制sk_buff结构,并不复制skb的数据缓冲区。Clone后的sk_buff结构与原始的sk_buff指向同一数据缓冲区。原始的和clone后的skb描述符的cloned值都会被置1,clone的skb描述符的users值置1,同时数据缓冲区的引用计数dataref增加1
skb_clone()操作的skb结构的数据缓冲区是不能被修改的
pskb_copy
struct sk_buff *pskb_copy(struct sk_buff *skb, gfp_t gfp_mask)
{
/*
* Allocate the copy buffer
*/
struct sk_buff *n;
#ifdef NET_SKBUFF_DATA_USES_OFFSET
n = alloc_skb(skb->end, gfp_mask);
#else
n = alloc_skb(skb->end - skb->head, gfp_mask);
#endif
if (!n)
goto out;
/* Set the data pointer */
skb_reserve(n, skb->data - skb->head);
/* Set the tail pointer and length */
skb_put(n, skb_headlen(skb));
//复制线性数据段
skb_copy_from_linear_data(skb, n->data, n->len);
//更新相关域
n->truesize += skb->data_len;
n->data_len = skb->data_len;
n->len = skb->len;
//下面只是复制切片数据的指针
if (skb_shinfo(skb)->nr_frags) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < skb_shinfo(skb)->nr_frags; i++) {
skb_shinfo(n)->frags[i] = skb_shinfo(skb)->frags[i];
get_page(skb_shinfo(n)->frags[i].page);
}
skb_shinfo(n)->nr_frags = i;
}
copy_skb_header(n, skb);
out:
return n;
}pskb_copy()与skb_copy()重量级拷贝,还拷贝skb->data指向的数据
skb_copy
struct sk_buff *skb_copy(const struct sk_buff *skb, gfp_t gfp_mask)
{
int headerlen = skb->data - skb->head;
/*
* Allocate the copy buffer
*/
//先alloc一个新的skb
struct sk_buff *n;
#ifdef NET_SKBUFF_DATA_USES_OFFSET
n = alloc_skb(skb->end + skb->data_len, gfp_mask);
#else
n = alloc_skb(skb->end - skb->head + skb->data_len, gfp_mask);
#endif
if (!n)
return NULL;
/* Set the data pointer */
skb_reserve(n, headerlen);
/* Set the tail pointer and length */
skb_put(n, skb->len);
//然后复制所有的数据
if (skb_copy_bits(skb, -headerlen, n->head, headerlen + skb->len))
BUG();
copy_skb_header(n, skb);
return n;
}kfree_skb
void kfree_skb(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
if (unlikely(!skb))
return;
if (likely(atomic_read(&skb->users) == 1))
smp_rmb();
//减一,然后判断
else if (likely(!atomic_dec_and_test(&skb->users)))
return;
trace_kfree_skb(skb, __builtin_return_address(0));
__kfree_skb(skb);
}其他函数
#ifdef NET_SKBUFF_DATA_USES_OFFSET
static inline unsigned char *skb_transport_header(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return skb->head + skb->transport_header;
}
static inline void skb_reset_transport_header(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
skb->transport_header = skb->data - skb->head;
}
static inline void skb_set_transport_header(struct sk_buff *skb,
const int offset)
{
skb_reset_transport_header(skb);
skb->transport_header += offset;
}
static inline unsigned char *skb_network_header(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return skb->head + skb->network_header;
}
static inline void skb_reset_network_header(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
skb->network_header = skb->data - skb->head;
}
static inline void skb_set_network_header(struct sk_buff *skb, const int offset)
{
skb_reset_network_header(skb);
skb->network_header += offset;
}
static inline unsigned char *skb_mac_header(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return skb->head + skb->mac_header;
}
static inline int skb_mac_header_was_set(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return skb->mac_header != ~0U;
}
static inline void skb_reset_mac_header(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
skb->mac_header = skb->data - skb->head;
}
static inline void skb_set_mac_header(struct sk_buff *skb, const int offset)
{
skb_reset_mac_header(skb);
skb->mac_header += offset;
}
#else /* NET_SKBUFF_DATA_USES_OFFSET */
不使用相对偏移的情况
static inline unsigned char *skb_transport_header(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return skb->transport_header;
}
static inline void skb_reset_transport_header(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
skb->transport_header = skb->data;
}
static inline void skb_set_transport_header(struct sk_buff *skb,
const int offset)
{
skb->transport_header = skb->data + offset;
}
static inline unsigned char *skb_network_header(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return skb->network_header;
}
static inline void skb_reset_network_header(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
skb->network_header = skb->data;
}
static inline void skb_set_network_header(struct sk_buff *skb, const int offset)
{
skb->network_header = skb->data + offset;
}
static inline unsigned char *skb_mac_header(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return skb->mac_header;
}
static inline int skb_mac_header_was_set(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return skb->mac_header != NULL;
}
static inline void skb_reset_mac_header(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
skb->mac_header = skb->data;
}
static inline void skb_set_mac_header(struct sk_buff *skb, const int offset)
{
skb->mac_header = skb->data + offset;
}
#endif /* NET_SKBUFF_DATA_USES_OFFSET *///获得sk_buff结构中TCP头的指针
static inline struct tcphdr *tcp_hdr(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return (struct tcphdr *)skb_transport_header(skb);
}
//获得TCP头的长度
static inline unsigned int tcp_hdrlen(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return tcp_hdr(skb)->doff * 4;
}
//获取tcp option的长度
static inline unsigned int tcp_optlen(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return (tcp_hdr(skb)->doff - 5) * 4;
}
//获得ip头
static inline struct iphdr *ip_hdr(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return (struct iphdr *)skb_network_header(skb);
}
//获得ipip头
static inline struct iphdr *ipip_hdr(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return (struct iphdr *)skb_transport_header(skb);
}
//获取802.3MAC头指针
static inline struct ebt_802_3_hdr *ebt_802_3_hdr(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return (struct ebt_802_3_hdr *)skb_mac_header(skb);
}
//获取以太网MAC头指针
static inline struct ethhdr *eth_hdr(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
return (struct ethhdr *)skb_mac_header(skb);
}skb_copy_expand
struct sk_buff *skb_copy_expand(const struct sk_buff *skb,
int newheadroom,
int newtailroom,
int gfp_mask)
{
struct sk_buff *n;
/*
* Allocate the copy buffer
*/
n=alloc_skb(newheadroom + skb->len + newtailroom,
gfp_mask);
if(n==NULL)
return NULL;
skb_reserve(n,newheadroom);
/* Set the tail pointer and length */
skb_put(n,skb->len);
/* 2.4的代码 ---- start ---------*/
/* Copy the data only. */
if (skb_copy_bits(skb, 0, n->data, skb->len))
BUG();
/* 2.4的代码 ---- end ---------*/
/* 2.6的代码 ---- start ---------*/
head_copy_len = skb_headroom(skb);
head_copy_off = 0;
if (newheadroom <= head_copy_len)
head_copy_len = newheadroom;
else
head_copy_off = newheadroom - head_copy_len;
/* Copy the linear header and data. */
if (skb_copy_bits(skb, -head_copy_len, n->head + head_copy_off,
skb->len + head_copy_len))
BUG();
/* 2.6的代码 ---- end ---------*/
copy_skb_header(n, skb);
return n;
}改变skb的数据域
先判断skb的tailroom,如果空间够大,则我们可以把需要添加的数据放在skb的tailroom里。如果tailroom不够大,则需要调用skb_copy_expand函数来扩充tailroom或者headroom
if(skb_tailroom(skb) < 16)
{
nskb = skb_copy_expand(skb, skb_headroom(skb), skb_tailroom(skb) + 16, GFP_ATOMIC);
if(!nskb)
{
printk("low memory..../n");
dev_kfree_skb(skb);
return -1;
}
else
{
kfree_skb(skb);
skb = nskb;
}
memcpy(skb_put(skb, 16), data, 16); //拷贝数据到skb tail
}