堡垒机前戏
开发堡垒机之前,先来学习Python的paramiko模块,该模块机遇SSH用于连接远程服务器并执行相关操作
SSHClient
用于连接远程服务器并执行基本命令
基于用户名密码连接:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import paramiko # 创建SSH对象ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()# 允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())# 连接服务器ssh.connect(hostname='c1.salt.com', port=22, username='wupeiqi', password='123') # 执行命令stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')# 获取命令结果result = stdout.read() # 关闭连接ssh.close() |

1 import paramiko 2 3 transport = paramiko.Transport(('hostname', 22)) 4 transport.connect(username='wupeiqi', password='123') 5 6 ssh = paramiko.SSHClient() 7 ssh._transport = transport 8 9 stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df') 10 print stdout.read() 11 12 transport.close()
基于公钥密钥连接:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import paramikoprivate_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file('/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa')# 创建SSH对象ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()# 允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())# 连接服务器ssh.connect(hostname='c1.salt.com', port=22, username='wupeiqi', key=private_key)# 执行命令stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')# 获取命令结果result = stdout.read()# 关闭连接ssh.close() |

1 import paramiko 2 3 private_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file('/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa') 4 5 transport = paramiko.Transport(('hostname', 22)) 6 transport.connect(username='wupeiqi', pkey=private_key) 7 8 ssh = paramiko.SSHClient() 9 ssh._transport = transport 10 11 stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df') 12 13 transport.close()
SFTPClient
用于连接远程服务器并执行上传下载
基于用户名密码上传下载
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import paramikotransport = paramiko.Transport(('hostname',22))transport.connect(username='wupeiqi',password='123')sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport)# 将location.py 上传至服务器 /tmp/test.pysftp.put('/tmp/location.py', '/tmp/test.py')# 将remove_path 下载到本地 local_pathsftp.get('remove_path', 'local_path')transport.close() |
基于公钥密钥上传下载
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
import paramikoprivate_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file('/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa')transport = paramiko.Transport(('hostname', 22))transport.connect(username='wupeiqi', pkey=private_key )sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport)# 将location.py 上传至服务器 /tmp/test.pysftp.put('/tmp/location.py', '/tmp/test.py')# 将remove_path 下载到本地 local_pathsftp.get('remove_path', 'local_path')transport.close() |

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 import paramiko 4 import uuid 5 6 class Haproxy(object): 7 8 def __init__(self): 9 self.host = '172.16.103.191' 10 self.port = 22 11 self.username = 'wupeiqi' 12 self.pwd = '123' 13 self.__k = None 14 15 def create_file(self): 16 file_name = str(uuid.uuid4()) 17 with open(file_name,'w') as f: 18 f.write('sb') 19 return file_name 20 21 def run(self): 22 self.connect() 23 self.upload() 24 self.rename() 25 self.close() 26 27 def connect(self): 28 transport = paramiko.Transport((self.host,self.port)) 29 transport.connect(username=self.username,password=self.pwd) 30 self.__transport = transport 31 32 def close(self): 33 34 self.__transport.close() 35 36 def upload(self): 37 # 连接,上传 38 file_name = self.create_file() 39 40 sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(self.__transport) 41 # 将location.py 上传至服务器 /tmp/test.py 42 sftp.put(file_name, '/home/wupeiqi/tttttttttttt.py') 43 44 def rename(self): 45 46 ssh = paramiko.SSHClient() 47 ssh._transport = self.__transport 48 # 执行命令 49 stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('mv /home/wupeiqi/tttttttttttt.py /home/wupeiqi/ooooooooo.py') 50 # 获取命令结果 51 result = stdout.read() 52 53 54 ha = Haproxy() 55 ha.run()
堡垒机的实现
实现思路:
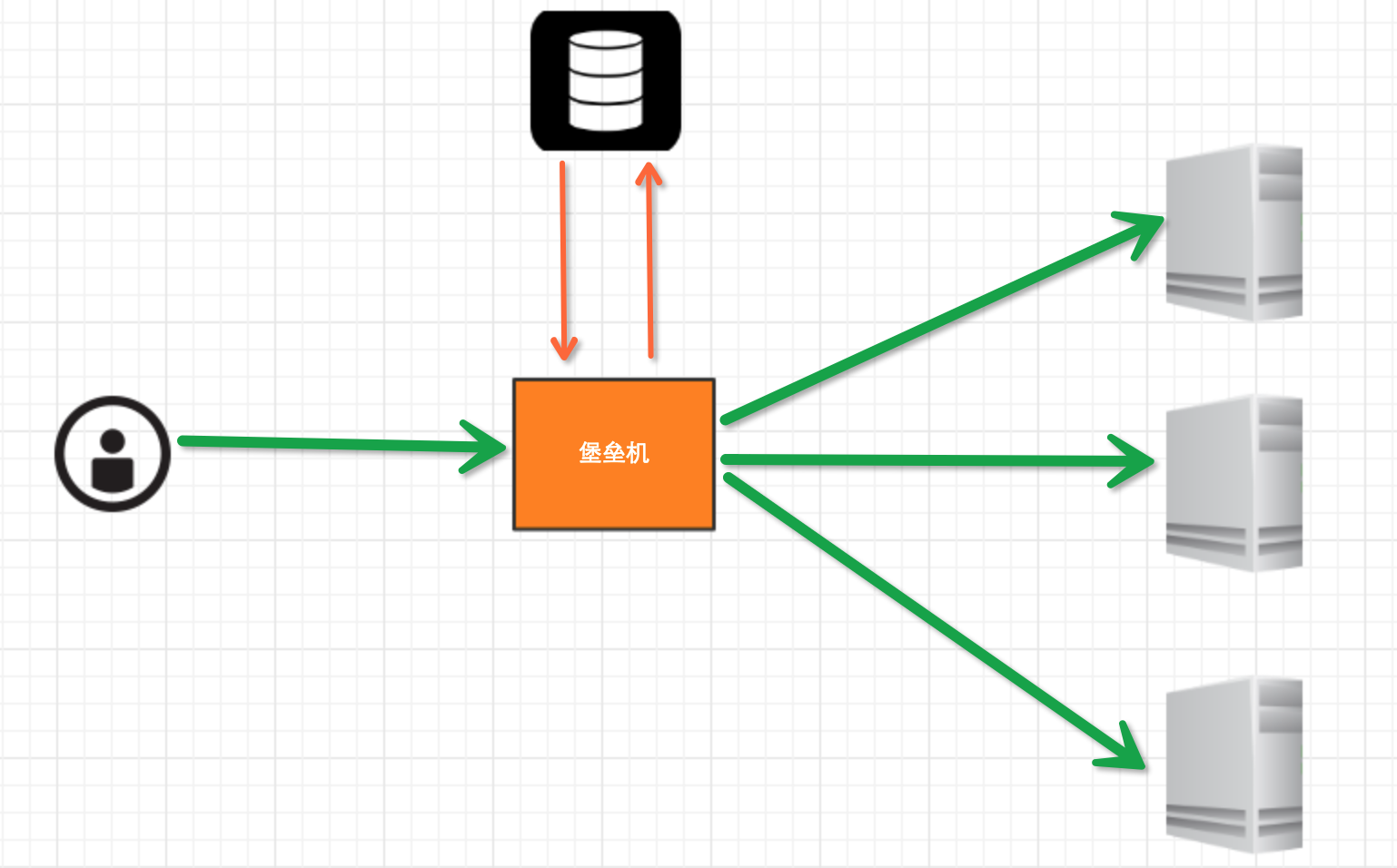
堡垒机执行流程:
- 管理员为用户在服务器上创建账号(将公钥放置服务器,或者使用用户名密码)
- 用户登陆堡垒机,输入堡垒机用户名密码,现实当前用户管理的服务器列表
- 用户选择服务器,并自动登陆
- 执行操作并同时将用户操作记录
注:配置.brashrc实现ssh登陆后自动执行脚本,如:/usr/bin/python /home/wupeiqi/menu.py
实现过程
步骤一,实现用户登陆
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
import getpassuser = raw_input('username:')pwd = getpass.getpass('password')if user == 'alex' and pwd == '123': print '登陆成功'else: print '登陆失败' |
步骤二,根据用户获取相关服务器列表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
dic = { 'alex': [ '172.16.103.189', 'c10.puppet.com', 'c11.puppet.com', ], 'eric': [ 'c100.puppet.com', ]}host_list = dic['alex']print 'please select:'for index, item in enumerate(host_list, 1): print index, iteminp = raw_input('your select (No):')inp = int(inp)hostname = host_list[inp-1]port = 22 |
步骤三,根据用户名、私钥登陆服务器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
tran = paramiko.Transport((hostname, port,))tran.start_client()default_path = os.path.join(os.environ['HOME'], '.ssh', 'id_rsa')key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(default_path)tran.auth_publickey('wupeiqi', key)# 打开一个通道chan = tran.open_session()# 获取一个终端chan.get_pty()# 激活器chan.invoke_shell()########## 利用sys.stdin,肆意妄为执行操作# 用户在终端输入内容,并将内容发送至远程服务器# 远程服务器执行命令,并将结果返回# 用户终端显示内容#########chan.close()tran.close() |

1 while True: 2 # 监视用户输入和服务器返回数据 3 # sys.stdin 处理用户输入 4 # chan 是之前创建的通道,用于接收服务器返回信息 5 readable, writeable, error = select.select([chan, sys.stdin, ],[],[],1) 6 if chan in readable: 7 try: 8 x = chan.recv(1024) 9 if len(x) == 0: 10 print ' *** EOF ', 11 break 12 sys.stdout.write(x) 13 sys.stdout.flush() 14 except socket.timeout: 15 pass 16 if sys.stdin in readable: 17 inp = sys.stdin.readline() 18 chan.sendall(inp)

# 获取原tty属性 oldtty = termios.tcgetattr(sys.stdin) try: # 为tty设置新属性 # 默认当前tty设备属性: # 输入一行回车,执行 # CTRL+C 进程退出,遇到特殊字符,特殊处理。 # 这是为原始模式,不认识所有特殊符号 # 放置特殊字符应用在当前终端,如此设置,将所有的用户输入均发送到远程服务器 tty.setraw(sys.stdin.fileno()) chan.settimeout(0.0) while True: # 监视 用户输入 和 远程服务器返回数据(socket) # 阻塞,直到句柄可读 r, w, e = select.select([chan, sys.stdin], [], [], 1) if chan in r: try: x = chan.recv(1024) if len(x) == 0: print ' *** EOF ', break sys.stdout.write(x) sys.stdout.flush() except socket.timeout: pass if sys.stdin in r: x = sys.stdin.read(1) if len(x) == 0: break chan.send(x) finally: # 重新设置终端属性 termios.tcsetattr(sys.stdin, termios.TCSADRAIN, oldtty)

1 def windows_shell(chan): 2 import threading 3 4 sys.stdout.write("Line-buffered terminal emulation. Press F6 or ^Z to send EOF. ") 5 6 def writeall(sock): 7 while True: 8 data = sock.recv(256) 9 if not data: 10 sys.stdout.write(' *** EOF *** ') 11 sys.stdout.flush() 12 break 13 sys.stdout.write(data) 14 sys.stdout.flush() 15 16 writer = threading.Thread(target=writeall, args=(chan,)) 17 writer.start() 18 19 try: 20 while True: 21 d = sys.stdin.read(1) 22 if not d: 23 break 24 chan.send(d) 25 except EOFError: 26 # user hit ^Z or F6 27 pass
注:密码验证 t.auth_password(username, pw)
详见:paramiko源码demo
