生命周期函数
什么是生命周期?
从Vue实例创建、运行、到销毁期间,总是伴随着各种各样的事件,这些事件,统称为生命周期!
beforeMount:此时已经完成了模板的编译,但是还没有挂载到页面中
mounted:此时,已经将编译好的模板,挂载到了页面指定的容器中显示
运行期间的生命周期函数
beforeUpdate:状态更新之前执行此函数, 此时 data 中的状态值是最新的,但是界面上显示的 数据还是旧的,因为此时还没有开始重新渲染DOM节点
updated:实例更新完毕之后调用此函数,此时 data 中的状态值 和 界面上显示的数据,都已经完成了更新,界面已经被重新渲染好了!
销毁期间的生命周期函数
beforeDestroy:实例销毁之前调用。在这一步,实例仍然完全可用
destroyed:Vue 实例销毁后调用。调用后,Vue 实例指示的所有东西都会解绑定,所有的事件监听器会被移除,所有的子实例也会被销毁
生命周期函数流程图
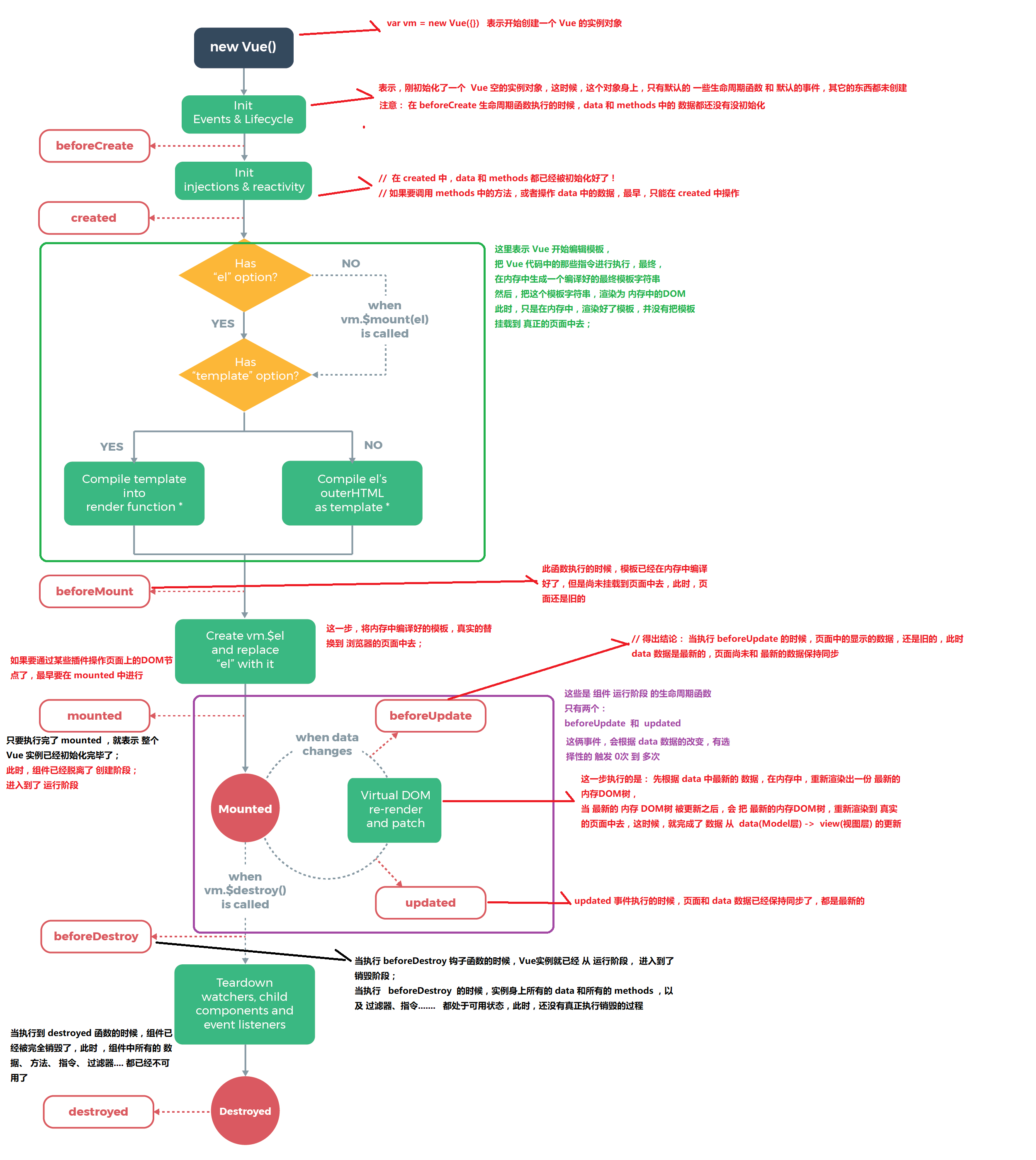
生命周期函数示例:

<div id="app"> <input type="button" value="修改msg" @click="msg='No'"> <h3 id="h3">{{ msg }}</h3> </div>

<script>
// 创建 Vue 实例,得到 ViewModel
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'ok'
},
methods: {
show() {
console.log('执行了show方法')
}
},
beforeCreate() { // 这是我们遇到的第一个生命周期函数,表示实例完全被创建出来之前,会执行它
// console.log(this.msg)
// this.show()
// 注意: 在 beforeCreate 生命周期函数执行的时候,data 和 methods 中的 数据都还没有没初始化
},
created() { // 这是遇到的第二个生命周期函数
// console.log(this.msg)
// this.show()
// 在 created 中,data 和 methods 都已经被初始化好了!
// 如果要调用 methods 中的方法,或者操作 data 中的数据,最早,只能在 created 中操作
},
beforeMount() { // 这是遇到的第3个生命周期函数,表示 模板已经在内存中编辑完成了,但是尚未把 模板渲染到 页面中
// console.log(document.getElementById('h3').innerText)
// 在 beforeMount 执行的时候,页面中的元素,还没有被真正替换过来,只是之前写的一些模板字符串
},
mounted() { // 这是遇到的第4个生命周期函数,表示,内存中的模板,已经真实的挂载到了页面中,用户已经可以看到渲染好的页面了
// console.log(document.getElementById('h3').innerText)
// 注意: mounted 是 实例创建期间的最后一个生命周期函数,当执行完 mounted 就表示,实例已经被完全创建好了,此时,如果没有其它操作的话,这个实例,就静静的 躺在我们的内存中,一动不动
},
// 接下来的是运行中的两个事件
beforeUpdate() { // 这时候,表示 我们的界面还没有被更新【数据被更新了吗? 数据肯定被更新了】
/* console.log('界面上元素的内容:' + document.getElementById('h3').innerText)
console.log('data 中的 msg 数据是:' + this.msg) */
// 得出结论: 当执行 beforeUpdate 的时候,页面中的显示的数据,还是旧的,此时 data 数据是最新的,页面尚未和 最新的数据保持同步
},
updated() {
console.log('界面上元素的内容:' + document.getElementById('h3').innerText)
console.log('data 中的 msg 数据是:' + this.msg)
// updated 事件执行的时候,页面和 data 数据已经保持同步了,都是最新的
}
});
</script>
vue-resource实现get post jsonp请求
除了 vue-resource 之外,还可以使用 axios 的第三方包实现实现数据的请求
1.之前的学习中,如何发起数据请求?
2.常见的数据请求类型? get post jsonp
3.测试的URL请求资源地址:
-
由于浏览器的安全性限制,不允许AJAX访问 协议不同、域名不同、端口号不同的 数据接口,浏览器认为这种访问不安全;
-
可以通过动态创建script标签的形式,把script标签的src属性,指向数据接口的地址,因为script标签不存在跨域限制,这种数据获取方式,称作JSONP(注意:根据JSONP的实现原理,知晓,JSONP只支持Get请求);
-
具体实现过程:
-
先在客户端定义一个回调方法,预定义对数据的操作;
-
再把这个回调方法的名称,通过URL传参的形式,提交到服务器的数据接口;
-
服务器数据接口组织好要发送给客户端的数据,再拿着客户端传递过来的回调方法名称,拼接出一个调用这个方法的字符串,发送给客户端去解析执行;
-
客户端拿到服务器返回的字符串之后,当作Script脚本去解析执行,这样就能够拿到JSONP的数据了;

getInfo() { // get 方式获取数据
this.$http.get('http://127.0.0.1:8899/api/getlunbo').then(res => {
console.log(res.body);
})
}
7.发送post请求

postInfo() { var url = 'http://127.0.0.1:8899/api/post'; // post 方法接收三个参数: // 参数1: 要请求的URL地址 // 参数2: 要发送的数据对象 // 参数3: 指定post提交的编码类型为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded this.$http.post(url, { name: 'zs' }, { emulateJSON: true }).then(res => { console.log(res.body); }); }
8.发送JSONP请求获取数据

jsonpInfo() { // JSONP形式从服务器获取数据
var url = 'http://127.0.0.1:8899/api/jsonp';
this.$http.jsonp(url).then(res => {
console.log(res.body);
});
}
vue-resource 改造品牌列表

<div id="app"> <div class="panel panel-primary"> <div class="panel-heading"> <h3 class="panel-title">添加品牌</h3> </div> <div class="panel-body form-inline"> <label> Name: <input type="text" v-model="name" class="form-control"> </label> <input type="button" value="添加" @click="add" class="btn btn-primary"> </div> </div> <table class="table table-bordered table-hover table-striped"> <thead> <tr> <th>Id</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Ctime</th> <th>Operation</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for="item in list" :key="item.id"> <td>{{item.id}}</td> <td>{{item.name}}</td> <td>{{item.ctime}}</td> <td> <a href="" @click.prevent="del(item.id)">删除</a> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div>

<script>
// 如果我们通过全局配置了,请求的数据接口 根域名,则 ,在每次单独发起 http 请求的时候,请求的 url 路径,应该以相对路径开头,前面不能带 / ,否则 不会启用根路径做拼接;
Vue.http.options.root = 'http://vue.studyit.io/';
// 全局启用 emulateJSON 选项
Vue.http.options.emulateJSON = true;
// 创建 Vue 实例,得到 ViewModel
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
name: '',
list: [ // 存放所有品牌列表的数组
]
},
created() { // 当 vm 实例 的 data 和 methods 初始化完毕后,vm实例会自动执行created 这个生命周期函数
this.getAllList()
},
methods: {
getAllList() { // 获取所有的品牌列表
// 分析:
// 1. 由于已经导入了 Vue-resource这个包,所以 ,可以直接通过 this.$http 来发起数据请求
// 2. 根据接口API文档,知道,获取列表的时候,应该发起一个 get 请求
// 3. this.$http.get('url').then(function(result){})
// 4. 当通过 then 指定回调函数之后,在回调函数中,可以拿到数据服务器返回的 result
// 5. 先判断 result.status 是否等于0,如果等于0,就成功了,可以 把 result.message 赋值给 this.list ; 如果不等于0,可以弹框提醒,获取数据失败!
this.$http.get('api/getprodlist').then(result => {
// 注意: 通过 $http 获取到的数据,都在 result.body 中放着
var result = result.body
if (result.status === 0) {
// 成功了
this.list = result.message
} else {
// 失败了
alert('获取数据失败!')
}
})
},
add() { // 添加品牌列表到后台服务器
// 分析:
// 1. 听过查看 数据API接口,发现,要发送一个 Post 请求, this.$http.post
// 2. this.$http.post() 中接收三个参数:
// 2.1 第一个参数: 要请求的URL地址
// 2.2 第二个参数: 要提交给服务器的数据 ,要以对象形式提交给服务器 { name: this.name }
// 3.3 第三个参数: 是一个配置对象,要以哪种表单数据类型提交过去, { emulateJSON: true }, 以普通表单格式,将数据提交给服务器 application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// 3. 在 post 方法中,使用 .then 来设置成功的回调函数,如果想要拿到成功的结果,需要 result.body
/* this.$http.post('api/addproduct', { name: this.name }, { emulateJSON: true }).then(result => {
if (result.body.status === 0) {
// 成功了!
// 添加完成后,只需要手动,再调用一下 getAllList 就能刷新品牌列表了
this.getAllList()
// 清空 name
this.name = ''
} else {
// 失败了
alert('添加失败!')
}
}) */
this.$http.post('api/addproduct', { name: this.name }).then(result => {
if (result.body.status === 0) {
// 成功了!
// 添加完成后,只需要手动,再调用一下 getAllList 就能刷新品牌列表了
this.getAllList()
// 清空 name
this.name = ''
} else {
// 失败了
alert('添加失败!')
}
})
},
del(id) { // 删除品牌
this.$http.get('api/delproduct/' + id).then(result => {
if (result.body.status === 0) {
// 删除成功
this.getAllList()
} else {
alert('删除失败!')
}
})
}
}
});
</script>
