栈Stack:
栈的概述:

虽然看起来它只是数组的子集,但是栈的这种结构对于计算机中组建逻辑有这非常非常大的作用。
入栈 出栈:
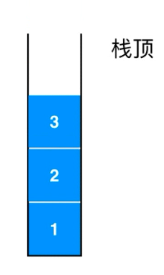
栈是一种先进后出(FILO First in Last Out )的结构。
![]()
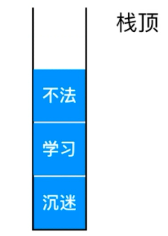
栈的应用01:撤销操作:
![]()
![]()
栈的应用02:程序调用的系统栈:
了解它有助于我们更加理解递归!!!


此时的系统栈中会记录下:
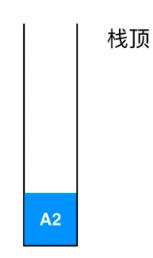
A2的意思是执行到A函数的第二行了。
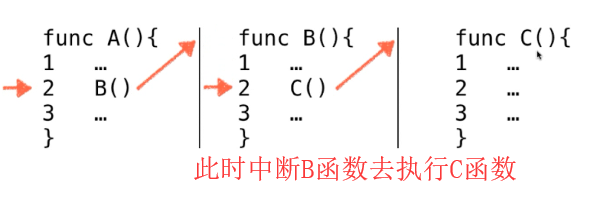
同样系统栈中会继续压入!!!


当C 函数执行完毕之后,我们的计算机就不知道该执行谁了,
它此时会看系统栈中的内容,
发现是B2 ,所以开始从B2继续执行。(同时会弹出B2)
当B函数也执行完毕时候,计算机又会看下系统栈,发现是A2
所以,它就会从A2开始执行。(同时会弹出A2)
当A函数也执行完毕的时候,系统栈中为空。所以函数执行完毕!!!
这个过程对理解递归有很大的帮助,后面会有关于递归的内容。
栈的实现:
栈基本的五种操作:

其中peek () 有的 语言中 喜欢叫它top() !

这里说一种 栈的底层实现(另外一种后面会说):
后面的队列会说两种不同的底层实现。
代码设计方式:
先设计一个接口,然后用ArrayStack 去实现它。

具体代码如下:
从头写一个自己的栈出来(主要利用数组,将数组封装成一个栈。)!!!注:数组也是我们自定义的可以动态改变长度的数组!

1 package cn.zcb.demo03; 2 3 public interface MyInterface<T> { 4 /*接口也是支持泛型的*/ 5 public abstract void push(T a); 6 public abstract T pop(); 7 public abstract T peek(); 8 public abstract int getSize(); 9 public abstract boolean isEmpty(); 10 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo03; 2 3 public class MyStack<T> implements MyInterface<T> { 4 /* 5 * 我们自己的栈 。 6 * */ 7 //它的内部用 我们之前自己写的数组 来做 。 8 private MyArray <T> array; //MyArray 是我们自己写的数组类。 9 //构造函数 10 public MyStack(int capacity){ 11 array = new MyArray<>(capacity); 12 } 13 public MyStack(){ 14 array = new MyArray<>(); 15 } 16 17 public void push(T a){ 18 array.addLast(a); 19 } 20 public T pop(){ 21 return array.removeLast(); 22 } 23 public T peek(){ 24 return array.getByIndex(array.getSize()-1); //栈顶元素 25 } 26 public int getSize(){ 27 return array.getSize(); 28 } 29 public boolean isEmpty(){ 30 return array.isEmpty(); 31 } 32 //下面的方法不是 接口中的方法 !!! 33 public int getCapacity(){ 34 return array.getCapacity(); 35 } 36 37 //为了打印方便 ,这里重写Object 中的toString 38 @Override 39 public String toString(){ 40 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 41 builder.append("Stack's data is below : "); 42 builder.append("["); 43 for (int i=0;i< array.getSize();i++){ 44 builder.append(array.getByIndex(i)); 45 if(i != array.getSize()-1){ 46 builder.append(" ,"); 47 } 48 } 49 builder.append("] top"); 50 return builder.toString(); 51 } 52 53 54 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo03; 2 3 public class MyArray<T> { 4 private T[] data; //数组 5 private int size; //数组实际大小, 6 //容量不用写,可以由data.length()得知 7 8 //满参构造函数 9 public MyArray(int capacity){ 10 // this.data = new int[capacity]; 11 // this.data = new T[capacity]; //不支持这样 12 this.data = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; //先new 出个 Object[] 类的,然后转为 T[] 13 this.size = 0; //开始时 实际大小size =0 14 } 15 //空参构造器 16 public MyArray(){ 17 this(10); //如果是空参的话,调用有参构造器。默认是10 18 } 19 20 //获取数组中的元素的个数 21 public int getSize(){ 22 return this.size; 23 } 24 25 //获取数组的容量 26 public int getCapacity(){ 27 return this.data.length; 28 } 29 30 //数组中是否为空 31 public boolean isEmpty(){ 32 return this.size ==0; 33 } 34 /////////////////////增//////////////////////////// 35 //向 数组的末尾添加一个新元素 36 public void addLast(T num){ 37 /* 38 if(size == this.data.length){ 39 //此时开辟的空间已经满了 40 //这里先抛出一个异常 41 throw new IllegalArgumentException("addLast failed.数组已经满了"); 42 } 43 this.data[size] = num; 44 size ++; //要维持数组 指针。 size 是当前数组中的个数。 45 */ 46 //此时其实可以直接复用 insert ()函数 47 insert(this.size,num); 48 } 49 // 向数组头添加元素 (直接复用 向指定位置添加元素的函数 ) 50 public void addFirst(T num){ 51 insert(0,num); 52 } 53 54 //向 指定数组位置添加一个新元素 55 public void insert(int idx,T num){ 56 if(this.size == this.data.length){ 57 // throw new IllegalArgumentException("数组已经放满了"); 58 /*此时对其扩容*/ 59 resize(2*this.data.length); 60 61 62 } 63 if(idx <0 || idx > this.size ) 64 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引非法"); 65 66 for(int i=this.size-1;i >= idx;--i){ 67 this.data[i+1] = this.data[i]; 68 } 69 this.data[idx] = num; 70 //更新size 71 this.size ++; 72 } 73 74 //////////////////////删/////////////////////////////////////// 75 //删除第一个 76 public T removeFirst(){ 77 return remove(0); //删除并将之返回出去 78 } 79 80 //删除最后一个 81 public T removeLast(){ 82 return remove(this.size-1); 83 } 84 85 //删除指定位置 的元素 86 public T remove(int idx){ //返回 删除的元素 87 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size -1) 88 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx错误!"); 89 T temp = this.data[idx]; 90 for (int i =idx;i<this.size - 1;i++){ 91 this.data[i] = this.data[i+1]; 92 } 93 this.size -- ; 94 95 //动态减少 当数组中的元素少于空间的四分之一的时候,缩减空间为原来的一半(这样可以有效的防止 复杂度震荡问题)。 96 if(this.size == this.data.length / 4 && this.data.length/2 != 0 ){ //第二个条件是防止 length =1 的时候 97 resize(this.data.length/2); 98 } 99 return temp; 100 } 101 102 //删除 某个元素 不根据其位置 //它之所以返回void 是因为调用着已经知道的element ,所以没必要再返回出来了。 103 public void removeElement(T element){ 104 //首先要 寻找是否有 element 105 int idx = find(element); 106 if(idx == -1){ 107 throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有该元素"); 108 }else{ 109 remove(idx); 110 } 111 } 112 113 //////////////////////改/////////////////////////////////////// 114 //修改索引为 idx 的元素为 num 115 public void setByIndex(int idx,T num){ 116 if(idx <0 || idx > this.size) 117 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 118 119 this.data[idx] = num; 120 } 121 122 123 //////////////////////查/////////////////////////////////////// 124 //获取整个数组的概括 125 //重写 toString() 当打印arr 时候,就会调用该方法! 126 @Override 127 public String toString(){ 128 StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); 129 res.append(String.format("Array:size = %d,capacity = %d ",this.size,this.data.length)); 130 res.append('['); 131 for (int i =0 ;i<this.size;i++){ 132 res.append(data[i]); 133 if(i != this.size -1) 134 res.append(", "); 135 } 136 res.append(']'); 137 return res.toString(); 138 } 139 //获取idx 索引位置的 元素 140 public T getByIndex(int idx){ 141 if (idx < 0 || idx >this.size) { 142 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引传入错误!"); 143 } 144 return this.data[idx]; 145 } 146 147 //////////////////////包含/////////////////////////////////////// 148 public boolean contains(T num){ 149 for (int i=0;i<this.size;i++){ 150 if(this.data[i] == num){ 151 return true; 152 } 153 } 154 return false; 155 } 156 //////////////////////寻找//////////////////////////////////// 157 public int find(T num){ 158 //寻找数组中是否有 num ,如果有返回其索引,反之 返回-1 159 for (int i =0;i<this.size;i++){ 160 if(this.data[i] == num){ 161 return i; 162 } 163 } 164 return -1; 165 } 166 //////////////////////实现动态数组 resize()//////////////////////////////////// 167 private void resize(int new_capacity){ //之所以 用 private 是不让用户调用, 数组如果空间不足会自己扩展的。 168 T[] new_data =(T[]) new Object[new_capacity]; 169 170 for (int i =0;i<this.size;i++){ 171 new_data[i] = this.data[i]; 172 } 173 // 174 this.data = new_data; //此时新数组的size 不变 , 新数组的length 也不用变 175 } 176 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo03; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 MyStack<Integer> stk = new MyStack(); //也可以给定容量 new MyStack(20); 6 for (int i = 0;i<5;i++){ 7 //模拟5次入栈操作 8 stk.push(i); 9 System.out.println(stk); 10 } 11 //一次出栈操作 12 stk.pop(); 13 System.out.println(stk); 14 } 15 }

这样我们就写了一个基于动态数组而实现的栈!!!
(封装动态数组使之成为一个栈!)
栈的另一个应用:括号匹配:
通过Leetcode 中的第20题来说,


1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 import java.util.Stack; 4 5 public class Test { 6 public boolean isValid(String s){ 7 if(s.length() == 0) return true; 8 char c_1 = s.charAt(0); 9 if(c_1 ==']' || c_1 =='}' || c_1 ==')'){ 10 return false; 11 } 12 Stack<Character> stk = new Stack<>(); 13 for (int i =0;i<s.length();i++){ 14 char c = s.charAt(i); 15 if(c == '{' || c =='[' || c=='('){ 16 stk.push(c); 17 } 18 if(c =='}'){ 19 if(!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek() =='{') { 20 stk.pop(); 21 }else{ 22 return false; 23 } 24 } 25 if(c ==']'){ 26 if(!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek() =='[') { 27 stk.pop(); 28 }else{ 29 return false; 30 } 31 } 32 if(c ==')'){ 33 if(!stk.isEmpty() && stk.peek() =='(') { 34 stk.pop(); 35 }else{ 36 return false; 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 return stk.isEmpty(); 41 } 42 43 }

1 class Solution { 2 public boolean isValid(String s){ 3 // if(s.length() == 0) return true; 这行用没必要有!!! 4 Stack<Character> stk = new Stack<>(); 5 for (int i =0;i<s.length();i++){ 6 char c = s.charAt(i); 7 if(c == '{' || c =='[' || c=='('){ 8 stk.push(c); 9 }else{ 10 if(stk.isEmpty()) return false; 11 char topChar = stk.pop(); //正常匹配的时候,每次都要弹出一个的。 12 if(c == ']' && topChar !='['){ 13 return false; 14 } 15 if(c == '}' && topChar !='{'){ 16 return false; 17 } 18 if(c == ')' && topChar !='('){ 19 return false; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 return stk.isEmpty(); 24 } 25 }
队列Queue:
队列概述:

![]()
FIFO First In First Out

下面我们将写一个基于 我们自己的数组MyArray 的队列!
代码如下:
队列也是要支持泛型!

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class MyArray<T> { 4 private T[] data; //数组 5 private int size; //数组实际大小, 6 //容量不用写,可以由data.length()得知 7 8 //满参构造函数 9 public MyArray(int capacity){ 10 // this.data = new int[capacity]; 11 // this.data = new T[capacity]; //不支持这样 12 this.data = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; //先new 出个 Object[] 类的,然后转为 T[] 13 this.size = 0; //开始时 实际大小size =0 14 } 15 //空参构造器 16 public MyArray(){ 17 this(10); //如果是空参的话,调用有参构造器。默认是10 18 } 19 20 //获取数组中的元素的个数 21 public int getSize(){ 22 return this.size; 23 } 24 25 //获取数组的容量 26 public int getCapacity(){ 27 return this.data.length; 28 } 29 30 //数组中是否为空 31 public boolean isEmpty(){ 32 return this.size ==0; 33 } 34 /////////////////////增//////////////////////////// 35 //向 数组的末尾添加一个新元素 36 public void addLast(T num){ 37 /* 38 if(size == this.data.length){ 39 //此时开辟的空间已经满了 40 //这里先抛出一个异常 41 throw new IllegalArgumentException("addLast failed.数组已经满了"); 42 } 43 this.data[size] = num; 44 size ++; //要维持数组 指针。 size 是当前数组中的个数。 45 */ 46 //此时其实可以直接复用 insert ()函数 47 insert(this.size,num); 48 } 49 // 向数组头添加元素 (直接复用 向指定位置添加元素的函数 ) 50 public void addFirst(T num){ 51 insert(0,num); 52 } 53 54 //向 指定数组位置添加一个新元素 55 public void insert(int idx,T num){ 56 if(this.size == this.data.length){ 57 // throw new IllegalArgumentException("数组已经放满了"); 58 /*此时对其扩容*/ 59 resize(2*this.data.length); 60 61 62 } 63 if(idx <0 || idx > this.size ) 64 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引非法"); 65 66 for(int i=this.size-1;i >= idx;--i){ 67 this.data[i+1] = this.data[i]; 68 } 69 this.data[idx] = num; 70 //更新size 71 this.size ++; 72 } 73 74 //////////////////////删/////////////////////////////////////// 75 //删除第一个 76 public T removeFirst(){ 77 return remove(0); //删除并将之返回出去 78 } 79 80 //删除最后一个 81 public T removeLast(){ 82 return remove(this.size-1); 83 } 84 85 //删除指定位置 的元素 86 public T remove(int idx){ //返回 删除的元素 87 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size -1) 88 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx错误!"); 89 T temp = this.data[idx]; 90 for (int i =idx;i<this.size - 1;i++){ 91 this.data[i] = this.data[i+1]; 92 } 93 this.size -- ; 94 95 //动态减少 当数组中的元素少于空间的四分之一的时候,缩减空间为原来的一半(这样可以有效的防止 复杂度震荡问题)。 96 if(this.size == this.data.length / 4 && this.data.length/2 != 0 ){ //第二个条件是防止 length =1 的时候 97 resize(this.data.length/2); 98 } 99 return temp; 100 } 101 102 //删除 某个元素 不根据其位置 //它之所以返回void 是因为调用着已经知道的element ,所以没必要再返回出来了。 103 public void removeElement(T element){ 104 //首先要 寻找是否有 element 105 int idx = find(element); 106 if(idx == -1){ 107 throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有该元素"); 108 }else{ 109 remove(idx); 110 } 111 } 112 113 //////////////////////改/////////////////////////////////////// 114 //修改索引为 idx 的元素为 num 115 public void setByIndex(int idx,T num){ 116 if(idx <0 || idx > this.size) 117 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 118 119 this.data[idx] = num; 120 } 121 122 123 //////////////////////查/////////////////////////////////////// 124 //获取整个数组的概括 125 //重写 toString() 当打印arr 时候,就会调用该方法! 126 @Override 127 public String toString(){ 128 StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); 129 res.append(String.format("Array:size = %d,capacity = %d ",this.size,this.data.length)); 130 res.append('['); 131 for (int i =0 ;i<this.size;i++){ 132 res.append(data[i]); 133 if(i != this.size -1) 134 res.append(", "); 135 } 136 res.append(']'); 137 return res.toString(); 138 } 139 //获取idx 索引位置的 元素 140 public T getByIndex(int idx){ 141 if (idx < 0 || idx >this.size) { 142 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引传入错误!"); 143 } 144 return this.data[idx]; 145 } 146 147 //////////////////////包含/////////////////////////////////////// 148 public boolean contains(T num){ 149 for (int i=0;i<this.size;i++){ 150 if(this.data[i] == num){ 151 return true; 152 } 153 } 154 return false; 155 } 156 //////////////////////寻找//////////////////////////////////// 157 public int find(T num){ 158 //寻找数组中是否有 num ,如果有返回其索引,反之 返回-1 159 for (int i =0;i<this.size;i++){ 160 if(this.data[i] == num){ 161 return i; 162 } 163 } 164 return -1; 165 } 166 //////////////////////实现动态数组 resize()//////////////////////////////////// 167 private void resize(int new_capacity){ //之所以 用 private 是不让用户调用, 数组如果空间不足会自己扩展的。 168 T[] new_data =(T[]) new Object[new_capacity]; 169 170 for (int i =0;i<this.size;i++){ 171 new_data[i] = this.data[i]; 172 } 173 // 174 this.data = new_data; //此时新数组的size 不变 , 新数组的length 也不用变 175 } 176 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 3 public interface MyInterface_Queue <T> { 4 public abstract void enqueue(T a); //入队 5 public abstract T dequeue(); //出队 6 public abstract T getFront(); //队头 7 public abstract int getSize(); //得到队列中的实际长度 8 public abstract boolean isEmpty(); //是否为空。 9 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 public class MyQueue <T> implements MyInterface_Queue <T> { 3 4 //我们自己的 队列,实际内部的结构还是数组(我们自己写的数组MyArray) 5 private MyArray <T> array; 6 //构造函数 7 public MyQueue(int capacity){ 8 array = new MyArray<>(capacity); 9 } 10 public MyQueue(){ 11 array = new MyArray<>(); 12 } 13 14 public void enqueue(T a){ 15 array.addLast(a); 16 } 17 public T dequeue(){ 18 return array.removeFirst(); 19 } 20 public T getFront(){ 21 return array.getByIndex(0); 22 } 23 public int getSize(){ 24 return array.getSize(); 25 } 26 public boolean isEmpty(){ 27 return array.isEmpty(); 28 } 29 public int getCapacity(){ 30 return array.getCapacity(); 31 } 32 @Override 33 public String toString(){ 34 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 35 builder.append("Queue's data is below: ["); 36 for (int i =0;i<array.getSize();i++){ 37 builder.append(array.getByIndex(i)); 38 if(i != array.getSize() -1){ 39 builder.append(" ,"); 40 } 41 } 42 builder.append("] 队尾"); 43 return builder.toString(); 44 } 45 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo04; 2 public class Test { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 MyQueue<Integer> quu = new MyQueue<>(24); //队列中有 24 个元素 5 for (int i =0;i<10;i++){ 6 quu.enqueue(i); 7 } 8 System.out.println(quu); 9 for (int i =0;i<5;i++){ 10 quu.dequeue(); //出队 五个。 11 System.out.println(quu); 12 } 13 quu.enqueue(90); //新入队 一个 14 System.out.println(quu); 15 } 16 }
时间复杂度分析:

入队受到 MyArray 的动态变化长度的影响,所以 是均摊!
出队就不是了,我们每次将第一个拿出后,后面的都要往前移动一个位置,所以是O(n)
那么这种出队的高复杂度的情况如何优化呢?
下节的循环队列会解决这个问题!
循环队列:
循环队列概述:
上面是数组队列 下面看循环队列
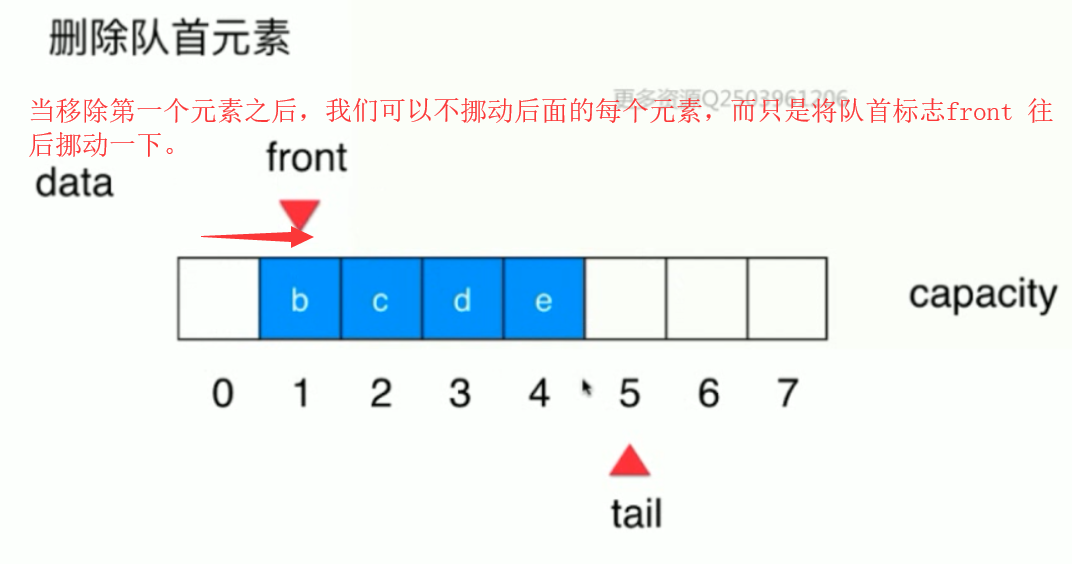
基于这样的想法,就有了循环队列的实现方式!
当队列为空的时候(此时的front 不知道指向谁(本应指第一个),只好和tail 一样):

当队列不为空的时候:
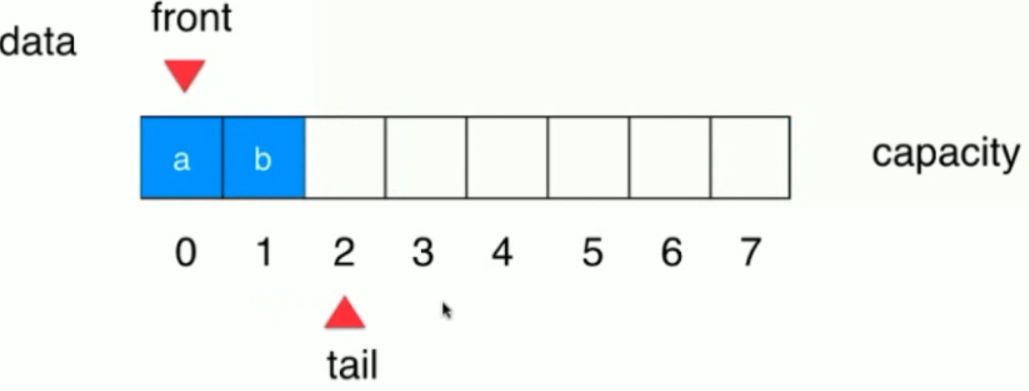
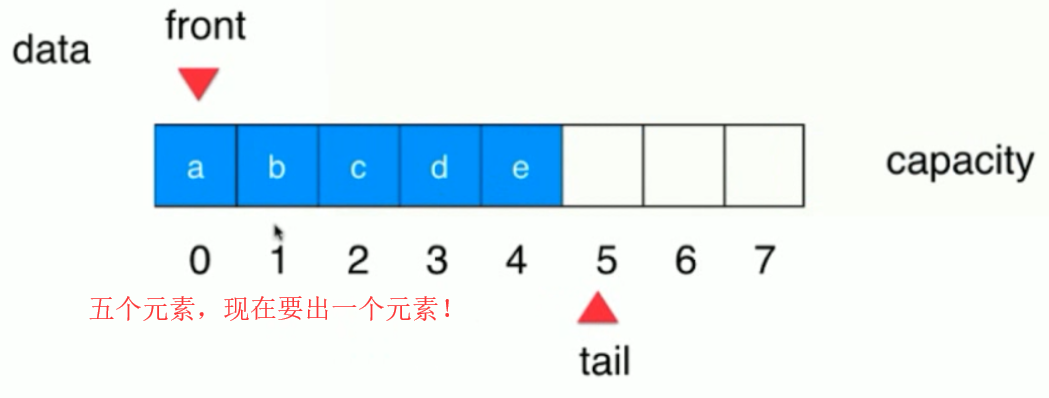
五个元素,现在出队一个,只需要将a弹出,front 向后移动一个!


此时如果后面一直push() 元素的话,此时tail就不能++了。
其实此时可以把它看做是个环,0-7 形成一个环,7之后就是0了。
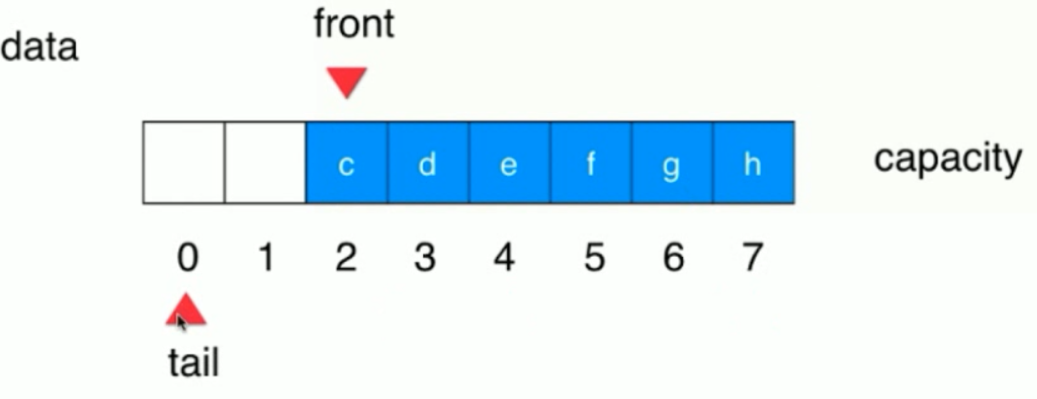
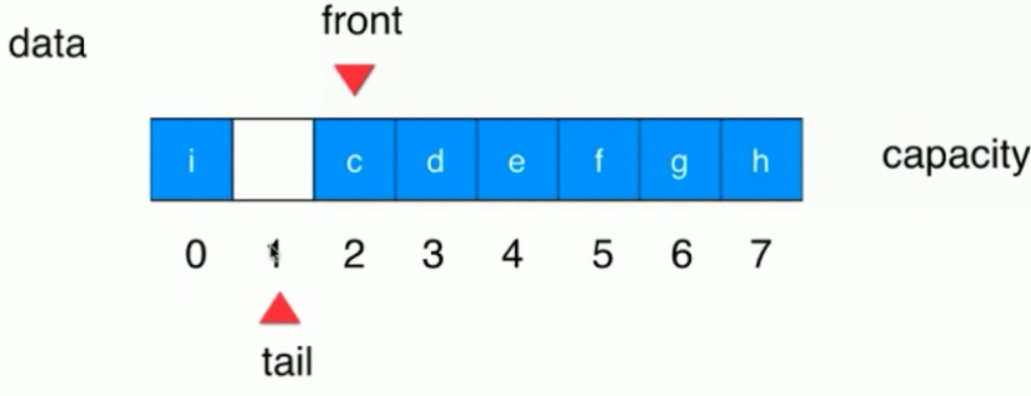
队列可以插入直到tail 比 front 小一个,即上图所示,就不能插入了(之所以不能继续插入,是因为front==tail 代表的是空队列!)。
综上给出如下定义:
![]()
当tail +1 = front 的时候就可以进行扩容了。(其实我们要知道,这里我们是有意识的浪费了一个空间!!!)
还有上述的tail +1 == front 是不准确的, 其实应该是 (tail +1 )% c == front%c , c是队列的容量! 。 因为front 和tail 是一直可以增加的。
总结:front 是当前第一个元素。tail 是指向下一个插入的地方!
代码如下:

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public interface MyInterface_Queue <T> { 4 public abstract void enqueue(T a); //入队 5 public abstract T dequeue(); //出队 6 public abstract T getFront(); //队头 7 public abstract int getSize(); //得到队列中的实际长度 8 public abstract boolean isEmpty(); //是否为空。 9 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class MyLoopQueue <T> implements MyInterface_Queue<T> { 4 private T[] data; 5 private int front,tail; 6 private int size; //其实不用它,也可以,是可以直接由front 和 tail 推出的,但是加上它会使得逻辑变得简单。 7 8 //构造函数 9 public MyLoopQueue(int capacity){ 10 data =(T[] ) new Object[capacity +1] ;//因为循环队列会浪费一个空间, 所以开辟的时候要多开辟一个 11 this.front = 0; 12 this.tail = 0; 13 this.size = 0; 14 } 15 public MyLoopQueue(){ 16 this(10); //用户所认为的是 10 ,但是实际上是 11 17 } 18 private void resize(int newCapacity){ 19 T[] newData = (T[]) new Object[newCapacity +1]; 20 for (int i =0;i<this.size ;i++){ //将旧的队列的 front 放到新的队列中的0号位置。 21 newData[i] = this.data[(i+front)%this.data.length]; //取余是为了防止越界! 22 } 23 data = newData ; 24 front = 0; 25 tail = this.size; 26 //size不需要变 27 } 28 public void enqueue(T a){ 29 if( (tail +1)%this.data.length == front ){ //看是否队列 满了。(其实没有满,浪费了一个) 30 this.resize(this.getCapacity() *2); //注意这里不能是 this.data.length ,它们是有一个的差距的。 31 } 32 data[tail] = a; 33 tail = (tail +1)%this.data.length; //取余是为了防止越界! 34 this.size ++; 35 } 36 public T dequeue(){ 37 if(this.isEmpty()){ 38 throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列为空!!!"); 39 } 40 T ret =this.data[front]; 41 this.data[front] = null; //出队! 42 front = (front+1)%this.data.length; //维护front 43 this.size --; 44 //出队之后,也可以进行缩容。 45 if(this.size == this.getCapacity() /4 && this.getCapacity()/2 !=0 ){ //当 size == 容量的1/4 时候,就将容量缩小为 1/2 这样做的目的是为了防止震荡的出现 46 this.resize(this.getCapacity()/2); //缩容的值不应该等于0 !!! 47 } 48 49 return ret; 50 } 51 public T getFront(){ 52 if(this.isEmpty()) 53 throw new IllegalArgumentException("队列为空!!!"); 54 return this.data[front]; 55 } 56 public int getSize(){ 57 return this.size; 58 } 59 public boolean isEmpty(){ 60 return front == tail; 61 } 62 63 public int getCapacity(){ 64 return this.data.length-1; 65 } 66 67 @Override 68 public String toString(){ //遍历队列的另一种方式, resize的方式是其中的一种,这是另外一种! 69 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 70 builder.append("LoopQueue's data is below: front["); 71 for (int i =front ;i != tail ; i = (i+1)%this.data.length){ 72 builder.append(this.data[i]); 73 if( (i+1)%this.data.length != tail ) 74 builder.append(" ,"); 75 } 76 builder.append(String.format("] 队尾 Capacity: %d Size :%d", this.getCapacity(),this.size )); 77 return builder.toString(); 78 } 79 }

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 MyLoopQueue <Integer> loopQueue = new MyLoopQueue<>(5); 6 for (int i =0;i<7;i++){ 7 loopQueue.enqueue(i); 8 System.out.println(loopQueue); 9 } 10 loopQueue.dequeue(); 11 System.out.println(loopQueue); 12 loopQueue.dequeue(); 13 System.out.println(loopQueue); 14 15 for (int i =0;i<20;i++){ 16 loopQueue.enqueue(i);//再入队 20个元素 17 System.out.println(loopQueue); 18 } 19 } 20 21 22 23 } 24 /* 输出: 我们也可以看出,从用户的角度来看,循环队列 一侧是队首,一侧是队尾,包括里面的capacity 是比真实空间小一个的,用户都不用关心。 25 LoopQueue's data is below: 26 front[0] 队尾 Capacity: 5 Size :1 27 LoopQueue's data is below: 28 front[0 ,1] 队尾 Capacity: 5 Size :2 29 LoopQueue's data is below: 30 front[0 ,1 ,2] 队尾 Capacity: 5 Size :3 31 LoopQueue's data is below: 32 front[0 ,1 ,2 ,3] 队尾 Capacity: 5 Size :4 33 LoopQueue's data is below: 34 front[0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4] 队尾 Capacity: 5 Size :5 35 LoopQueue's data is below: 36 front[0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :6 37 LoopQueue's data is below: 38 front[0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :7 39 LoopQueue's data is below: 40 front[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :6 41 LoopQueue's data is below: 42 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :5 43 LoopQueue's data is below: 44 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :6 45 LoopQueue's data is below: 46 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :7 47 LoopQueue's data is below: 48 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :8 49 LoopQueue's data is below: 50 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :9 51 LoopQueue's data is below: 52 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4] 队尾 Capacity: 10 Size :10 53 LoopQueue's data is below: 54 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :11 55 LoopQueue's data is below: 56 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :12 57 LoopQueue's data is below: 58 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :13 59 LoopQueue's data is below: 60 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :14 61 LoopQueue's data is below: 62 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :15 63 LoopQueue's data is below: 64 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :16 65 LoopQueue's data is below: 66 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :17 67 LoopQueue's data is below: 68 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :18 69 LoopQueue's data is below: 70 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ,13] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :19 71 LoopQueue's data is below: 72 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ,14] 队尾 Capacity: 20 Size :20 73 LoopQueue's data is below: 74 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ,14 ,15] 队尾 Capacity: 40 Size :21 75 LoopQueue's data is below: 76 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ,14 ,15 ,16] 队尾 Capacity: 40 Size :22 77 LoopQueue's data is below: 78 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ,14 ,15 ,16 ,17] 队尾 Capacity: 40 Size :23 79 LoopQueue's data is below: 80 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ,14 ,15 ,16 ,17 ,18] 队尾 Capacity: 40 Size :24 81 LoopQueue's data is below: 82 front[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ,14 ,15 ,16 ,17 ,18 ,19] 队尾 Capacity: 40 Size :25 83 * */
数组队列和循环队列的复杂度分析:
循环队列的时间复杂度分析:
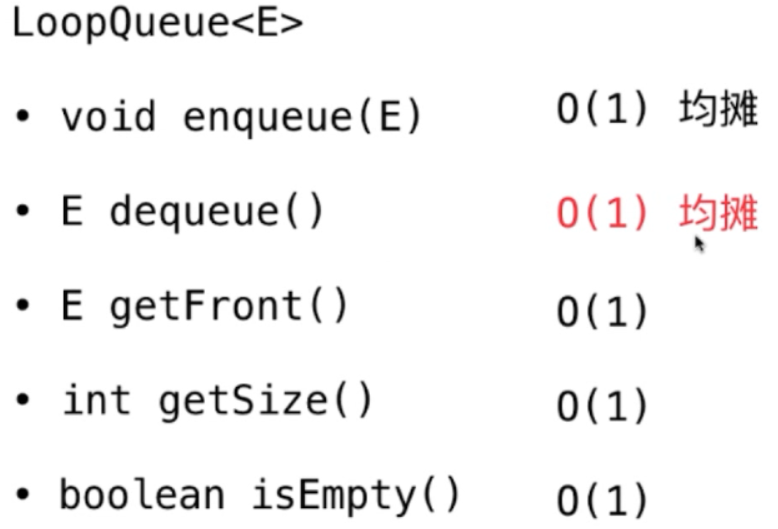
下面我们看O(n) 的时间复杂度比 O(1) 的时间复杂度到底有多快。实际证明我们在数据结构中设计低的时间复杂度是有意义的。
下面用程序测试 数组队列和 循环队列的效率!

1 package cn.zcb.demo05; 2 3 import java.util.Random; 4 public class Test { 5 private static double getRuntime(MyLoopQueue queue,int opCount){ 6 long startTime = System.nanoTime(); //以纳秒为单位! 7 8 Random random = new Random(); 9 for (int i =0;i<opCount; i++){ 10 queue.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); 11 } 12 for (int i =0;i<opCount; i++){ 13 queue.dequeue(); 14 } 15 long endTime = System.nanoTime(); 16 return (endTime -startTime)/1000000000.0; 17 } 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 int opCount = 100000; 21 MyLoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new MyLoopQueue<>(); 22 double time = getRuntime(loopQueue,opCount); 23 System.out.println("循环队列所消耗的时间是: "+time); 24 } 25 } 26 /* 输出:循环队列所消耗的时间是: 0.0291362 27 * */
上述十万次操作:
![]()
数组队列用了 8.42s
循环对类用了 0.06s
它们相差100多倍,所以分析时间复杂度是很有必要的。
