动手动脑1:
package learn;
import javax.swing.*;
class AboutException {
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
k=i/j;
try
{
k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception
//throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!");
}
catch ( ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("被0除");
else
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
finally
{
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK");
}
}
}
结果截图

认识:
当j=0时出现异常,所以捕获错误,catch处理异常,不管是否有异常发生,finally语句块中的语句始终保证被执行。如果没有提供合适的异常处理代码,JVM将会结束掉整个应用程序。
Throwable类有两个直接子类:
Exception:出现的问题是可以被捕获的;
Error:系统错误,通常由JVM处理。
可捕获的异常又可以分为两类:
(1)Check异常:直接派生自Exception的异常类,必须被捕获或再次声明抛出
(2)Runtime异常:派生自RuntimeException的异常类。使用throw语句可以随时抛出这种异常对象:
throw new ArithmeticException(…);
动手动脑2:
package learn;
public class CatchWho2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
截图

动手动脑3:
public class EmbededFinally {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result;
try {
System.out.println("in Level 1");
try {
System.out.println("in Level 2");
// result=100/0; //Level 2
try {
System.out.println("in Level 3");
result=100/0; //Level 3
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 3 finally");
}
// result=100/0; //Level 2
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 2 finally");
}
// result = 100 / 0; //level 1
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
. System.out.println("In Level 1 finally");
}
}
}
截图:

动手动脑4:
public class SystemExitAndFinally {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try{
System.out.println("in main");
throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main");
//System.exit(0);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
}
截图
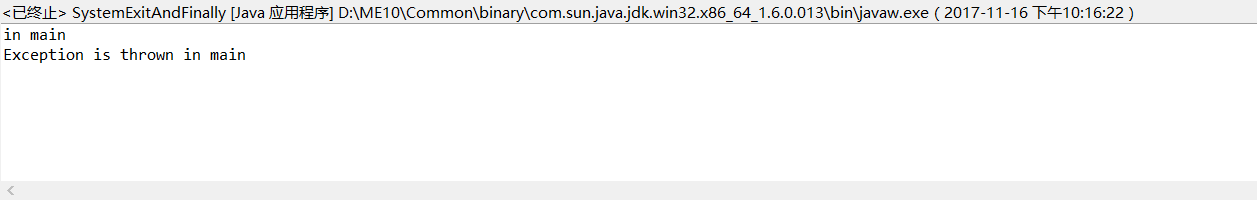
当存在try中有throw new Exception(...)finally不会执行。
成绩程序
package learn;
import java.util.*;
public class Score{
int score;
void Setscore() {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入成绩:");
try{ //try输入
score=in.nextInt(); //输入成绩
if(score<100&&score>=90)
{
System.out.println("优");
}
if(score<90&&score>=80)
{
System.out.println("良");
}
else if(score<80&&score>=70)
{
System.out.println("中");
}
else if(score<70&&score>=60)
{
System.out.println("及格");
}
else if(score<60&&score>=0)
{
System.out.println("不及格");
}
else if(score<0||score>100)
{
System.out.println("超出范围!!");
Setscore();
}
}
catch (Exception e) //捕获异常
{
System.out.println("错误输入!! ");
Setscore(); //返回输入
}
finally //结束
{
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Score s=new Score();
s.Setscore();
}
}
实验截图
