大家好,我是一叶,今天我们继续踩坑。今天的内容是vuex快速入门,页面传值不多的话,不建议vuex,直接props进行父子间传值就行,使用vuex就显得比较臃肿。
我们先预览一下效果,如图1所示。

图1
1、创建vue-cli项目
如果不会用vue-cli构建项目的小伙伴可以看看以前我发过的文章:
http://www.yyzhiqiu.com/?post=14
目录结构如图2所示。
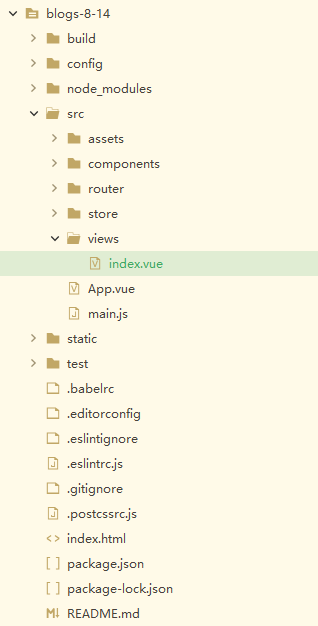
图2
2、下载、引入vuex、axios
执行命令行:
cnpm install vuex
cnpm install axios
在src目录下创建store目录,再创建store.js文件。在main.js中引入vuex,如图3所示。
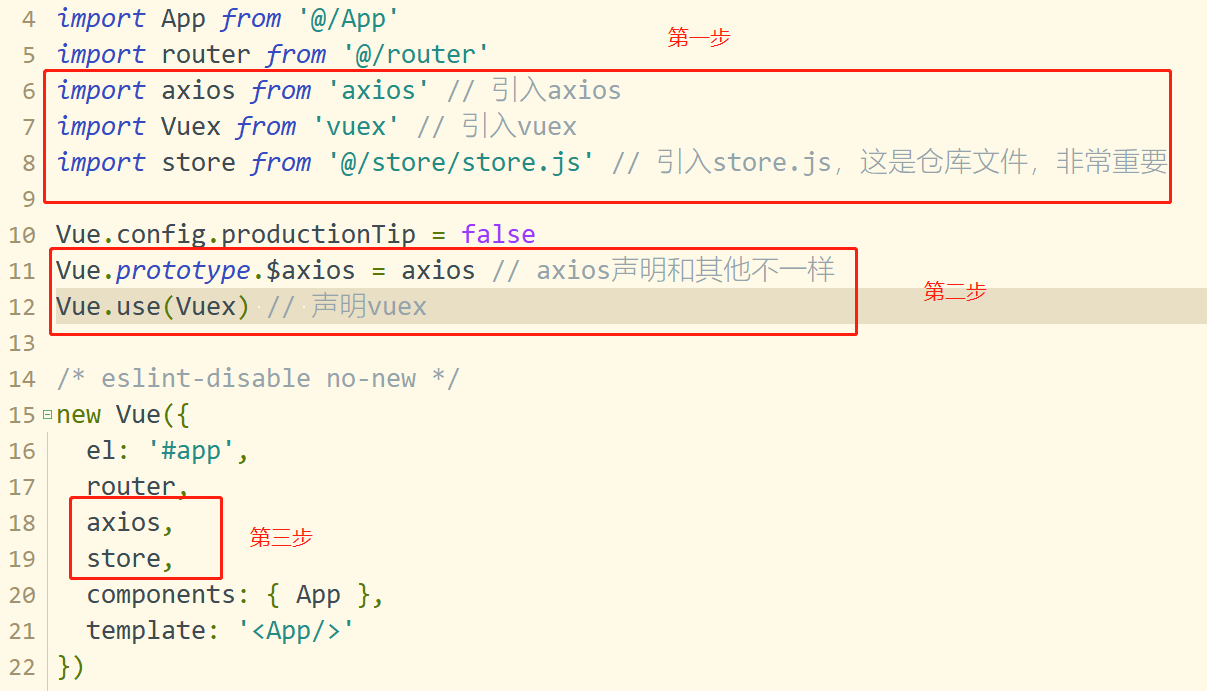
图3
如果有的小伙伴不想敲代码,直接复制就可以运行。
代码如下,按需引入:
main.js:
1 import Vue from 'vue' 2 import App from '@/App' 3 import router from '@/router' 4 import axios from 'axios' // 引入axios 5 import Vuex from 'vuex' // 引入vuex 6 import store from '@/store/store.js' // 引入store.js,这是仓库文件,非常重要 7 8 Vue.config.productionTip = false 9 Vue.prototype.$axios = axios // axios声明和其他不一样 10 Vue.use(Vuex) // 声明vuex 11 12 /* eslint-disable no-new */ 13 new Vue({ 14 el: '#app', 15 router, 16 axios, 17 store, 18 components: { App }, 19 template: '<App/>' 20 })
直接po代码,结合底下的注解就能明白了。
App.vue:
1 <template> 2 <div id="app"> 3 <img src="./assets/logo.png"> 4 <router-view/> 5 </div> 6 </template> 7 8 <script> 9 export default { 10 name: 'App' 11 } 12 </script> 13 14 <style> 15 #app { 16 font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; 17 -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; 18 -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; 19 text-align: center; 20 color: #2c3e50; 21 margin-top: 60px; 22 } 23 </style>
store.js:

1 import Vue from 'vue' 2 import App from '@/App.vue' 3 import Vuex from 'vuex' 4 5 Vue.use(Vuex) 6 7 const state = { 8 studentData: [ 9 {name: '蔡徐坤', sex: '男', age: 21}, 10 {name: '鸡你太美', sex: '女', age: 21}, 11 {name: '蔡唱', sex: '男', age: 21}, 12 {name: '蔡跳', sex: '女', age: 21}, 13 {name: '蔡rap', sex: '男', age: 21}, 14 {name: '蔡篮球', sex: '女', age: 21} 15 ] 16 } 17 18 const getters = { 19 getStudents: (state) => { 20 let getStudents = state.studentData.map(student => { 21 return { 22 name: student.name, 23 sex: student.sex, 24 age: student.age 25 } 26 }) 27 return getStudents 28 } 29 } 30 31 const mutations = { 32 getStuData (state, payload) { 33 let newstudent = state.studentData.forEach(student => { 34 student.age = student.age + payload 35 }) 36 } 37 } 38 39 const actions = { 40 getStuDataAsync (context, payload) { 41 setTimeout(() => { 42 context.commit('getStuData', payload) // context提交 43 }, 2000) 44 } 45 } 46 47 export default new Vuex.Store({ 48 state, getters, mutations, actions 49 })
index.vue:

1 <template> 2 <div> 3 <h2>vuex学习使用案例</h2> 4 <div class="test"> 5 <ul> 6 <li><span>姓名</span><span>性别</span><span>年龄</span></li> 7 <li v-for="(student,index) in students" :key="index"> 8 <span class="name">{{ student.name }}</span> 9 <span class="sex">{{ student.sex}}</span> 10 <span class="sex">{{ student.age}}</span> 11 </li> 12 <button @click="getStuData">增加年龄</button> <!-- //添加按钮 --> 13 <button @click="getStuDataAsync">异步增加年龄</button> <!-- //添加按钮 --> 14 </ul> 15 </div> 16 </div> 17 </template> 18 19 <script> 20 // import store from '@/store/store.js' 21 import store from '@/store/store.js'; 22 export default { 23 name: 'index', 24 data() { 25 return { 26 students : this.$store.state.studentData 27 }; 28 }, 29 mounted() { 30 }, 31 methods: { 32 getStuData() { 33 this.$store.commit('getStuData', 2); //提交`getStuData,payload为2 34 }, 35 getStuDataAsync() { 36 this.$store.dispatch('getStuDataAsync', 5); //分发actions中的getStuDataAsync这个异步函数 37 } 38 }, 39 components: { 40 } 41 }; 42 </script> 43 44 <style> 45 .test ul li{ 500px;height: 50px;list-style: none;margin: 0 auto;border: #42B983 1px solid;} 46 .test ul li span{ 33%;height: 50px;line-height: 50px;font-size: 24px;float: left;} 47 button{ 150px;height: 50px;margin: 20px;background: #42B983;color: #fff;border: 0;font-size: 20px;border-radius: 5px;} 48 </style>
3、核心概念
3.1、state:
state 就是Vuex中的公共的状态,可以把 state 看作是所有组件的data,用于保存所有组件的公共数据。
代码如下:
1 const state = { 2 studentData: [ 3 {name: '蔡徐坤', sex: '男', age: 21}, 4 {name: '鸡你太美', sex: '女', age: 21}, 5 {name: '蔡唱', sex: '男', age: 21}, 6 {name: '蔡跳', sex: '女', age: 21}, 7 {name: '蔡rap', sex: '男', age: 21}, 8 {name: '蔡篮球', sex: '女', age: 21} 9 ] 10 }
3.2、getters:
getters 属性可以理解为所有组件的 computed 属性, 也就是计算属性。 vuex的官方文档也是说到可以将getter理解为store的计算属性,getters的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
代码如下:
1 const getters = { 2 getStudents: (state) => { 3 let getStudents = state.studentData.map(student => { 4 return { 5 name: student.name, 6 sex: student.sex, 7 age: student.age 8 } 9 }) 10 return getStudents 11 } 12 }
其中map()函数的功能是循环,需要返回值,即return,功能和for循环一致。
3.3、mutaions:
mutaions 可以理解为 store 中的 methods, mutations 对象中保存着更改数据的回调函数,该函数名官方规定叫 type ,第一个参数是 state , 第二参数是 payload , 也就是自定义的参数。
getStuData回调函数将用于年龄的增加,增加payload岁。代码如下:
1 const mutations = { 2 getStuData (state, payload) { 3 let newstudent = state.studentData.forEach(student => { 4 student.age = student.age + payload 5 }) 6 } 7 }
其中 forEach()函数也是循环函数,不需要返回值。循环函数的优缺点感兴趣的小伙伴可以自行百度,我就不赘述了。
增加年龄的功能 getStuData()写好了,我们得去触发才行啊。所以进入到 index.vue 里添加一个按钮,按钮触发 getStuData()
代码如下:
1 <template> 2 <div> 3 <h2>vuex学习使用案例</h2> 4 <div class="test"> 5 <ul> 6 <li><span>姓名</span><span>性别</span><span>年龄</span></li> 7 <li v-for="(student,index) in students" :key="index"> 8 <span class="name">{{ student.name }}</span> 9 <span class="sex">{{ student.sex}}</span> 10 <span class="sex">{{ student.age}}</span> 11 </li> 12 <button @click="getStuData">增加年龄</button> 13 </ul> 14 </div> 15 </div> 16 </template>
在 js 里注册一下 getStuData 方法,在该方法中commit一下mutaions中的 getStuData 这个回调函数。
注意:调用mutaions中回调函数, 只能使用store.commit(type, payload)
1 <script> 2 // import store from '@/store/store.js' 3 import store from '@/store/store.js'; 4 export default { 5 name: 'index', 6 data() { 7 return { 8 students : this.$store.state.studentData 9 }; 10 }, 11 mounted() { 12 }, 13 methods: { 14 getStuData() { 15 this.$store.commit('getStuData', 2); //提交`getStuData,payload为2 16 } 17 }, 18 components: { 19 } 20 }; 21 </script>
点击按钮,会发现年龄增加了2岁,即增加了payload。
3.4、actions:
actions 类似于 mutations,不同在于:
actions提交的是mutations而不是直接变更状态actions中可以包含异步操作,mutations中不能出现异步actions中的回调函数的第一个参数是context, 是一个与store实例具有相同属性和方法的对象
在store.js中,增加 actions 方法,代码如下:
1 const actions = { 2 getStuDataAsync (context, payload) { 3 setTimeout(() => { 4 context.commit('getStuData', payload) // context提交 5 }, 1000) 6 } 7 }
到index.vue中添加按钮,注册getStuDataAsync方法,并触发该方法,实现异步增加年龄。添加按钮,在html中如图4所示。
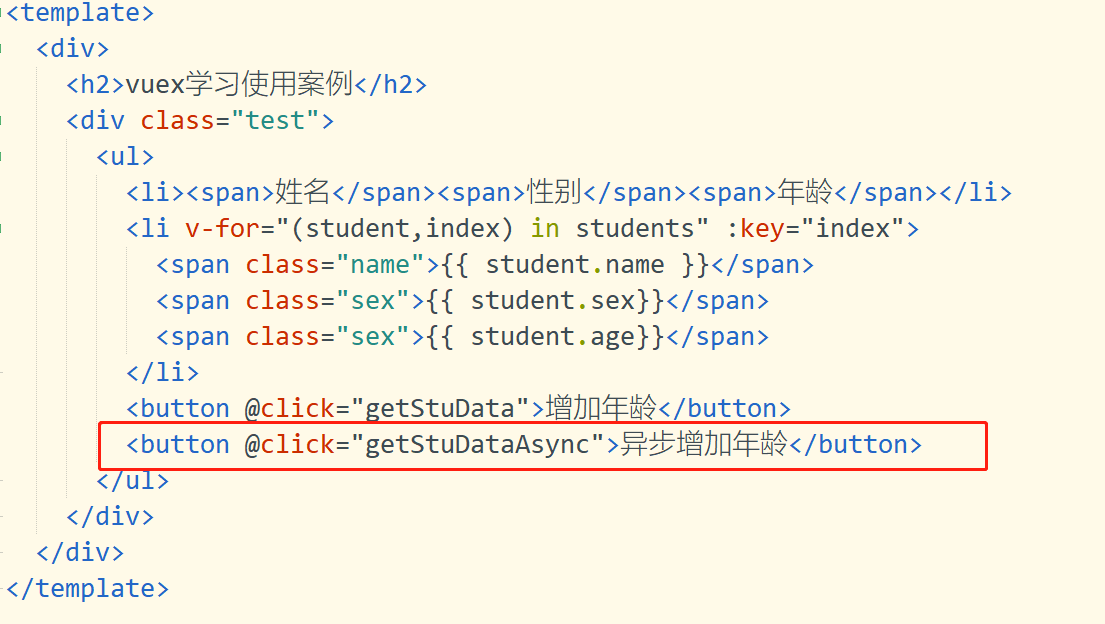
图4
注册方法,在js中如图5所示。
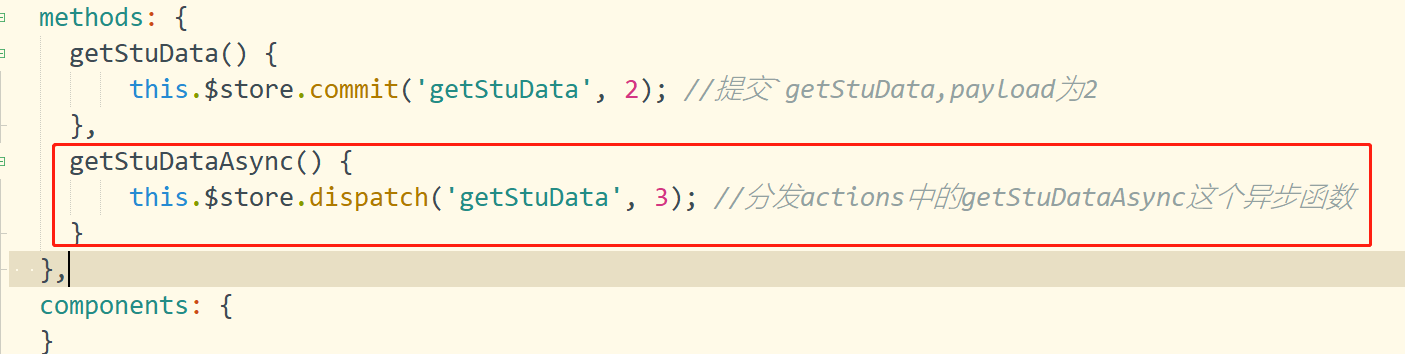
图5
注册getStuDataAsync方法时,需要dispatcha ctions 中的getStuDataAysnc()回调函数。
3.5、modules:
当存在多个state的数据时,使用store便显得臃肿和麻烦,所以便产生了modules(模块)。每个modules都有一套完整的store,即state、getters、mutations、actions。用法如下:
1 const moduleA = { 2 state: { ... }, 3 mutations: { ... }, 4 actions: { ... }, 5 getters: { ... } 6 } 7 8 const moduleB = { 9 state: { ... }, 10 mutations: { ... }, 11 actions: { ... } 12 } 13 14 const store = new Vuex.Store({ 15 modules: { 16 a: moduleA, 17 b: moduleB 18 } 19 }) 20 21 store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态 22 store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
好了,vuex的入门差不多就到这里了,对文中的错误和疑惑希望大家指出来。对了,欢迎点赞留言。
