一.BIO与NIO以及AIO的概念
BIO是同步阻塞式的IO
NIO是同步非阻塞的IO (NIO1.0,JDK1.4)
AIO是非同步非阻塞的IO(NIO2.0,JDK1.7)
二.BIO简单分析
1.简单分析
BIO是阻塞的IO,原因在于accept和read会阻塞。所以单线程的BIO是无法处理并发的。
2.案例
服务端:
public class BioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//在开发中不要直接抛出去,有可能出现异常导致连接未关闭
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9999));
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
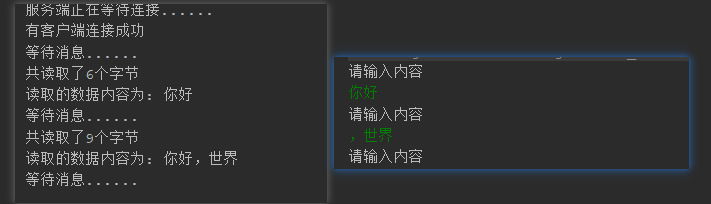
System.out.println("服务端正在等待连接......");
Socket socketAccept = serverSocket.accept();//这里会阻塞
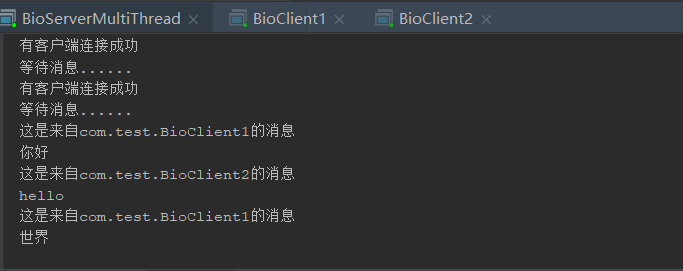
System.out.println("有客户端连接成功");
while (true){
System.out.println("等待消息......");
int read = socketAccept.getInputStream().read(b);//这里会阻塞
System.out.println("共读取了"+read+"个字节");
String str = new String(b);
sb.append(str);
System.out.println("读取的数据内容为: " + sb);
}
}
}
客户端:
public class BioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9999));
while(true){
System.out.println("请输入内容");
String next = scanner.next();
socket.getOutputStream().write(next.getBytes());
}
}
}
测试如下:
3.多线程下的BIO
多线程的BIO是可以处理并发的,但频繁的创建线程,运行线程以及销毁线程无疑是非常消耗资源的(即便可以使用线程池限制线程数量,但海量并发时,BIO的方式效率相比于NIO还是太低了)
下面是一个多线程的BIO案例:
服务端:
public class BioServerMultiThread { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(); serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9999)); System.out.println("服务端正在等待连接......"); while (true){ Socket socketAccept = serverSocket.accept();//这里会阻塞 System.out.println("有客户端连接成功"); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try{ System.out.println("等待消息......"); String msg = ""; while (true){ byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len = socketAccept.getInputStream().read(b); if (len < 0){ continue; } msg = new String(b,0,len); System.out.println(msg); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); } } }
客户端(创建多个客户端,代码相同):
public class BioClient1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9999)); String className = "这是来自"+Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace()[1].getClassName()+"的消息"; while(true){ System.out.println("请输入内容"); String next = scanner.next(); socket.getOutputStream().write(className.getBytes()); socket.getOutputStream().write(next.getBytes()); } } }
测试如下:
三.NIO简单分析
NIO是非阻塞IO,其原因在于数据准备就绪后,由选择器通知给服务端,而在数据准备完毕之前,服务器无需等待。
1.缓冲区
在BIO操作中,所有的数据都是以流的形式操作的,而在NIO中,则都是使用缓冲区来操作。
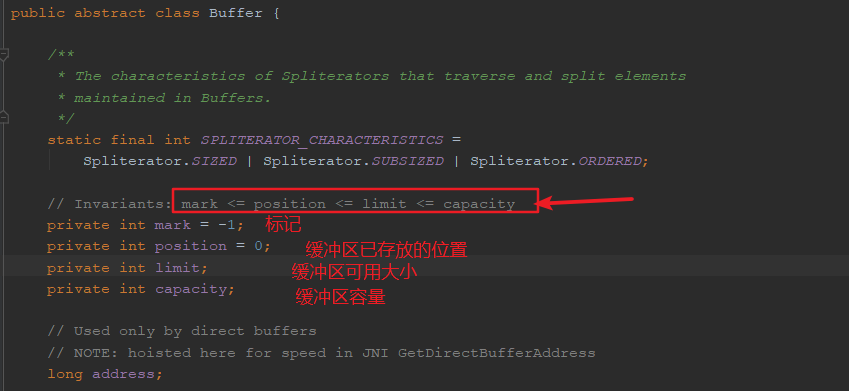
NIO中的缓冲区是Buffer类,它是java.nio包下的一个抽象类,详情可以查看JDK的API文档,例如下图

打开Buffer类,可以看到如下图(其中带有的方法可以查看JDK文档)
2.直接缓冲区和非直接缓冲区
直接缓冲区是指将缓冲区建立在物理内存中,通过allocateDirect方法建立(效率高,但不安全)
非直接缓冲区是指将缓冲区建立在JVM中,通过allocate方法建立(效率低,但安全)
3.管道
管道是NIO中传输数据的桥梁,它是java.nio包下的一个接口,若需查看其详细信息可以参考JDK的API文档,例如下图

4.使用NIO实现文件拷贝两种方式案例
直接缓冲区的方式:
@Test public void test1() throws IOException { long statTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); //创建管道 FileChannel inChannel= FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E://test/aaa.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ); FileChannel outChannel= FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E://test/bbb.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //定义映射文件 MappedByteBuffer inMappedByte = inChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY,0, inChannel.size()); MappedByteBuffer outMappedByte = outChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE,0, inChannel.size()); //直接对缓冲区操作 byte[] dsf=new byte[inMappedByte.limit()]; inMappedByte.get(dsf); outMappedByte.put(dsf); inChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("操作直接缓冲区耗时时间:"+(endTime-statTime)); }
非直接缓冲区的方式:
@Test public void test2() throws IOException { long statTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); // 读入流 FileInputStream fst = new FileInputStream("E://test/bbb.txt"); // 写入流 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E://test/ccc.txt"); // 创建通道 FileChannel inChannel = fst.getChannel(); FileChannel outChannel = fos.getChannel(); // 分配指定大小缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); while (inChannel.read(buf) != -1) { // 开启读取模式 buf.flip(); // 将数据写入到通道中 outChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } // 关闭通道 、关闭连接 inChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); fos.close(); fst.close(); long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("操作非直接缓冲区耗时时间:"+(endTime-statTime)); }
5.选择器(Selector)
它是Java NIO核心组件中的一个,用于检查一个或多个NIO Channel(通道)的状态是否处于可读、可写。如此可以实现单线程管理多个channels,也就是可以管理多个网络链接。使用Selector的好处在于: 使用更少的线程来就可以来处理通道了, 相比使用多个线程,避免了线程上下文切换带来的开销。详细用法可以参考JDK的API文档
NIO服务端实现同步非阻塞代码如下
public class NioServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open(); ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9999)); ssc.configureBlocking(false);//设置成非阻塞模型 System.out.println("server started, listening on :" + ssc.getLocalAddress()); Selector selector = Selector.open(); ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); while(true) { selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = it.next(); it.remove(); handle(key); } } } private static void handle(SelectionKey key) { if(key.isAcceptable()) { try { ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept(); sc.configureBlocking(false); sc.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { } } else if (key.isReadable()) { SocketChannel sc = null; try { sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel(); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512); buffer.clear(); int len = sc.read(buffer); if(len != -1) { System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(), 0, len)); } ByteBuffer bufferToWrite = ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloClient".getBytes()); sc.write(bufferToWrite); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(sc != null) { try { sc.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } }
四.AIO简单分析
AIO(NIO2.0)和 NIO的主要区别是前者是异步的,而后者是同步的。(NIO每隔一段时间用Selector轮询查看是否有事件发生,而AIO是在等有事件发生的时候,Selector通知服务端)
与NIO不同,当进行读写操作时,AIO只须直接调用API的read或write方法即可。这两种方法均为异步的,对于读操作而言,当有流可读取时,操作系统会将可读的流传入read方法的缓冲区,并通知应用程序;对于写操作而言,当操作系统将write方法传递的流写入完毕时,操作系统主动通知应用程序。 即可以理解为,read/write方法都是异步的,完成后会主动调用回调函数。
AIO服务端简单案例如下
public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open() .bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888)); serverChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() { @Override public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel client, Object attachment) { serverChannel.accept(null, this); try { System.out.println(client.getRemoteAddress()); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); client.read(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() { @Override public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) { attachment.flip(); System.out.println(new String(attachment.array(), 0, result)); client.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloClient".getBytes())); } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) { exc.printStackTrace(); } }); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) { exc.printStackTrace(); } }); } }