如果需要使用的Map中的key无序,选择HashMap;如果要求key有序,则选择TreeMap。
但是选择TreeMap就会有性能问题,因为TreeMap的get操作的时间复杂度是O(log(n))的,
相比于HashMap的O(1)还是差不少的,LinkedHashMap的出现就是为了平衡这些因素,使得
能够以
O(1)时间复杂度增加查找元素,又能够保证key的有序性
此外,LinkedHashMap提供了两种key的顺序:
- 访问顺序(access order)。非常实用,可以使用这种顺序实现LRU(Least Recently Used)缓存
- 插入顺序(insertion orde)。同一key的多次插入,并不会影响其顺序
一。HashMap
1.HashMap构造函数
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; threshold = initialCapacity; init(); //注意这个模板函数,在LinkHashMap中有使用 }
2.默认参数
//容量必须为2的指数(默认为16),想想原因? static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //默认的平衡因子为0.75,这是权衡了时间复杂度与空间复杂度之后的取值 //过高的因子可以增加存储空间利用率但是查找的时间就会增加。 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
3.重设索引
void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); table = newTable; threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); } /** * Transfers all entries from current table to newTable. */ void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); //占用哪个槽位 e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } }
4.
static int indexFor(int h, int length) { // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; return h & (length-1); }
二。LinkedHashMap
1.Entry
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> { // These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration. Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } }
2.删除
//删除一个节点时,需要把 //1. 前继节点的后继指针 指向 要删除节点的后继节点 //2. 后继节点的前继指针 指向 要删除节点的前继节点 private void remove() { before.after = after; after.before = before; }

3.增加
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) { after = existingEntry; //当前节点的后继节点 指向 新节点 before = existingEntry.before; // before.after = this; // after.before = this; // }
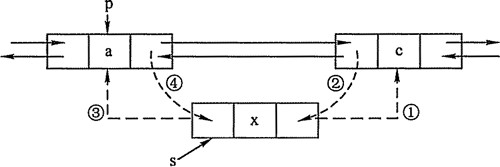
4.重写的init
@Override void init() { header = new Entry<>(-1, null, null, null); header.before = header.after = header; }
5.重写transfer
/** * Transfers all entries to new table array. This method is called * by superclass resize. It is overridden for performance, as it is * faster to iterate using our linked list. */ @Override void transfer(HashMap.Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e = header.after; e != header; e = e.after) { //把链表里的元素重排序 if (rehash) e.hash = (e.key == null) ? 0 : hash(e.key); int index = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[index]; newTable[index] = e; } }