官网教程:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.2/topics/auth/customizing/
app下的model.py
from django.db import models from django.contrib.auth.models import ( BaseUserManager, AbstractBaseUser,PermissionsMixin ) # Create your models here. class UserProfileManager(BaseUserManager): def create_user(self, email, name, password=None): """ 创建用户 """ if not email: raise ValueError('用户必须有一个邮箱地址') user = self.model( email=self.normalize_email(email), name=name, ) user.set_password(password) user.save(using=self._db) return user def create_superuser(self, email, name, password): """ 创建并保存超级用户 """ user = self.create_user( email, password=password, name=name, ) user.is_superuser = True user.save(using=self._db) return user class UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser,PermissionsMixin): email = models.EmailField( verbose_name='邮箱', max_length=255, unique=True, ) name = models.CharField(max_length=32,verbose_name="用户名") is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True) is_staff = models.BooleanField(default=True) objects = UserProfileManager() USERNAME_FIELD = 'email' # 登录的字段 REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name'] # 必须要有的字段 def __str__(self): return self.email def get_full_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email def get_short_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email class Meta: permissions = ( ('make_myself', '自定制权限'), )
settings.py文件中需配置:
AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'app01.UserProfile'
在app下的admin.py中配置:
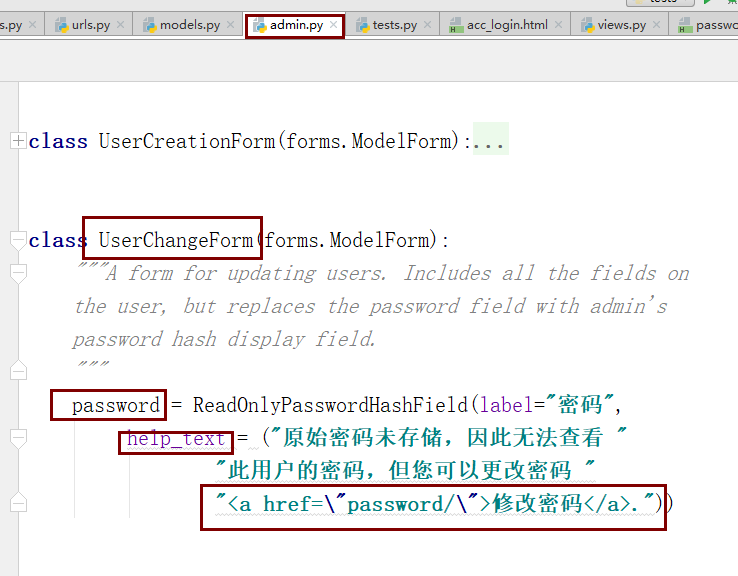
from django import forms from django.contrib.auth.models import Group from django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin as BaseUserAdmin from django.contrib.auth.forms import ReadOnlyPasswordHashField from app01.models import UserProfile class UserCreationForm(forms.ModelForm): """A form for creating new users. Includes all the required fields, plus a repeated password.""" password1 = forms.CharField(label='密码', widget=forms.PasswordInput) password2 = forms.CharField(label='确认密码', widget=forms.PasswordInput) class Meta: model = UserProfile fields = ('email', 'name') def clean_password2(self): # Check that the two password entries match password1 = self.cleaned_data.get("password1") password2 = self.cleaned_data.get("password2") if password1 and password2 and password1 != password2: raise forms.ValidationError("密码不匹配") return password2 def save(self, commit=True): user = super().save(commit=False) # 密码明文根据算法改成密文 user.set_password(self.cleaned_data["password1"]) if commit: user.save() return user class UserChangeForm(forms.ModelForm): """A form for updating users. Includes all the fields on the user, but replaces the password field with admin's password hash display field. """ password = ReadOnlyPasswordHashField() class Meta: model = UserProfile fields = ('email', 'password', 'name', 'is_active',"is_superuser") def clean_password(self): # Regardless of what the user provides, return the initial value. # This is done here, rather than on the field, because the # field does not have access to the initial value return self.initial["password"] class UserProfileAdmin(BaseUserAdmin): # The forms to add and change user instances form = UserChangeForm add_form = UserCreationForm # The fields to be used in displaying the User model. # These override the definitions on the base UserAdmin # that reference specific fields on auth.User. list_display = ('email', 'name', 'is_staff', 'is_active','is_superuser') list_filter = ('is_superuser',) fieldsets = ( (None, {'fields': ('email', 'password')}), ('用户信息', {'fields': ('name',)}), ('系统权限', {'fields': ('is_superuser','is_staff', 'is_active','user_permissions','groups')}), ) # add_fieldsets is not a standard ModelAdmin attribute. UserAdmin # overrides get_fieldsets to use this attribute when creating a user. add_fieldsets = ( (None, { 'classes': ('wide',), 'fields': ('email', 'name', 'password1', 'password2')} ), ) search_fields = ('email',) ordering = ('email',) filter_horizontal = ('user_permissions','groups')
最后在pycharm的命令行生成记录,并同步到数据库
输入命令:python3 manage.py makemigrations
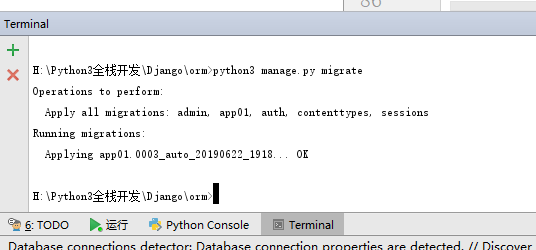
再次输入:python3 manage.py migrate
注意:我这里是python3进入python3交互界面,你的可能是python。根据自己情况而定!
最后一步:创建超级用户

启动django项目后,输入admin进入后台管理:


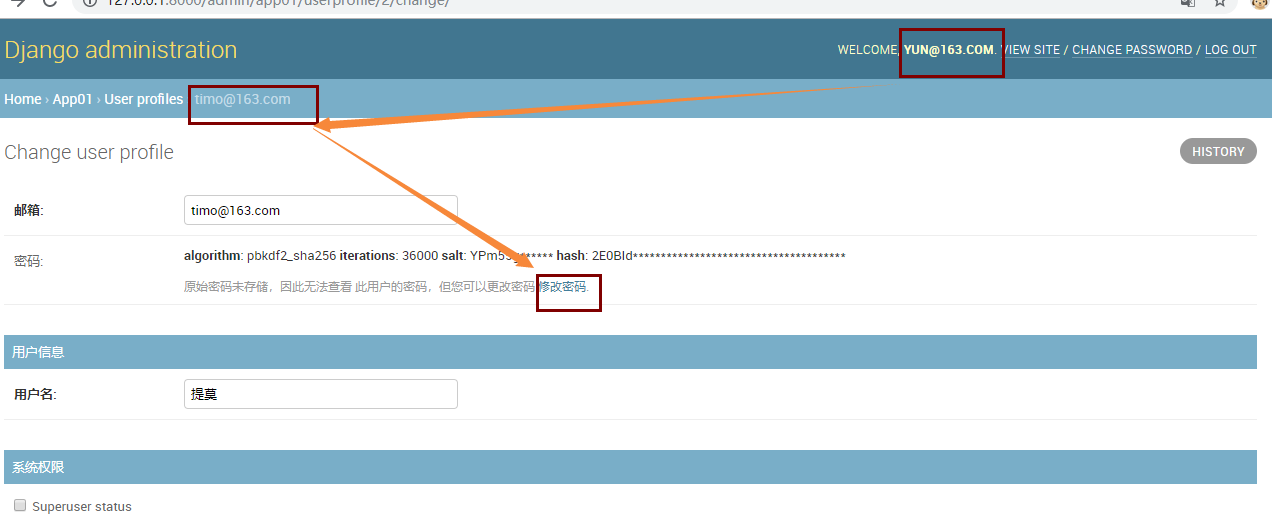
此时,你发现我们的密码是密文,我们必须支持管理员可以在后台修改所有人的密码。
具体步骤如下:
step1
step2
step3
templates/password_change.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>修改密码</title> </head> <body> <h1>修改密码</h1> <form action="" method="post"> {% csrf_token %} <p> <input type="password" name="pwd1" placeholder="密码"> </p> <p> <input type="password" name="pwd2" placeholder="确认密码"> </p> <p> <input type="submit" value="修改"> </p> </form> </body> </html>
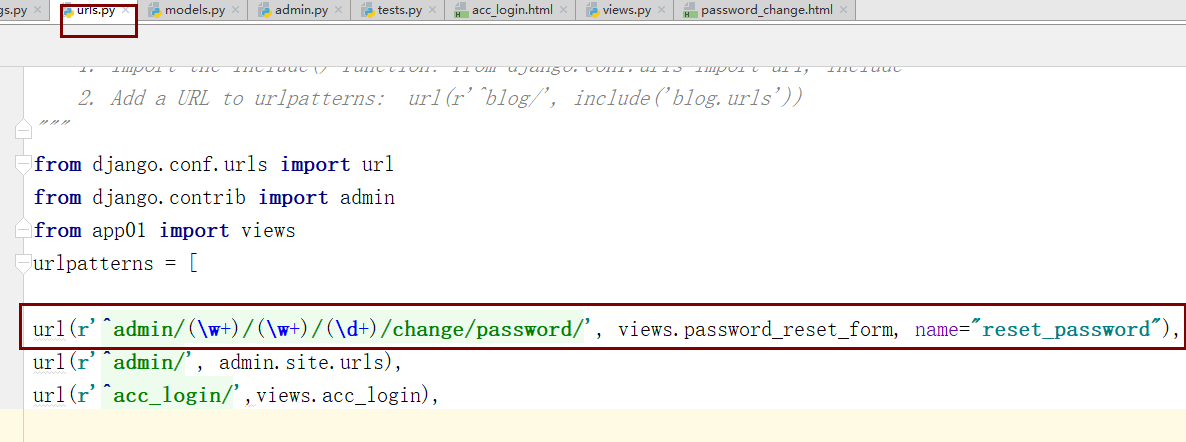
app01/views.py
def password_reset_form(request,app_name,table_db_name,user_id): # 获取被修改对象 user_obj = request.user._meta.model.objects.get(id=user_id) print("**********:{}".format(user_obj)) can_change_user_password = False # 管理员修改其他人的密码/管理员修改自己的密码 if request.user.is_superuser or request.user.id == user_obj.id: print(request.user.is_superuser) can_change_user_password = True if can_change_user_password: if request.method == "GET": return render(request,"password_change.html") else: if request.POST.get("pwd1") != "" and request.POST.get("pwd1") == request.POST.get("pwd2"): user_obj = User.objects.filter(id=user_obj.id).first() user_obj.set_password(request.POST.get("pwd2")) user_obj.save() print(request.POST.get("pwd2")) return redirect("/admin/") else: return HttpResponse("只有管理员可以修改密码")
此时,我们就实现了管理员可以在后台修改任何用户的密码