第一步:扩展 Thread 类或者实现 Runnable 接口;
第二步:用希望的执行代码来实现 run() 方法;
第三步: 通过 new 关键字实例化该类的一个新对象(即一个线程);
第四步: 通过调用 start() 方法启动线程。
多线程修改静态数据和堆数据的实验:

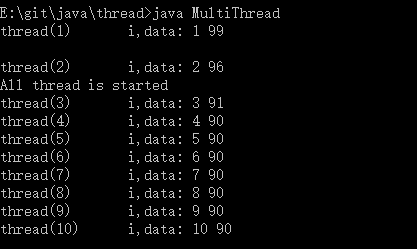
public class MultiThread extends Thread{//栈内数据是线程私有的 static int i = 0;//静态数据存放在方法区 int[] data;//引用指向的内存在堆中,通过堆共享数据 改成int[] data = new int[1]就不能被多线程共享了。 MultiThread(int[] data){ this.data = data; data[0]++; i++; } public void run(){ data[0]=data[0]+1; System.out.println("thread("+i+") "+"i,data[0]: "+i+" "+data[0]+" "); return; } public static void main(String[] args){ MultiThread[] multithread = new MultiThread[10]; int[] data = new int[1]; for(MultiThread thread:multithread){ thread = new MultiThread(data); thread.start(); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("All thread is started"); return; } }
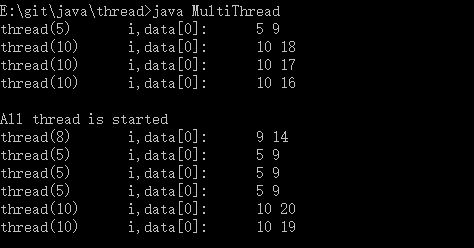

public class MultiThread implements Runnable{//栈内数据是线程私有的 static int i = 0;//静态数据存放在方法区 int[] data;//引用指向的内存在堆中,通过堆共享数据 这里可以改成改成int[] data = new int[1];data[0] = 100; MultiThread(int[] data){ this.data = data; } public void run(){ i++; //sychronnized(){ data[0]--; //} System.out.println("thread("+i+") "+"i,data[0]: "+i+" "+data[0]+" "); return; } public static void main(String[] args){ int[] data = new int[1]; MultiThread multithread = new MultiThread(data);//不同点 data[0] = 100; int n =10; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ new Thread(multithread).start();//不同点,也可用new Thread(new MultiThread(data)) } System.out.println(); System.out.println("All thread is started"); return; } }
实现 Runnable 接口(与上面代码只有在创建类时有不同、可以只创建一个类,一个类创建多个线程):
同步与互斥:java 通过标记一段代码或者一个方法为 synchronized (同步)来设定同步区域,这个锁可以自己设定,如果没有设定,系统隐式使用 this 作为 sysnchronized 的锁对象,如果方法是 static 的,静态方法是没有 this 指针的,这时候就使用此方法所在的类对象。如果有多个 synchronized 的方法,且逻辑上是隔离的,这时就需要显式声明多个锁对象用于同步。

public class MultiThread implements Runnable{//栈内数据是线程私有的 static int i = 0;//静态数据存放在方法区 int data = 100; MultiThread(){} Object lock = new Object(); public void run(){//run方法里的栈是线程私有的 data--; synchronized(lock){ i++; int temp_i = i; System.out.println("thread("+i+") "+"i,data: "+temp_i+" "+data+" "); } return; } public static void main(String[] args){ MultiThread multithread = new MultiThread(); int n =10; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ new Thread(multithread).start(); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("All thread is started"); return; } }
data 数据没有同步,i 实现了同步:
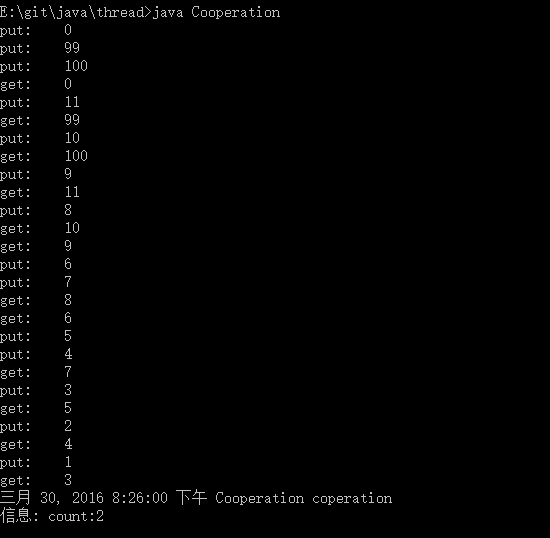
线程之间的协作:Object.wait(),Object.notify()只能出现在synchronized限制的代码段内,否则虽然编译能通过但是会有违例;

1 import java.util.logging.*; 2 public class Cooperation{ 3 Object[] item; 4 Object lock = new Object(); 5 Object empty_lock = new Object(); 6 int pos_put,pos_get,count; 7 int COUNT; 8 Logger Log; 9 Cooperation(int n){ 10 Log = Logger.getGlobal(); 11 COUNT = n; 12 item = new Object[COUNT]; 13 } 14 public void coperation(){ 15 for(int i =0;i<12;i++){ 16 new Puter(i).start(); 17 new Taker().start(); 18 } 19 new Puter(100).start(); 20 new Puter(99).start(); 21 try{ 22 Thread.sleep(13000); 23 }catch(Exception e){} 24 Log.info("count:"+count); 25 } 26 public class Puter extends Thread{ 27 Object x; 28 Puter(Object x){ 29 this.x = x; 30 } 31 public void run(){//返回类型为空,不可带参数 32 synchronized(lock){ 33 while(count == COUNT){ 34 try{ 35 lock.wait();//注意不是wait,等get取走 36 }catch(InterruptedException e){} 37 } 38 item[pos_put] = x; 39 Integer data = (Integer)x; 40 System.out.println("put: "+data.intValue()); 41 try{ 42 sleep(500); 43 }catch(Exception e){} 44 pos_put++; 45 if(pos_put == COUNT){ 46 pos_put = 0; 47 } 48 count++; 49 lock.notify(); 50 } 51 return; 52 } 53 } 54 public class Taker extends Thread{ 55 Taker(){} 56 public void run(){ 57 Object o; 58 synchronized(lock){ 59 while(count == 0){ 60 try{ 61 lock.wait(); 62 }catch(InterruptedException e){} 63 } 64 o = item[pos_get]; 65 pos_get++; 66 if(pos_get == COUNT){ 67 pos_get = 0; 68 } 69 count--; 70 Integer data = (Integer)o; 71 System.out.println("get: "+data.intValue()); 72 try{ 73 sleep(500); 74 }catch(Exception e){} 75 lock.notify();//通知put线程 76 return; 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 public static void main(String[] args){ 81 Cooperation application = new Cooperation(10); 82 application.coperation(); 83 return; 84 } 85 }
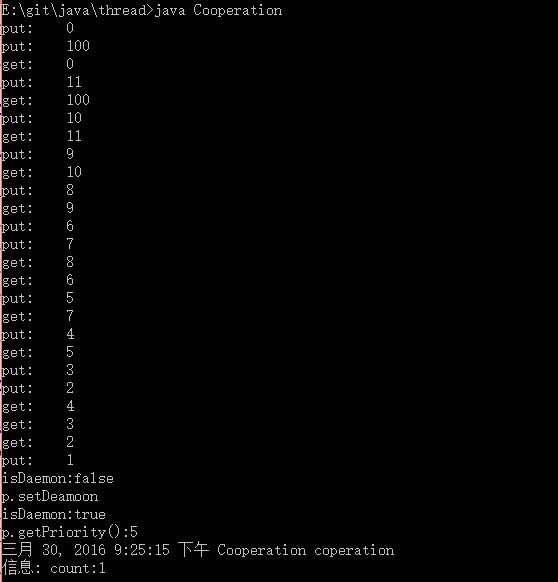
守护线程,线程优先级的设置:

import java.util.logging.*; public class Cooperation{ Object[] item; Object lock = new Object(); Object empty_lock = new Object(); int pos_put,pos_get,count; int COUNT; Logger Log; Cooperation(int n){ Log = Logger.getGlobal(); COUNT = n; item = new Object[COUNT]; } public void coperation(){ for(int i =0;i<12;i++){ new Puter(i).start(); new Taker().start(); } Puter q = new Puter(100); q.setPriority(4); q.start(); try{ Thread.sleep(13000); }catch(Exception e){} Puter p =new Puter(99); System.out.println("isDaemon:"+p.isDaemon()); p.setDaemon(true); System.out.println("p.setDeamoon isDaemon:"+p.isDaemon()); System.out.println("p.getPriority():"+p.getPriority()); //setPriority(4);java优先级分10级,最高优先级MAX_PRIORITY对应值是10,MIN_PRIORITY为1,默认优先级NORM_PRIORITY对应值为6 try{ Thread.sleep(1000); }catch(Exception e){} Log.info("count:"+count); } public class Puter extends Thread{ Object x; Puter(Object x){ this.x = x; } public void run(){//返回类型为空,不可带参数 synchronized(lock){ while(count == COUNT){ try{ lock.wait();//注意不是wait,等get取走 }catch(InterruptedException e){} } item[pos_put] = x; Integer data = (Integer)x; System.out.println("put: "+data.intValue()); try{ sleep(500); }catch(Exception e){} pos_put++; if(pos_put == COUNT){ pos_put = 0; } count++; lock.notify(); } return; } } public class Taker extends Thread{ Taker(){} public void run(){ Object o; synchronized(lock){ while(count == 0){ try{ lock.wait(); }catch(InterruptedException e){} } o = item[pos_get]; pos_get++; if(pos_get == COUNT){ pos_get = 0; } count--; Integer data = (Integer)o; System.out.println("get: "+data.intValue()); try{ sleep(500); }catch(Exception e){} lock.notify();//通知put线程 return; } } } public static void main(String[] args){ Cooperation application = new Cooperation(10); application.coperation(); return; } }