一、IIC驱动框架简介
1、IIC物理总线
- SCL:时钟线,数据收发同步。
- SDL:数据线,具体数据
支持一主多从,各设备地址独立,标准模式传输速率为100kbit/s,快速模式为400kbit/s
2、常见IIC设备
- EEPROM
- 触摸芯片
- 温湿度传感器
- mpu6050
3、框架图
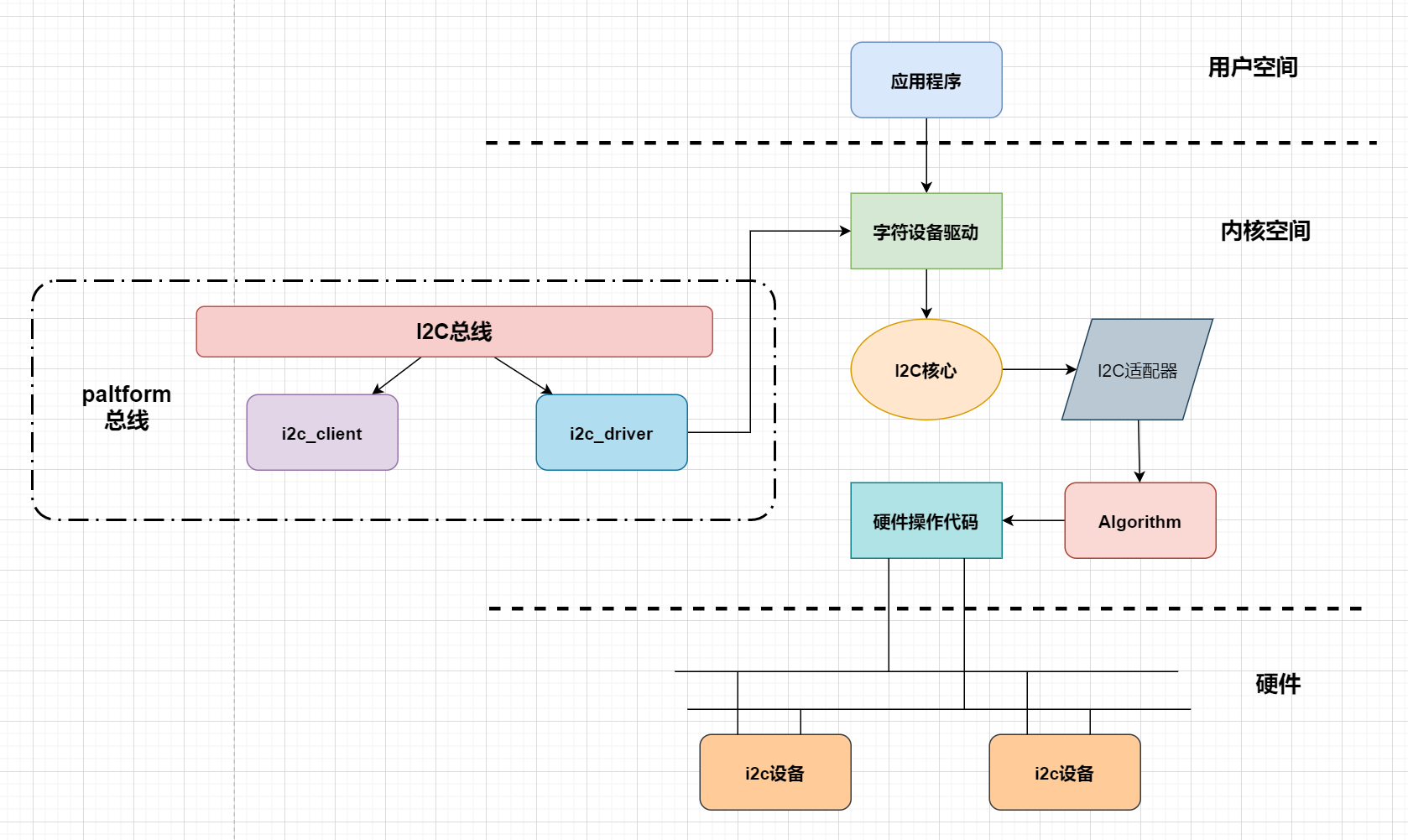
- I2C核心
提供I2C总线驱动和设备驱动的注册方法、注销方法、I2C通信硬件无关代码。
- I2C总线驱动
主要包含I2C硬件体系结构中适配器(IIC控制器)的控制,用于I2C读写时序。
主要数据结构:I2C_adapter、 I2C_algorithm.
- I2C设备驱动
通过I2C适配器与CPU交换数据。
主要数据结构:i2c_driver和i2c_client.
- I2C适配器
i2c adapter是软件上抽象出来的i2c总线控制器接口,物理上一条i2c总线可以挂接多个硬件设备(slave),一个CPU可以挂接多条i2c总线(想象一下PCI总线),i2c总线控制器就是CPU访问I2C总线的硬件接口,也就是你说的那几个寄存器
简单来说,你的开发板上有几个I2C接口,就有几个adapter , 也就是有几条I2C bus , I2C CLIENT 对应的就是你的外围I2C 设备,有几个就有几个CLIENT , 把这些设备插入开发板, 对应其中的一条BUS, 那么相应的就对应了其中的一个ADAPTER , 接下来的就是 CLIENT 与 ADAPTER 勾搭成对了, 后面就是做该做的事了
二、I2C驱动文件分析
1、i2c-dev.c
(1)初始化
static int __init i2c_dev_init(void)
{
int res;
printk(KERN_INFO "i2c /dev entries driver\n");
//1、注册字符设备
res = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, 0), I2C_MINORS, "i2c");
if (res)
goto out;
//2、创建类
i2c_dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "i2c-dev");
if (IS_ERR(i2c_dev_class)) {
res = PTR_ERR(i2c_dev_class);
goto out_unreg_chrdev;
}
i2c_dev_class->dev_groups = i2c_groups;
//3、追踪哪个i2c适配器被添加或者移除
/* Keep track of adapters which will be added or removed later */
res = bus_register_notifier(&i2c_bus_type, &i2cdev_notifier);
if (res)
goto out_unreg_class;
//4、立即绑定已经存在的适配器
/* Bind to already existing adapters right away */
i2c_for_each_dev(NULL, i2cdev_attach_adapter);
return 0;
out_unreg_class:
class_destroy(i2c_dev_class);
out_unreg_chrdev:
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, 0), I2C_MINORS);
out:
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: Driver Initialisation failed\n", __FILE__);
return res;
}
(2)文件操作集合
i2c设备驱动的文件操作集合中有两个ioctl:
static const struct file_operations i2cdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read = i2cdev_read, //读
.write = i2cdev_write, //写
.unlocked_ioctl = i2cdev_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = compat_i2cdev_ioctl,
.open = i2cdev_open,
.release = i2cdev_release,
};
两者的区别在于:
- 64位的用户程序运行在64位的kernel上,调用的是compat_ioctl,
- 32位的APP运行在32位的kernel上,调用的也是unlocked_ioctl。
(3)读操作
static ssize_t i2cdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *offset) { char *tmp; int ret; struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data; //最多读8192个字节 if (count > 8192) count = 8192; tmp = kzalloc(count, GFP_KERNEL); if (tmp == NULL) return -ENOMEM; pr_debug("i2c-dev: i2c-%d reading %zu bytes.\n", iminor(file_inode(file)), count); //接收到i2c传过来的数据 ret = i2c_master_recv(client, tmp, count); if (ret >= 0)
//将数据拷贝到用户空间 if (copy_to_user(buf, tmp, ret)) ret = -EFAULT; kfree(tmp); return ret; }
(4)写操作
static ssize_t i2cdev_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *offset)
{
int ret;
char *tmp;
struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data;
if (count > 8192)
count = 8192;
//分配一块内存空间,将用户空间的数据拷贝进去
tmp = memdup_user(buf, count);
if (IS_ERR(tmp))
return PTR_ERR(tmp);
pr_debug("i2c-dev: i2c-%d writing %zu bytes.\n",
iminor(file_inode(file)), count);
//i2c发送
ret = i2c_master_send(client, tmp, count);
kfree(tmp);
return ret;
}
memdup_user函数
/**
* memdup_user - duplicate memory region from user space
*
* @src: source address in user space
* @len: number of bytes to copy
*
* Return: an ERR_PTR() on failure. Result is physically
* contiguous, to be freed by kfree().
*/
void *memdup_user(const void __user *src, size_t len)
{
void *p;
//分配内核态的空间
p = kmalloc_track_caller(len, GFP_USER | __GFP_NOWARN);
if (!p)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
//从用户空间拷贝数据
if (copy_from_user(p, src, len)) {
kfree(p);
return ERR_PTR(-EFAULT);
}
return p;
}
(5)i2cdev_ioctl
static long i2cdev_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) { struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data; unsigned long funcs; dev_dbg(&client->adapter->dev, "ioctl, cmd=0x%02x, arg=0x%02lx\n", cmd, arg); switch (cmd) {
//设置从机地址
//I2C_SLAVE和I2C_SLAVE_FORCE的区别在于I2C_SLACE会检查设备地址,如果地址已经使用,就不能使用重复的地址,否则会返回-EBUSY,而I2C_SLACE_FORCE会跳过检查 case I2C_SLAVE: case I2C_SLAVE_FORCE: if ((arg > 0x3ff) || (((client->flags & I2C_M_TEN) == 0) && arg > 0x7f)) return -EINVAL; if (cmd == I2C_SLAVE && i2cdev_check_addr(client->adapter, arg)) return -EBUSY; /* REVISIT: address could become busy later */ client->addr = arg; return 0;
//设置10bit地址模式
//如果select不等于0选择10bit地址模式,如果等于0选择7bit模式,默认7bit。只有适配器支持I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR,这个请求才是有效的 case I2C_TENBIT: if (arg) client->flags |= I2C_M_TEN; else client->flags &= ~I2C_M_TEN; return 0;
//设置传输后增加PEC标志(用于数据校验)
//这个命令只对SMBus传输有效。这个请求只在适配器支持I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_PEC时有效;如果不支持这个命令也是安全的,它不做任何工作 case I2C_PEC: /* * Setting the PEC flag here won't affect kernel drivers, * which will be using the i2c_client node registered with * the driver model core. Likewise, when that client has * the PEC flag already set, the i2c-dev driver won't see * (or use) this setting. */ if (arg) client->flags |= I2C_CLIENT_PEC; else client->flags &= ~I2C_CLIENT_PEC; return 0;
//获取适配器支持的功能:SMbus或者普通的I2C case I2C_FUNCS: funcs = i2c_get_functionality(client->adapter); return put_user(funcs, (unsigned long __user *)arg); //i2c读写,和i2c_read、i2c_write的区别在于这两个函数一次只能处理一条消息,而i2c_RDWR一次可以处理多条消息 case I2C_RDWR: { struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data rdwr_arg; struct i2c_msg *rdwr_pa; if (copy_from_user(&rdwr_arg, (struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data __user *)arg, sizeof(rdwr_arg))) return -EFAULT; if (!rdwr_arg.msgs || rdwr_arg.nmsgs == 0) return -EINVAL; /* * Put an arbitrary limit on the number of messages that can * be sent at once */
//最多处理42条message if (rdwr_arg.nmsgs > I2C_RDWR_IOCTL_MAX_MSGS) return -EINVAL; rdwr_pa = memdup_user(rdwr_arg.msgs, rdwr_arg.nmsgs * sizeof(struct i2c_msg)); if (IS_ERR(rdwr_pa)) return PTR_ERR(rdwr_pa); return i2cdev_ioctl_rdwr(client, rdwr_arg.nmsgs, rdwr_pa); } //smbus协议 case I2C_SMBUS: { struct i2c_smbus_ioctl_data data_arg; if (copy_from_user(&data_arg, (struct i2c_smbus_ioctl_data __user *) arg, sizeof(struct i2c_smbus_ioctl_data))) return -EFAULT; return i2cdev_ioctl_smbus(client, data_arg.read_write, data_arg.command, data_arg.size, data_arg.data); }
//设置重试次数
//这句话设置适配器收不到ACK时重试的次数为m。默认的重试次数为1。
case I2C_RETRIES: if (arg > INT_MAX) return -EINVAL; client->adapter->retries = arg; break;
//超时时间,时间单位为jiffes case I2C_TIMEOUT: if (arg > INT_MAX) return -EINVAL; /* For historical reasons, user-space sets the timeout * value in units of 10 ms. */ client->adapter->timeout = msecs_to_jiffies(arg * 10); break; default: /* NOTE: returning a fault code here could cause trouble * in buggy userspace code. Some old kernel bugs returned * zero in this case, and userspace code might accidentally * have depended on that bug. */ return -ENOTTY; } return 0; }
I2C_RDWR应用实例:i2c驱动之调用ioctl函数进行读写at24c08
i2c数据传输主要通过i2c_transfer函数:
/**
* i2c_transfer - execute a single or combined I2C message
* @adap: Handle to I2C bus
* @msgs: One or more messages to execute before STOP is issued to
* terminate the operation; each message begins with a START.
* @num: Number of messages to be executed.
*
* Returns negative errno, else the number of messages executed.
*
* Note that there is no requirement that each message be sent to
* the same slave address, although that is the most common model.
*/
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
int ret;
if (!adap->algo->master_xfer) {
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "I2C level transfers not supported\n");
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
}
/* REVISIT the fault reporting model here is weak:
*
* - When we get an error after receiving N bytes from a slave,
* there is no way to report "N".
*
* - When we get a NAK after transmitting N bytes to a slave,
* there is no way to report "N" ... or to let the master
* continue executing the rest of this combined message, if
* that's the appropriate response.
*
* - When for example "num" is two and we successfully complete
* the first message but get an error part way through the
* second, it's unclear whether that should be reported as
* one (discarding status on the second message) or errno
* (discarding status on the first one).
*/
ret = __i2c_lock_bus_helper(adap);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = __i2c_transfer(adap, msgs, num);
i2c_unlock_bus(adap, I2C_LOCK_SEGMENT);
return ret;
}
(6)退出函数
static void __exit i2c_dev_exit(void)
{
bus_unregister_notifier(&i2c_bus_type, &i2cdev_notifier);
i2c_for_each_dev(NULL, i2cdev_detach_adapter);
class_destroy(i2c_dev_class);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, 0), I2C_MINORS);
}
2、i2c_algorithm
两种i2c算法,一种是普通的I2c数据通讯协议,一种是SMbus协议,是两种不同的通信方法
/**
* struct i2c_algorithm - represent I2C transfer method
* @master_xfer: Issue a set of i2c transactions to the given I2C adapter
* defined by the msgs array, with num messages available to transfer via
* the adapter specified by adap.
* @master_xfer_atomic: same as @master_xfer. Yet, only using atomic context
* so e.g. PMICs can be accessed very late before shutdown. Optional.
* @smbus_xfer: Issue smbus transactions to the given I2C adapter. If this
* is not present, then the bus layer will try and convert the SMBus calls
* into I2C transfers instead.
* @smbus_xfer_atomic: same as @smbus_xfer. Yet, only using atomic context
* so e.g. PMICs can be accessed very late before shutdown. Optional.
* @functionality: Return the flags that this algorithm/adapter pair supports
* from the I2C_FUNC_* flags.
* @reg_slave: Register given client to I2C slave mode of this adapter
* @unreg_slave: Unregister given client from I2C slave mode of this adapter
*
* The following structs are for those who like to implement new bus drivers:
* i2c_algorithm is the interface to a class of hardware solutions which can
* be addressed using the same bus algorithms - i.e. bit-banging or the PCF8584
* to name two of the most common.
*
* The return codes from the @master_xfer{_atomic} fields should indicate the
* type of error code that occurred during the transfer, as documented in the
* Kernel Documentation file Documentation/i2c/fault-codes.rst.
*/
struct i2c_algorithm {
/*
* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer
* to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set
* smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated
* using common I2C messages.
*
* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully
* processed, or a negative value on error
*/
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,
int num);
int (*master_xfer_atomic)(struct i2c_adapter *adap,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num);
int (*smbus_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,
unsigned short flags, char read_write,
u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);
int (*smbus_xfer_atomic)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,
unsigned short flags, char read_write,
u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);
/* To determine what the adapter supports */
u32 (*functionality)(struct i2c_adapter *adap);
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_I2C_SLAVE)
int (*reg_slave)(struct i2c_client *client);
int (*unreg_slave)(struct i2c_client *client);
#endif
};
3、i2c总线驱动分析(i2c-core-base.c)
(1)i2c总线定义
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = "i2c",
.match = i2c_device_match,
.probe = i2c_device_probe,
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
};
(2)总线注册
static int __init i2c_init(void)
{
int retval;
retval = of_alias_get_highest_id("i2c");
down_write(&__i2c_board_lock);
if (retval >= __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num)
__i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num = retval + 1;
up_write(&__i2c_board_lock);
retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type);
if (retval)
return retval;
is_registered = true;
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
i2c_adapter_compat_class = class_compat_register("i2c-adapter");
if (!i2c_adapter_compat_class) {
retval = -ENOMEM;
goto bus_err;
}
#endif
retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver);
if (retval)
goto class_err;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC))
WARN_ON(of_reconfig_notifier_register(&i2c_of_notifier));
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ACPI))
WARN_ON(acpi_reconfig_notifier_register(&i2c_acpi_notifier));
return 0;
class_err:
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class);
bus_err:
#endif
is_registered = false;
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
return retval;
}
(3)i2c设备和驱动匹配规则
static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
/* Attempt an OF style match */
if (i2c_of_match_device(drv->of_match_table, client))
return 1;
/* Then ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);
/* Finally an I2C match */
if (i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client))
return 1;
return 0;
}
- i2c_of_match_device:设备树匹配方式
比较I2C设备节点的compatible属性和of_device_id中的compatible属性
- acpi_driver_match_device: ACPI匹配方式
- i2c_match_id: i2c总线传统匹配方式
比较i2c设备名字和i2c驱动的id_table->name字段是否相等
三、SMbus介绍
1、介绍
- 系统管理总线(SMBus)是一个两线接口。通过它,各设备之间以及设备与系统的其他部分之间可以互相通信。
- 它基于I2C操作原理。SMBus为系统和电源管理相关的任务提供一条控制总线。一个系统利用SMBus可以和多个设备互传信息,而不需使用独立的控制线路。
- 系统管理总线(SMBus)标准涉及三类设备。从设备-接收或响应命令的设备。主设备-用来发布命令,产生时钟和终止发送的设备。主机,是一种专用的主设备,它提供与系统CPU的主接口。主机必须具有主-从机功能,并且必须支持SMBus通报协议。
- 在一个系统里只允许有一个主机。
2、SMBus和I2C之间的相似点
- 2条线的总线协议(1个时钟,1个数据) + 可选的SMBus提醒线
- 主-从通信,主设备提供时钟
- 多主机功能
- SMBus数据格式类似于I2C的7位地址格式
3、SMBus和I2C之间的不同点
| SMbus | i2c |
| 传输速度 10khz~100khz | 最小传输速度 10kHz 无最小传输速度 |
| 最小传输速度 35ms时钟低超时 | 无时钟超时 |
| 固定的逻辑电平 | 逻辑电平由VDD决定 |
| 不同的地址类型(保留、动态等) | 7位、10位和广播呼叫从地址类型 |
| 不同的总线协议(快速命令、处理呼叫等) | 无总线协议 |
4、SMBus应用用途
利用系统管理总线,设备可提供制造商信息,告诉系统它的型号/部件号,保存暂停事件的状态,报告不同类型的错误,接收控制参数,和返回它的状态。SMBus为系统和电源管理相关的任务提供控制总线。