20172332 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》第九周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
- 1.异常处理
- 异常抛出的问题
- 处理异常的方法
- 2.未捕获的异常。
- 3.try-catch语句。
- 没有异常,将继续执行try语句后的语句块,所有catch子句后的语句。
- 有异常,则控制立刻转移到相应的catch子句处理异常。
- 4.finally子句。
- 一条try-catch语句可以有一个可选的finally子句,用于定义一段无论是否有异常发生都将执行的代码。
- 如果有finally子句,则必须跟在所有的catch子句后面。
- try语句块可以没有catch子句,但仍然可以使用finally子句。
- finally语句与return语句的关系:
- ①如果finally语句中没有return语句,先执行finally语句中的代码,然后在执行try语句块或catch语句块中的return语句;
- ②若finally语句中有return语句,则finally语句中的return语句覆盖其他语句块中的语句,最后返回的是finally中的return语句。
- 5.异常的传递。(就与传递性一样,举个例子:程序一存在异常,程序二调用程序一,程序二就会存在与程序一相同的异常。)
- 6.异常类层次结构。(许多类型的异常类都由Exception类派生,但定义各种异常的子类却分散定义在其他几个包中,继承关系可以跨越包边界。)
- 7.自定义异常。(说白了就是自己写代码,定义一种异常)
- 8.可检测异常与不可检测异常。
- 可检测异常必须由方法捕获,或者必须在可能抛出或传递异常方法的throws子句中列出来。
- throws子句用在方法头。throw子句用在方法中。
- java中唯一的不可检测异常是RuntimeException类的对象或该类的后代类对象。
- 9.I/O异常(其中还有老师上课讲的把数据写入文本,和从文本中读取数据内容)
- 三种标准I/O流(in、out、err)
- 可检测的IOExceptions异常
- 10.递归思想(一个调用自己的方法)
- 11.无穷递归(类似于无限循环)
- 12.数学中的递归运算(阶乘和求和)。
- 13.递归与迭代的比较:
- 所有的问题都可以用循环迭代的方法求解,但某些情况下循环迭代会很复杂,递归方法可以写出更简洁而精良的程序。
- 14.直接递归和简介递归。
- 方法调用自己的递归——直接递归
- 方法调用其他方法,最终导致再次调用自己——间接递归。
- 15.递归的应用:
- ①迷宫旅行。
- ②汉诺塔问题。
教材学习中的问题和解决过程(其实现在老师开始先讲然后在让我们学的模式之后,教材上的问题是愈发的少了= =,不知道写什么)
- 问题1:这种在字符串中的索引值和长度是怎么算的
- 问题1解决方案:索引值和长度都不算入字符串内。(写个小程序验证了一下)
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:
- 问题1解决方案:StackOverflowError是由于当前线程的栈满了 ,也就是函数调用层级过多导致。改为
- 问题2:pp11.2中为什么字符串的索引值要输20,按理说,字符串第一个索引值为0,所以第20个字符的索引值应是19。
-
问题2解决方案:emmmm,这是我想错了,输出第20个字符以后的,应该从21开始算起,所以索引值应为20。
-
问题3:pp12.1中
- 问题3解决方案:索引值越界了,因为我的字符串变了,索引值也跟着变,就会出问题。应该变成字符串不变,索引值变。
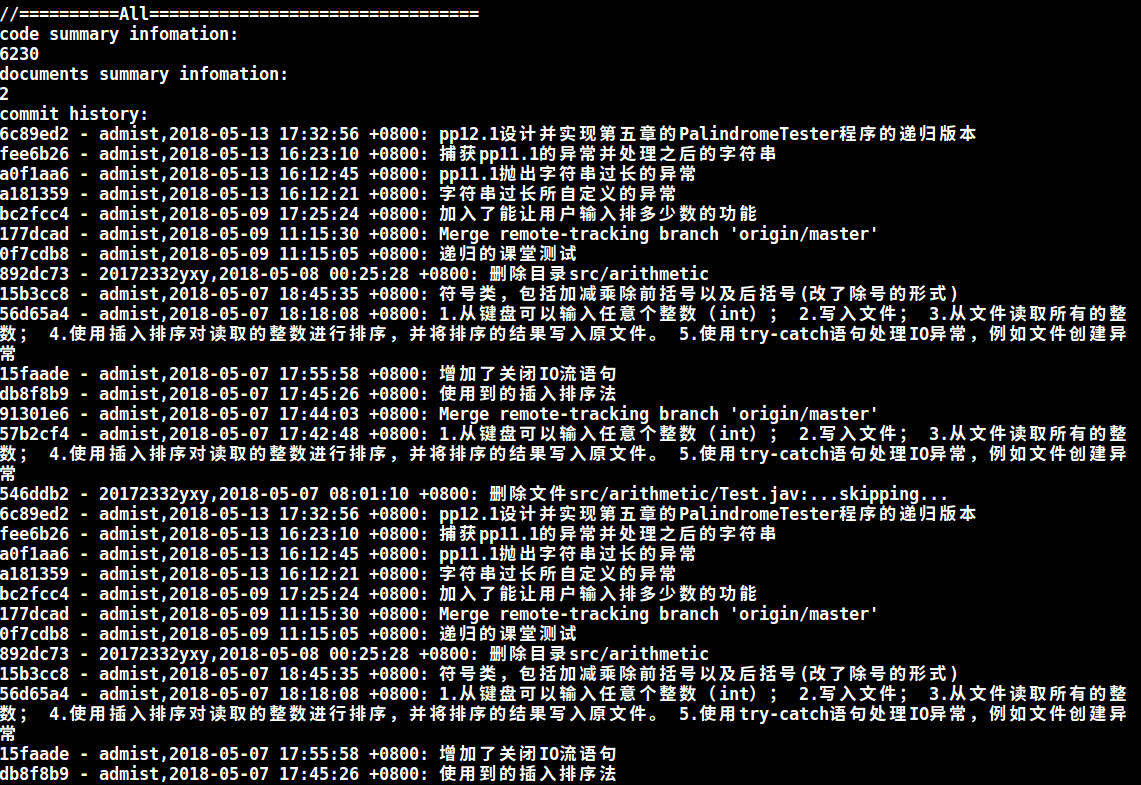
代码托管
很奇怪我的代码量变少了!不过已经上5000了,就不统计了吧!让代码量就定格在那一瞬间!
上周考试错题总结
1.A Java program can handle an exception in several different ways. Which of the following is not a way that a Java program could handle an exception?
- A . ignore the exception
- B . handle the exception where it arose using try and catch statements
- C . propagate the exception to another method where it can be handled
- D . throw the exception to a pre-defined Exception class to be handled
- E . all of the above are ways that a Java program could handle an exception
- 答案:D ;我选的:E
- 分析:异常不会被抛出异常类。
- 单词:1.handle:处理。2.exception:异常。3.exception:传送。
2.An exception can produce a "call stack trace" which lists
- A . the active methods in the order that they were invoked
- B . the active methods in the opposite order that they were invoked
- C . the values of all instance data of the object where the exception was raised
- D . the values of all instance data of the object where the exception was raised and all local variables and parameters of the method where the exception was raised
- E . the name of the exception thrown
- 答案:B ;我选的:D
- 分析:栈是最先放的最后出来,所以顺序是相反的。
- 单词:1.invoke:调用。2.parameters:参数。
3.Character streams manage
- A . byte-sized data
- B . binary data
- C . Unicode characters
- D . ASCII characters
- E . compressed data
- 答案:C ;我选的:B
- 分析:字符流用于管理16位的Unicode字符
- 单词:1.Character:字符。2.compressed:压缩。
4.PrintWriter is a better output stream class that PrintStream because PrintWriter
- A . has both print and println methods and PrintStream only has print
- B . can output both byte and character streams and PrintStream can only output byte streams
- C . has error checking mechanisms as part of the class and PrintStream does not
- D . will not throw checked exceptions and PrintStream will
- E . all of the above
- 答案:C ;我选的:B
- 分析:PrintWriter类是一个Writer类,而PrintStream类是一个流类。主要的区别在于PrintWriter是专门为文件而设计的,因此有错误检查机制而不是PrintStream的一部分。(意思就是说PrintWriter比PrintStream好在有错误检查机制)
- 单词:1.mechanisms:机制。
5.The following defines a new Exception called AnewException.
public Exception ANewException
{
public ANewException(String message)
{
super(message);
}
}
- A . true
- B . false
- 答案:B ;我选的:A
- 分析:自定义异常必须定位为类而不是异常
- 单词:1.exception:异常。
点评过的同学博客和代码
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
- 大部分知识老师在课上已经讲了,还扩展了内容,所以学起来并不费劲。
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 182/182 | 1/1 | 10/10 | |
| 第二周 | 458/640 | 1/2 | 15/25 | |
| 第三周 | 469/1109 | 2/4 | 18/43 | 学会IDEA的使用和调试,学会jdb调试。 |
| 第四周 | 1536/2645 | 1/5 | 24/67 | |
| 第五周 | 980/3625 | 1/6 | 25/92 | |
| 第六周 | 870/4495 | 1/7 | 16/108 | |
| 第七周 | 455/4950 | 2/9 | 22/130 | |
| 第八周 | 1322/6272 | 2/11 | 28/158 | |
| 第九周 | 2/13 | 28/186 |
-
计划学习时间:20小时
-
实际学习时间:28小时
-
改进情况:课后的pp除了pp12.9我认为有难度以外,别的还好,大部分时间依旧花在了四则运算的结对编程中。