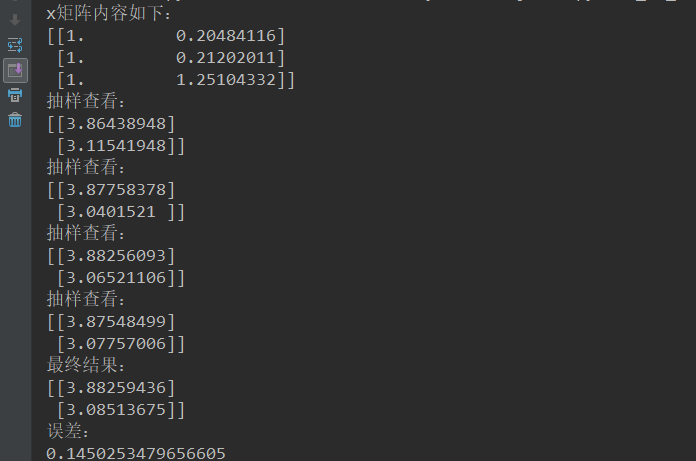
实现:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
"""
练习使用随机梯度下降算法
"""
import numpy as np
import math
__author__ = 'zhen'
# 生成测试数据
x = 2 * np.random.rand(100, 1) # 随机生成100*1的二维数组,值分别在0~2之间
y = 4 + 3 * x + np.random.randn(100, 1) # 随机生成100*1的二维数组,值分别在4~11之间
x_b = np.c_[np.ones((100, 1)), x]
print("x矩阵内容如下:
{}".format(x_b[0:3]))
n_epochs = 100
t0, t1 = 1, 10
m = n_epochs
def learning_schedule(t): # 模拟实现动态修改步长
return t0 / (t + t1)
theta = np.random.randn(2, 1)
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for i in range(m):
random_index = np.random.randint(m)
x_i = x_b[random_index:random_index+1]
y_i = y[random_index:random_index+1]
gradients = 2 * x_i.T.dot(x_i.dot(theta)-y_i) # 调用公式
learning_rate = learning_schedule(epoch * m + i)
theta = theta - learning_rate * gradients
if epoch % 30 == 0:
print("抽样查看:
{}".format(theta))
print("最终结果:
{}".format(theta))
# 计算误差
error = math.sqrt(math.pow((theta[0][0] - 4), 2) + math.pow((theta[1][0] - 3), 2))
print("误差:
{}".format(error))
结果: