Composite:
definition
|
Compose objects into tree structures to represent part-whole hierarchies. Composite lets clients treat individual objects and compositions of objects uniformly. |
:将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分整体”的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象和使用具有一致性。
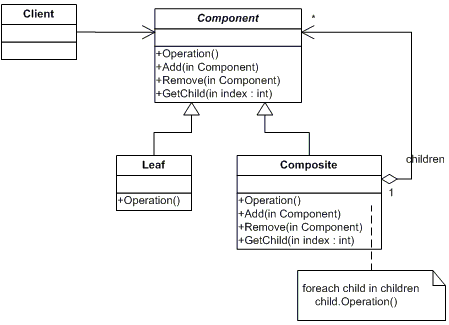
涉及角色:
1.Component 是组合中的对象声明接口,在适当的情况下,实现所有类共有接口的默认行为。声明一个接口用于访问和管理Component
子部件。
2.Leaf 在组合中表示叶子结点对象,叶子结点没有子结点。
3.Composite 定义有枝节点行为,用来存储子部件,在Component接口中实现与子部件有关操作,如增加(add)和删除
public abstract class Component { protected String name; public Component(String name) { this.name=name; } public abstract void add(Component c); public abstract void remove(Component c); public abstract void display(int depth); }
叶子节点:
public class Leaf extends Component{ public Leaf(String name) { super(name); } public void add(Component c) { System.out.println("Can't add to a leaf"); } public void remove(Component c) { System.out.println("Can't remvoe from a leaf"); } public void display(int depth) { for(int i=0;i<depth;i++) { System.out.print('-'); } System.out.println(name); } }
z子节点:
public class Composite extends Component{ private List<Component> children=new ArrayList<Component>(); public Composite(String name) { super(name); } public void add(Component c) { children.add(c); } public void remove(Component c) { children.remove(c); } public void display(int depth) { for(int i=0;i<depth;i++) { System.out.print('-'); } System.out.println(name); for(Component component : children) { component.display(depth+1); } } }
Test类:
public static void main(String[] args) { Composite root=new Composite("root"); root.add(new Leaf("Leaf A")); root.add(new Leaf("Leaf B")); Composite comp=new Composite("Composite X"); comp.add(new Leaf("Leaf XA")); comp.add(new Leaf("Leaf XB")); root.add(comp); root.display(1); } }
输出:
-root
--Leaf A
--Leaf B
--Composite X
---Leaf XA
---Leaf XB
安全性与透明性
叶子节点有add和remove方法的争议。
组合模式中必须提供对子对象的管理方法,不然无法完成对子对象的添加删除等等操作,也就失去了灵活性和扩展性。但是管理方法是在Component中就声明还是在Composite中声明呢?
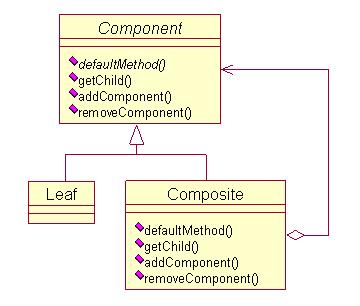
一种方式是在Component里面声明所有的用来管理子类对象的方法,以达到Component接口的最大化(如下图所示)。目的就是为了使客户看来在接口层次上树叶和分支没有区别——透明性。但树叶是不存在子类的,因此Component声明的一些方法对于树叶来说是不适用的。这样也就带来了一些安全性问题。
另一种方式就是只在Composite里面声明所有的用来管理子类对象的方法(如下图所示)。这样就避免了上一种方式的安全性问题,但是由于叶子和分支有不同的接口,所以又失去了透明性。
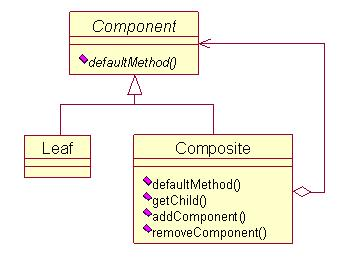
《设计模式》一书认为:在这一模式中,相对于安全性,我们比较强调透明性。对于第一种方式中叶子节点内不需要的方法可以使用空处理或者异常报告的方式来解决。