关于快读
普通的快读大家应该都会写, 我就不再赘述, 这里讲一下用fread的快读。
fread
首先函数原型
size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
函数fread从stream流中读取nmemb个长度为size字节大小的数据,并将它们存储在ptr给定的位置, 返回读取的字节数。
比如fread(buf, 1, 10, stdin);就是从标准输入流中读取10个1字节大小的字符, 存在buf数组里。
因为它是一下子读一大堆, 所以比较快, 那么怎么使用呢?
使用
首先定义一个字符数组, 大小为(2^{20}) (1 mb), 作为缓存, 每次读取1 mb数据存在数组里, 读数字的时候扫描数组, 像普通快读一样转成数字, 读完缓存就再读 1 mb。
char buf[1<<20], *p1, *p2; //buf 缓存, p1 为指向缓存开头的指针, p2 为指向缓存结束的指针
char gc() {
if (p1 == p2) { // 判断是否第一次执行或读取完缓存
p1 = buf; // 重置开头指针
p2 = buf + fread(buf, 1, 1<<20, stdin); //读取数据, 重置结尾指针
if (p1 == p2) return EOF;
}
return *p1++; // 返回第一个字符并指针后移
}
inline int read() { //普通的快读
int f = 1, x = 0;
char c = gc();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') {
if (c == '-') f = -1;
c = gc();
}
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = gc();
return f * x;
}
去注释, 压行版本
char buf[1<<20], *p1, *p2;
char gc() { return p1 == p2 ? p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1<<20, stdin), (p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++ : *p1++; }
inline int read(int f = 1, char c = gc(), int x = 0) {
while(c < '0' || c > '9') f = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1, c = gc();
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = gc();
return f * x;
}
宏函数版本
char buf[1<<20],*p1,*p2;
#define gc() (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? EOF : *p1++) : *p1++)
#define read() ({
int x = 0, f = 1;
char c = gc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') f = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1, c = gc();
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + (c & 15), c = gc();
f * x;
})
宏函数一定会内联, 比如以下代码
#include <cstdio>
char buf[1<<20],*p1,*p2;
#define gc() (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? EOF : *p1++) : *p1++)
#define read() ({
int x = 0, f = 1;
char c = gc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') f = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1, c = gc();
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + (c & 15), c = gc();
f * x;
})
int a[100];
int main() {
int n = read(), m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = read();
}
就会展开为
#include <cstdio>
char buf[1<<20],*p1,*p2;
#define gc() (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? EOF : *p1++) : *p1++)
#define read() ({
int x = 0, f = 1;
char c = gc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') f = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1, c = gc();
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + (c & 15), c = gc();
f * x;
})
int a[100];
int main() {
int n = ({ int x = 0, f = 1; char c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); while(c < '0' || c > '9') f = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1, c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + (c & 15), c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); f * x;}), m = ({ int x = 0, f = 1; char c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); while(c < '0' || c > '9') f = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1, c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + (c & 15), c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); f * x;});
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = ({ int x = 0, f = 1; char c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); while(c < '0' || c > '9') f = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1, c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + (c & 15), c = (p1 == p2 ? (p2 = buf + fread(p1 = buf, 1, 1 << 20, stdin), p1 == p2 ? (-1) : *p1++) : *p1++); f * x;});
}
其他要注意的
-
调试的时候, 输入完成后请手动输入EOF(linux上为ctrl + d, windows上为ctrl + z)。
-
使用此快读请不要使用其他输入方式, 否则会因为缓存问题产生错误。
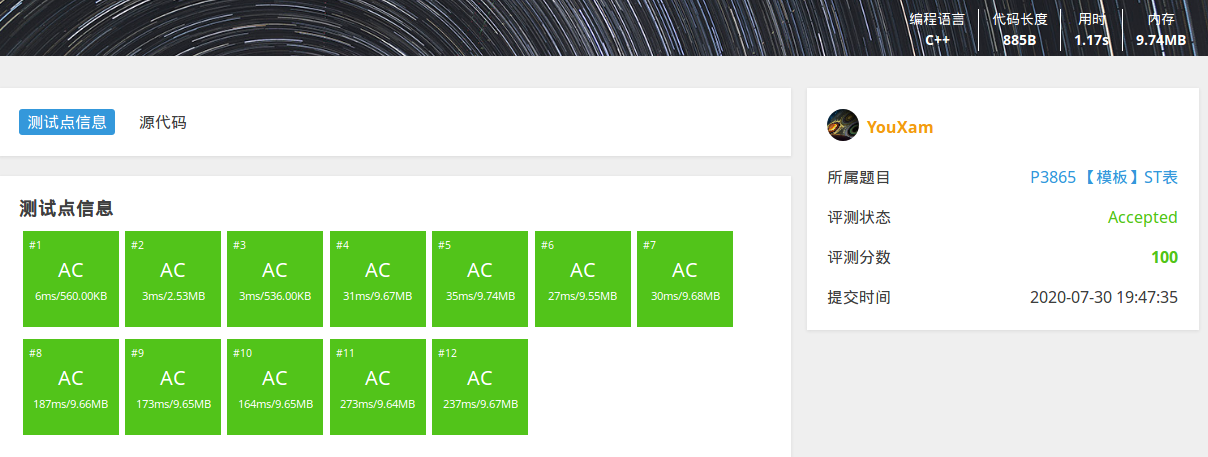
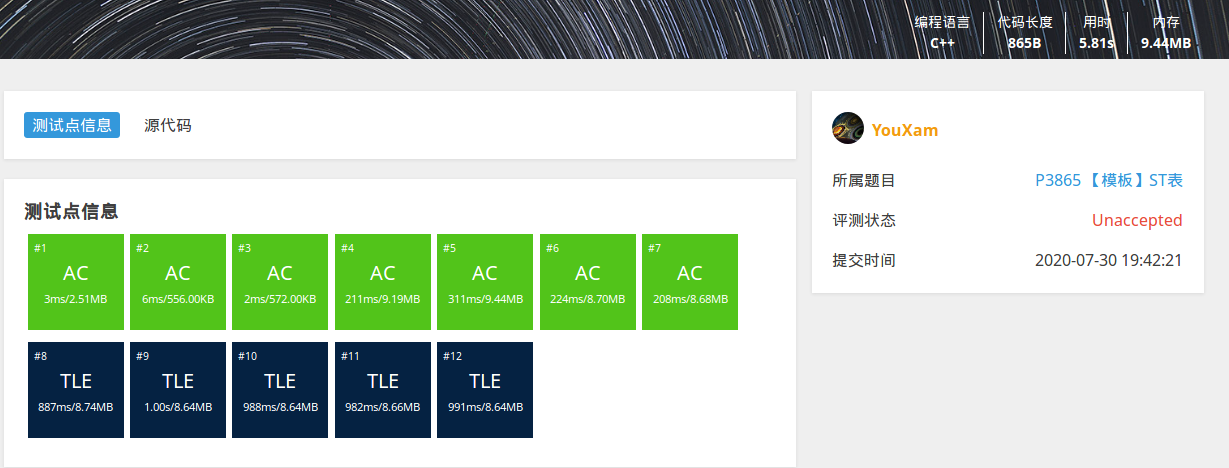
读入速度比较
测试题目 P3865 【模板】ST表, 均未开启O2优化
使用cin和printf
使用scanf和printf
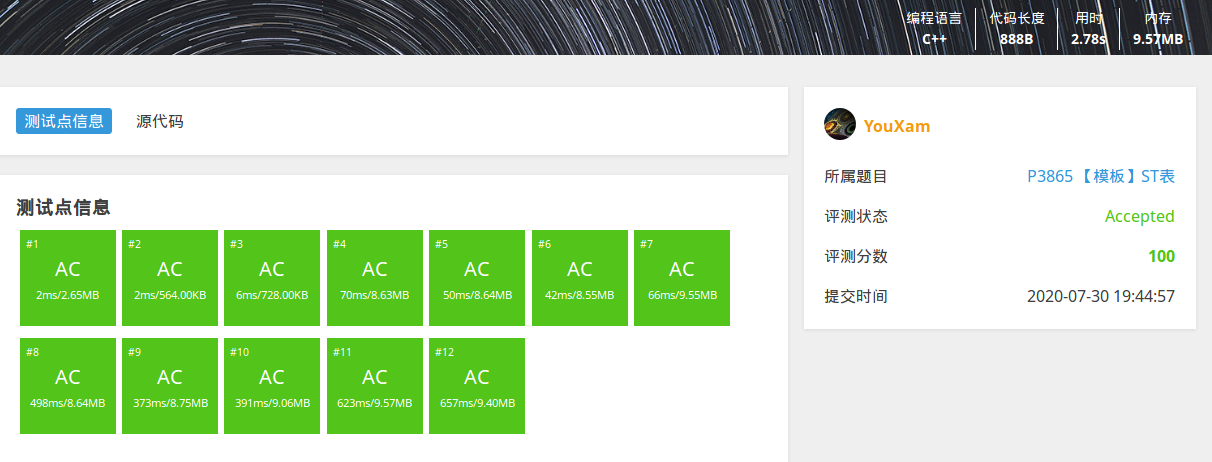
使用getchar版本快读和printf

使用fread版本快读和printf