一、MVC设计模式
1、什么是MVC模式
1.1、MVC —— Model View Controller模型视图控制器
1.2、Model:模型 一个功能 一般用JavaBean
1.3、View:视图 用于展示以及用户交互。一般使用html,jsp,ccs等这些前端技术实现
1.4、Controller:控制器 接收请求,将请求跳转到模型进行处理,待模型处理完毕之后,再将处理的结果返回给请求处,一般用Servlet实现控制器
我感觉MVC就是简单前后端交互模式,其中最重要的模块是Servlet。
2、我自己画个图来展示下
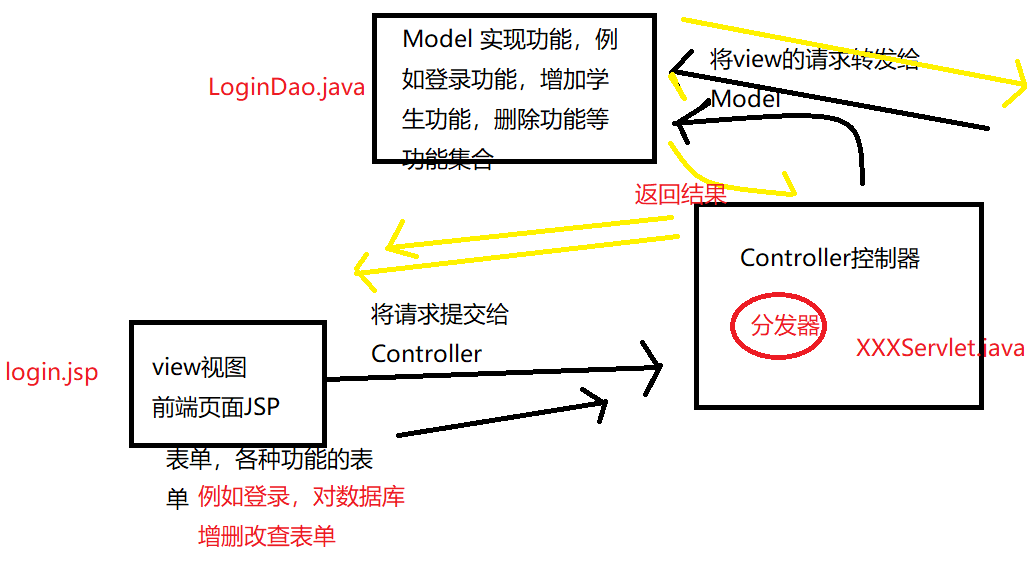
3、简单MVC登录实例
3.1、框架
3.2、 View层
login.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>登录页面</title> </head> <body> <form action="<%= request.getContextPath() %>/LoginServlet" method="post"> <input type="text" name="uname"><br/> <input type="password" name="upwd"><br/> <input type="submit" value="登录"><br/> </form> </body> </html>
welcom.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> 登录成功,欢迎您 </body> </html>
3.3、Dao层
Dao功能操作
//model层,实现某种功能 public class LoginDao { private static String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"; private static String user="root"; private static String password="root"; public static int Login(user s){ Connection conn=null; PreparedStatement pst=null; ResultSet re=null; int result=0;//1:登录成功 0:登录失败 用户或密码有误 try{ Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn= DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password); pst=conn.prepareStatement("select count(*) from user where username=? and password=? "); pst.setString(1,s.getUserName()); pst.setString(2,s.getPassword()); re=pst.executeQuery(); if(re.next()){ result=re.getInt(1); } }catch (ClassNotFoundException e1){ e1.printStackTrace(); }catch (Exception e2){ e2.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { //进行非空判断,防止re,comm,pst抛出空异常 if (re != null) re.close(); if(pst !=null) pst.close(); if(conn !=null) conn.close(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } return result; } }
Dao层实体user
/** * 实体user,将传入的数据封装成一个实体 */ public class user { private int id; private String userName; private String password; public user(){ } public user(String userName, String passqord) { this.userName = userName; this.password = passqord; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
3.4、控制层Controller
LoginServlet
/** * Controller控制器 */ @WebServlet(name = "LoginServlet",value = "/LoginServlet") public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); String usename=request.getParameter("uname"); String password=request.getParameter("upwd"); user s=new user(usename,password); int i=LoginDao.Login(s); if(i==1){ //一定要加request.getContextPath(),不然找不到路径 response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/MVCExample/welcome.jsp"); }else{ response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/MVCExample/login.jsp"); } } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(request, response); } }
调用过程:从前端页面Login.jsp登录,登录之后将请求页面和登录信息username和password传给控制层,在控制层Controller中调用Model层来实现登录LoginDao,最终Model层将查到的结果返回给控制层ServletLogin,控制层再将结果返回给前端展示。在此过程中控制层相当于分发器,前端和后端通过他来进行信息的交互。