三道题:
T1:玩具迷题
T2:组合数问题
T3:联合权值
T1:
模拟大水题,只需要按照题目中说的做就好了
只给代码,,,
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
#define go(i,j,n,k) for(int i=j;i<=n;i+=j)
#define fo(i,j,n,k) for(int i=j;i>=n;i-=k)
#define rep(i,x) for(int i=h[x];i;i=e[i].nxt)
#define mn 200100
#define inf 2147483647
#define ll long long
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9' || ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')f=-f;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0' && ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
struct node{
int poi;
string na;
} lxx[mn];
int now, n, m;
int main(){
freopen("toy.in","r",stdin);
freopen("toy.out","w",stdout);
n = read(),m = read();
go(i,1,n,1){
lxx[i].poi=read();
cin>>lxx[i].na;
}
int now=1;
go(i,1,m,1){
int s=read(),x=read();
// s == 0 zuo s == 1 you
// lxx[now].poi == 0 ? nei : wai
// shun jian ni jia
// nei : zuo shun you ni
// wai : you shun zuo ni
// bu gou qu ling
// duo yu qu mo
if(lxx[now].poi == 0){
if(s==0){
now -= (x % n);
if(now <= 0)
now += n;
}else{
now += (x % n);
if(now > n)
now %= n;
}
}else{
if(s==0){
now += (x % n);
if(now > n)
now %= n;
}else{
now -= (x % n);
if(now <= 0)
now += n;
}
}
}
cout << lxx[now].na << "
";
return 0;
}
T2:
我们不难想到在维护杨辉三角的时候直接取模k,
如果每一个询问要重新遍历一遍杨辉三角,时间复杂度O(tnm),明显过不去。
这不就是求区间和吗?
我们明显可以拿一个二维前缀和去维护。
记住,维护的时候一定不要把非杨辉三角的部分计算上。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
#define go(i,j,n,k) for(int i=j;i<=n;i+=k)
#define fo(i,j,n,k) for(int i=j;i>=n;i-=k)
#define rep(i,x) for(int i=h[x];i;i=e[i].nxt)
#define mn 2018
#define inf 2147483647
#define ll long long
#define mod
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9' || ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')f=-f;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0' && ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
ll C[mn][mn];
ll sum[mn][mn];
int T, n, m, k;
// er wei qian zhui he
int cnt;
inline void get_C(int x = 2000){
//puts("lala");
//memset(C,-1,sizeof(C));
go(i,0,x,1)
C[i][0] = 1,C[i][i] = 1;
go(i,1,x,1)
go(j,1,i,1)
C[i][j] = ( C[i - 1][j - 1] + C[i - 1][j] ) % k;
sum[0][0] = sum[1][0] = sum[0][1] = 0;
go(i,1,x,1){
go(j,1,i,1){
sum[i][j] = sum[i - 1][j] + sum[i][j - 1] - sum[i - 1][j - 1] + ( (C[i][j] == 0 ) ? 1 : 0);
}
go(j,i+1,x,1){
sum[i][j] = sum[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
inline void Debug(int x = 2000){
//puts("lala");
go(i,0,10,1){
go(j,0,i,1)
printf("%4d ", C[i][j]);
puts("");
}
puts("");
go(i,0,10,1){
go(j,0,i,1)
printf("%4d ", sum[i][j]);
puts("");
}
}
int main(){
freopen("combination.in","r",stdin);
freopen("combination.out","w",stdout);
memset(sum,0,sizeof(sum));
T = read(),k = read();
get_C();
//Debug();
while(T--){
n = read(), m = read();
int ans = sum[n][m];
cout << ans << "
";
}
return 0;
}
T3:
我先贴出来我比赛时写的代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
#define go(i,j,n,k) for(int i=j;i<=n;i+=j)
#define fo(i,j,n,k) for(int i=j;i>=n;i-=k)
#define rep(i,x) for(int i=h[x];i;i=e[i].nxt)
#define mn 110
#define inf 2147483647
#define ll long long
#define mod 10007
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9' || ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')f=-f;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0' && ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
struct edge{
int v,nxt;
}e[mn << 1];
int p,h[mn];
inline void add(int a,int b){
e[++p].nxt=h[a],h[a]=p,e[p].v=b;
}
ll w[mn];
int n;
ll maxx=-1,sum=0;
int main(){
freopen("union.in","r",stdin);
freopen("union.out","w",stdout);
n = read();
go(i,1,n-1,1){
int a = read(), b = read();
add(a,b),add(b,a);
}
go(i,1,n,1)
w[i]=read();
go(u,1,n,1){
rep(i,u){
int v=e[i].v;
rep(j,v){
int vv=e[j].v;
if(vv == u)
continue;
maxx = max(maxx,(w[u] * w[vv]));
sum = (sum + (w[u] * w[vv]) % mod) % mod;
}
}
}
cout << maxx << " " << sum << "
";
return 0;
}
明显是个暴力。但是这个代码如果把mn改为2010,这个题就可以到70分。
为什么?
代码中显然是三层循环,但是,我们如果两两配对,n个点就只能配对成(n^{2})个点对,所以可以成联合权值的点对就更少了,所以里面嵌套的两个遍历邻接表的循环就只可能比(n^{2})更小了。再加上这个题的数据比较松,所以,,,
100做法:
我们可以对这棵树做一个dfs,在dfs的同时维护最大值和总和。然后向上推,直到树顶,最顶上的就是我们要求的答案。
说白了,就是 树形DP
代码:
如果最后出结果不取模就会只剩50
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
#define go(i,j,n,k) for(int i=j;i<=n;i+=k)
#define fo(i,j,n,k) for(int i=j;i>=n;i-=k)
#define rep(i,x) for(int i=h[x];i;i=e[i].nxt)
#define mn 200010
#define inf 2147483637
#define ll long long
//#define LOCAL
#define Debug(...) fprintf(stderr, __VA_ARGS__)
#define mod 10007
inline ll read(){
ll x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')f=-f;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int n,w[mn];
struct edge{
int v,nxt;
edge(int _v = 0, int _nxt = 0):v(_v),nxt(_nxt) {}
}e[mn<<1];
int p,h[mn];
inline void add(int a,int b){
e[++p].nxt=h[a],h[a]=p,e[p].v=b;
}
ll sum[mn], fa[mn], maxx[mn];
inline void dfs(int now,int f,int deep){
ll fmax = -1, smax = -1, res = 0;
fa[now] = f;
if(deep >= 3){
sum[now] += w[fa[fa[now]]] * w[now];
sum[now] %= mod;
maxx[now] = sum[now];
}
if(!h[now])
return ;
rep(i,now){
int v = e[i].v;
if(v == f)
continue;
dfs(v, now, deep + 1);
res += w[v];
sum[now] += sum[v];
sum[now] %= mod;
maxx[now] = max(maxx[now], maxx[v]);
if(w[v] >= fmax){
smax = fmax;
fmax = w[v];
}else if(w[v] >= smax){
smax = w[v];
}
}
maxx[now] = max(maxx[now], fmax * smax);
rep(i,now){
int v = e[i].v;
if(v == f)
continue;
res -= w[v];
sum[now] += (res * w[v]) % mod;
sum[now] %= mod;
}
}
int main(){
n=read();
go(i,1,n-1,1){
int a=read(),b=read();
add(a,b),add(b,a);
}
go(i,1,n,1)
w[i]=read();
dfs(1, 0, 1);
cout << maxx[1] << " " << (sum[1] << 1) % mod;
#ifdef LOCAL
Debug("
My Time: %.3lfms
", (double)clock() / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#endif
return 0;
}
这个做法实际上是把求最大值和求和分开写的。
求最大值不难,我们只需要维护最大值和次大值就好了,记得更新子节点。
如果一棵树的部分是这样的:
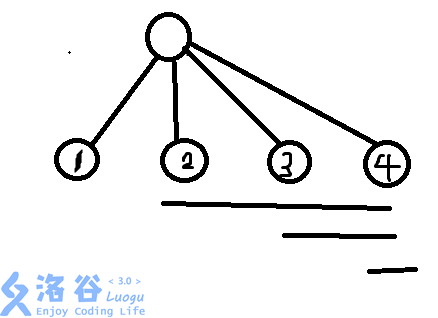
我们如何求这一部分的和?我们可以把这个写成
( 1*2 + 1*3 + 1*4 + 2*3 + 2*4 + 3*4 ) * 2
我们可以通过结合律写成:
( 1 * (2+3+4) + 2 * (3+4) + 3 * 4 ) * 2
这样,我们就可以把这个父节点的子节点和在遍历时求出来。我们在求和时,遍历子节点,遍历到每个子节点时,把之前求出的和减去当前的点权值,然后乘以当前点权值,是不是就是有关这个子节点的全部的联合权值和?记得我们在dfs中要把这个子节点的爷爷节点也要算在求的子节点和中。
记得取模!!!
所以,我的成绩:
T1 : 100
T2 : 100
T3 : 30 (70)
比赛较水